
Animal production 2021 revision questions

Animal production 2021
By Mungudit Davious
+256 394847/7531322587
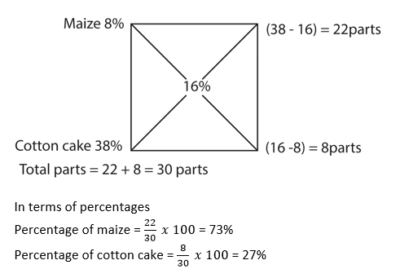
- (a) A farmer wants to mix 16% proteins ration using maize which is 8% and cotton cake which is 38% protein, in what proportions would he mix the maize and cotton cake? Using appropriate method show your working (06marks)
(b) Describe the factors a farmer would consider before mixing animal feeds (08marks)
It is necessary to mix feeds because no feed contains all the necessary nutrients. The final composition of the animal feeds is based on
- Palatability of the feed, ratios should be chosen to make the final mixture palatable
- Age of the animal; younger animals require higher proportion of proteins
- Health of the animals; sick animals require high proportion of vitamins
- Productivity of animals; Heavy worker may require more minerals such as calcium
- Types of animals- ruminant can handle higher proportions of roughage
- Safety of ingredients; some ingredients may require processing before mixing.
- Cost of the feed stuffs
- Availability of feeds
- Nutritional content of the feed.
(c) Outline the factors affecting utilization of rations by animals (06marks)
- Nutrient content of feed; feeds that are more wholesome give higher conversion rates than those that are not balanced in composition
- Digestibility of the feed- feeds that have higher digestibility can be utilized better than those with low digestibility.
- Types of animals. Ruminants are more efficient at the utilization of coarse fodder while pigs have a very high feed conversion ratio once given good quality food with low fibres
- Age of animal – actively growing animals have higher efficiency in utilization of rations because they have higher nutrient requirements than finishers.
- Amount of food given to the animal per day
- Healthy of animal
- Weather conditions
- Processing
- Additives added
- (a) Outline the differences between ruminants and non-ruminant animals? (10marks)
| Ruminants | Non-ruminants |
| Saliva contains lipase | Saliva lacks lipase |
| Have four stomach compartments | Have one stomach compartment |
| Saliva lacks amylase | Saliva contains amylase |
| Chew cud | Do not chew cud |
| Fermentation is possible due to the presence of rumen | Fermentation not possible |
| Contain bacteria that digest cellulose | Contain no bacteria for digestion of cellulose |
| Depend on volatile fatty acids for energy | Depend on glucose for energy |
| Most digestion and absorption occurs in the rumen | Most absorptions occur in the small intestines |
(b) Write short notes on the following
(your description should include symptoms, cause, and prevention)
- Bloat (06marks)
It is distension of the rumen caused by excessive accumulation of gases produce by fermentation of food stuffs in the rumen. It occurs in ruminants
Cause
- Plant factor; plants with high protein contents such legumes may cause bloat
- Animal factor; some animals are more likely to suffer from bloat than others
- Microbial factor
Symptoms
- Distended stomachs with pronounced movements at the left side of the animal
- Difficulty in breathing as a result of much pressure exerted to the diaphragm
- Lack of appetite
- Animal may die due to little oxygen in the blood streams because respiration is interfered with.
Prevention
- Graze animals on proper legume mixture
- Practice zero grazing in order to reduce selectivity
- Feed animals on good quality roughage
- Treat animals with antibiotics e.g. penicillin
- Avoid feeding excessive succulent feeds
Treatment
- Use antibiotics
- Milk fever (04marks)
It is brought about by low levels of calcium and phosphorus
Symptoms
- Fever
- Animal staggers and muscular spasm
- Loud and high breath
- Suffer paralysis
- Loss of appetite
Prevention
- Increase the blood calcium by feeding the animal on high calcium diet
- Give calcium supplements
Treatment
Give an injection of calcium gluconate
Give calcium and phosphorus supplements.
- (a) Outline the importance of water in the body of animals (06marks)
- solvent for nutrient and waste products
- component of cell
- reagent in hydrolysis
- medium for enzymatic reactions
- transport medium
- medium for fertilization
(b) Describe the factors that influence water intake in the body of animals (12marks)
- salinity of water; salty water encourages intake
- Types of feed eaten. Proteins and dry foods encourage water up take
- level of productivity- high yielding cows take a lot of water
- Size of the animal; big animals take a lot of water
- Weather animals take a lot of water on hot weather
- Animal health
(c) Outline the sources of water in animals’ body. (02marks)
- Through drinking
- From wet feeds
- metabolism
- (a) State reasons why milk is highly perishable (03marks)
- Milk has high water content
- Milk contains fats and proteins which can easily go bad
- Has high nutrient contents that encourage growth microorganisms.
- Readily absorb bad odors.
(b) Describe how a lactometer is used and state its importance in the quality milk production (03marks)
- Lactometer measure the specific gravity of milk which is about 1.03.
- The bulb is dipped into the milk, when it sinks it means that solids such as maize flour have been added and increase the specific gravity above 1.030
- When it floats, water has been added or it is dilute.
(c) Explain the factors affecting the quality and quantity of milk production. (12marks)
- Age : there is an increase in milk production with the age until maturity and then decline
- Pregnancy; hormones for pregnancy inhibit milk production
- Stage of lactation; milk yield tends to increase for the two to three weeks
- Environmental temperature, high temperature reduces milk production
- Amount of water consumed; high water intake leads to high milk production
- Healthy status of the animal
- drugs
- (a) Describe the following as used in parasite management in livestock and in each case give an example.
- Periodic parasite (01mark)
These live on the host for a short time e.g. fleas
- Obligatory parasite (01marks)
The cannot survive without the host e.g. tapeworm
- Facultative parasite (01marks)
These may survive without a host e.g. blowfly larvae
(b) Describe with example the adaptations of ecto-parasites to parasitic life (09marks)
- Have sharp mouth parts for piercing the host skin
- Have strong mouth parts for anchoring on the animals
- Are mobile to look for host
- Have tough skin not to be damaged
- Have color similar to that of host foe camouflage
- Have dormant stages
- High production rate
(c) Outline the effects of external parasites on host animals. (08marks)
- suck blood causing anemia
- cause irritation
- transmit diseases
- cause skin rashes
- reduce milk production
- cause weight loss
Good luck
Yours
Mungudit Davious
Please Subscribe to promote this website. Subscription is free
Share with a friend
Your comments are highly welcome
Thank you so much

Wel sir
Good work
Thank you sir that good for me
Waw perfect sir
I have enjoyed your product
We miss pdf notes
We miss pdf notes
Thank you sir
Wow..perfect notes sir!!
Nice work