
Determinations of freezing point constant of a solvent using Rast’s method.

Rast’s method of determining the freezing point constant of a solvent
This is based on the use of melted camphor as a solvent because it has un usually high cryoscopic constant. An ordinary (360 degree) thermometer is used instead of Beckmann’s thermometer.
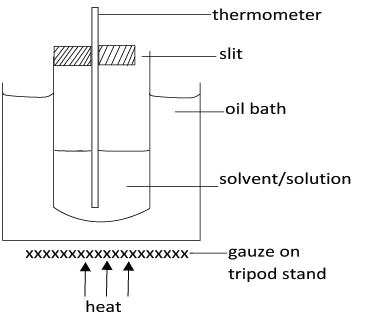
- The freezing point of M1 g of the pure solvent T1, is determined.
- A given mass of solute m2 is introduced into the solvent stirred until completely dissolved and freezing point (T2) is determined
Treatment of results
Mass of solvent = M1
Mass of solute = m2
∆t = (T1-T2)
Molecular mass of solute = Mr

Please Subscribe to promote this website. Subscription is free
Share with a friend
Your comment is valuable
Thank you so much
CATEGORIES Inorganic chemistry questions
TAGS Dr. Bbosa Science
