
Human circulatory system-Upper Primary Science

The circulatory system
The circulatory system consists of three independent systems that work together:
- the heart (cardiovascular),
- lungs (pulmonary),
- and arteries, veins, coronary and portal vessels (systemic).
The system is responsible for the flow of blood, nutrients, oxygen and other gases, and as well as hormones to and from cell
The figure below shows the main blood vessels in the human Circulatory system

BLOOD VESSELS
Blood vessels are tubes which carry blood around the body. Blood flows in the blood vessels. These vessels are:
- arteries,
- veins and
- cappilaries
Arteries are the blood vessels which carry blood away from the heart to the rest of the body. All arteries except the pulmonary artery carry pure blood which is rich in oxygen. This blood is called oxygenated blood. However, the pulmonary artery carries blood which is rich in carbon dioxide from the heart to the lungs.
Veins are the blood vessels that carry blood from other parts of the body to the heart. All veins carry deoxygenated blood, which has a lot of carbon dioxide and less oxygen, apart from the pulmonary vein. The pulmonary vein carries blood rich in oxygen from the lungs to the heart.
Capillaries are small blood vessels which connect arteries to veins.
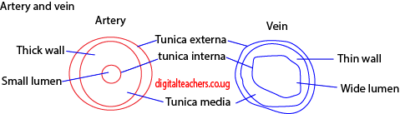
Differences between arteries and veins
| Arteries | veins | |
| 1 | Thick wall | Thin walls |
| 2. | Narrow lumen | Broad lumen |
| 3. | Have no valves except pulmonary artery and aorta | Have valves |
| 4. | Carry oxygenated blood except pulmonary artery | Carry deoxygenated blood except
pulmonary vein |
Adaptation of the artery
-thick wall to accommodate high pressure
– have a narrow lumens to maintain high pressures
– some arteries like aorta valves to prevent back flow of blood.
Adaptation of veins
-wide lumen to lower resistance to blood flow
-valves allow blood tom flow in one direction
Capillaries
They connect the arteries and veins.
They allow exchange between blood and cells.
Adaptation of capillaries
- thin walls for fast diffusion
- Ramify the body to increase surface area for exchange
The heart
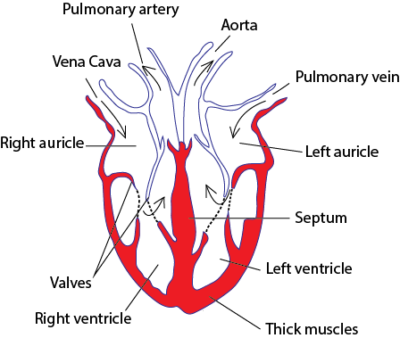
The heart pumps blood around the body. The heart has four parts, two upper ones called auricles and two lower ones called ventricles.
The left ventricle is usually thicker than the right ventricle due to its greater function of pumping blood to all parts of the body through the aorta.
Septa separates oxygenated form deoxygenated blood from oxygenated blood
Valves in the heart prevent back flow of blood
Blood
This is the red fluid that flows around the body. An adult human being has about five litres
Blood vessel
COMPOSITION OF BLOOD
Blood is composed of blood cells, plasma and platelets.
Blood cells
There are two types of blood cells namely:
- The red blood cells

The red blood cells contain hemoglobin a red coloring matter, which makes blood red.
They are disc shaped
They lack a nucleus
Hemoglobin carries oxygen and transports it around the body.
Lack of red blood cells or iron in blood causes a disease called anemia
- The white blood cells

The white blood cells are fewer than red blood cells and are colorless.
They have a nucleus
They are larger than the red blood cells
They fight diseases causing germs. They are the soldiers that defend our bodies against diseases.
Causing germs
Plasma
Plasma is the liquid part of blood, which is pale yellow in color. It is mainly made up of water and contains digested food, salts and proteins. Plasma helps in holding the other components of blood.
Functions of plasm
- Transports waste products to excretory organs
- Distribute digested food
- Transports other components of blood
Platelets
These are small pieces (fragments) of cells whose function is to help blood to clot when a blood vessel is cut or injured.
Diseases of the circulatory system
- Anemia or lack of red blood cells in the body. Anemia is treated with blood transfusion and balanced diet
- Infections treat by antibiotics
- Malaria
- Leukemia
- High blood pressure
- Dehydration
Causes of dehydration
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Excessive exercise
Sign of dehydration in children
Sunken eyes
Pale skin
Thin skin
Treatment of dehydration
- Taking Oral rehydration solution (ORS)
- Intravenous fluids
- Drinking a lot of juice or water
Preparation of oral rehydration salt solution
- Wash your hands
- Put two 0.5L cups of water in a clean container
- Add a sachet of ORS and stir to dissolve
- Use within 24 hours.
- The more ORS solution one drinks the better. ORS solution has no over dose
Fainting
This a condition where a person loses consciousness due to lack of enough blood to the brain
Conditions that lead to fainting
- Hunger
- Happiness
- Anger
- sickness
First Aid for fainting
- Remove a person from dangerous place
- Loosen tight clothes
- Check to see whether the person is breathing.
- Lie the victim on his back and raise the legs above the heart to increase blood to flow the head.
- Call for help.
For revision question download PDF
Circulatory system (upper primary)

It’s a very good website as far as improving students’ academic excellence is concerned