
Describe the factors that determine the rate of chemical reaction

Factors that affect the rate of reaction
The main factor which influence reaction rate are
(i) concentration of the reactant
(ii) temperature
(iii) Pressure
(iv) presence of light
(v) the size of the particles for solid reactants.
(vi) Catalyst
- Particle size
The smaller the particle sizes the faster the reaction in solid state because of increase surface area for contact. e.g.
CaCO3(s) + 2HCl (aq) → CO2(g) + CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l)
The reaction is faster when CaCO3 is in powder form than big chips.
- Concentration
The higher the concentration of reactants; the faster is the rate of reaction due to increase in the rate of collision among the reacting molecules.
- Pressure
Pressure increases the rate of reaction when the reactants are in gaseous phase because it increases the proximity and the rate of collision of the reacting molecules.
- Temperature
Temperature increases the rate of reaction because
- Particles gain kinetic energy which increases the rate collision
- it increases the fraction of molecules with energy equal or higher than the activation energy that enables the reaction to take place in case collision take place between molecules.
The graph below shows the distribution of kinetic energies of molecules of a gas at temperatures T1 and T2; T2 being higher than T1.
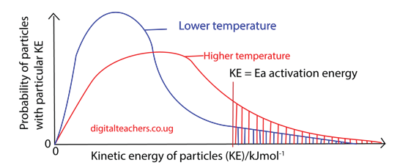
The number of molecules with energy equal to or greater then Ea increases rapidly with temperature as shown by the shaded area under graph above
- Light
Some reactions are catalyzed by light such as photosynthesis and formation of silver from silver salts that take place when a photographic film is exposed to light. The higher the light intensity, the higher the rate of reaction will be.
6. Surface area
Increasing surface area of the reactant increase the rate of reaction because it brings the reacting substances into more intimate contact to facilitate their interaction.
7. Catalyst
Increase the rate of reaction by lowering the activation energy
The energy diagram for the reaction for exothermic reaction in absence and presence of a catalyst
Please Subscribe to promote this website. Subscription is free
Share with a friend
Your comment is valuable
Thank you so much
