
To what extent was faulting responsible for the formation of relief landforms in East Africa?

Candidates should defi.ne the term faulting
Faulting is s the fracturing/ breaking/ rapturing/cracking of rocks due to strain and stress which subsequently leads to the dislocation and displacement of rock strata.
Faulting is caused by convectivity and radio-activity within the mantle which generates heat that melts mantle rocks; creating convection currents which exert forces on the earth’s crust responsible for the formation of a wide range of features in East Africa which include rift valley, block mountains, grabens, tilt block, escarpments, fault guided valleys.
The Rift Valley
A riff valley is an elongated trough bordered by two or more inward facing fault scarps.
The rift valley in East Africa is in two arms: i.e. the Eastern arm and Western arm
The formation of the rift valley has been explained three theories:-
- The Tension force theory by Gregory
- The compression force by Wayland
- Vertical displacement theory by Dixey
NB: Candidates is required to choose only one theory to explain the formation of the rift valley with relevant illustrations
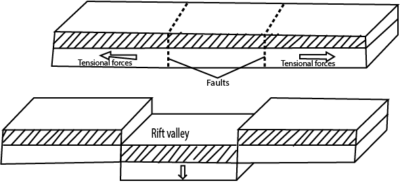
Tension theory by J. W. Gregory
- The radio-active and convective currents produced tension forces within the earth crust.
- Tension forces acted/ pulled apart/ in opposite directions.
- Normal faults were produced, displacing rock strata.
- Side blocks were separated from the middle block, which was later lowered/ sunk under its own weight forming a rift valley with gentle
- Erosion and mass wasting modified the slopes.
- The theory is more applicable to the Eastern Kenya Rift valley (Gregory Rift).
Compression force theory by1:,J. Wayland
- That strain developed in the East Africa crust as compressional forces pushed/moved in the same directions (convergent).
- Reversed faults were produced.
- The side blocks were forced to over-ride (up thrust), hanging above the central block. The central block thus formed rift valley with steep/ sharp edges.
- The sharp edges were later modified by erosion and mass wasting.
- The theory is more relevant to Western arm of the East African Rift Valley, especially the Albertine Rift valley.

Other theories include:
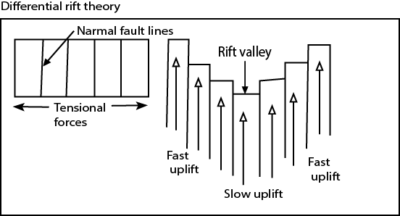
Differential uplift theory
- Dealt with the Nairobi part of the E t African Rift valley of Kenya that is step faulted.
- That there was a period of general uplift of part of the East African Crust .
- It led to the formation of several parallel fault-lines.
- Blocks on either side of the central block rose faster as the middle lagged behind in stages.
- At each stage, a mass or of block formed a terrace·
- Examples include Kendang scar near Nairobi appearing as several terraces rising from the Rift Valley floor.
- The gap in the middle of terraces formed the rift valley.
- Diagrammatic illustration of differential uplift
Relative Sinking (subsidence theory)
- Just like in differential uplift theory, there was extensive faulting in East Africa which created multiple parallel faults.
- Within the mantle / interior of the earth, there is intense heat originating from radioactivity and geochemical reactions.
- The heat melts down the interior rocks and they begin to move in form of convective currents upwards towards the crustal plates.
- When they become colder and therefore heavy, they sink or flow back down in the mantle and as they do so they exert a drag force which pull the crustal blocks downwards thus sagging of crustal blocks along each fault.
- The central blocks sagged more than those or, the extreme ends to form a step or terraced rift valley

Tilt block land scape
This is upland of inclined crustal block
It has angular inclined ridges and depressions formed by multiple faulting and vertical movements which displaced the faulted crustal blocks at different rates to & series of tilted faulted blocks.
Examples are Aberdare ranges in Kenya, Kichwamba in Uganda etc.

BLOCK MOUNTAIN OR HORST
A block mountain is an upland bordered by fault scarps on either side. Examples of the Block Mountains are Rwenzori ranges in Uganda, Usambara, Pare in Tanzania.
The formation of Block Mountains is explained by three theories:
- The compression force theory by Wayland
- The Tension force theory by Gregory
- Vertical displacement theory by Dixey
NB: Candidates should choose only one theory to explain the formation of a Horst with relevant diagrams
Formation of a block mountain by compression forces
- Compression forces pushed a crystal block of land on either sides resulting into stressing hence the development of reversed fault lines.
- The fault lines divided the crystal block into three parts.
- As the action of compression forces continued the middle/ central block was thrust upwards above the two adjacent blocks/ surrounding blocks to form a block mountain.
- This is illustrated as shown below:

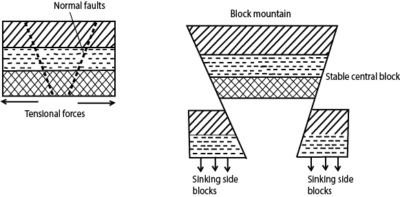
Formation of a block mountain by tension forces
- Tension forces act on the earth’s crust by pulling in opposite direction from each other.
- This is when convectional currents move horizontally in different directions hence the development of parallel normal faults in the crust.
- The faults divide the crust into three parts.
- The continued tension forces lead to the subsidence (sinking) of the side blocks.
- The middle block remains stable high above the side blocks as a block mountain
Formation of a block mountain by differential uplift theory;
- This is due to multiple faulting which forms series of crystal blocks of varying sizes and densities
- When the forces of uplift acted on the crystal blocks with varying strength.
- Uplift force was strongest on the central blocks; they were forced to rise higher to from peaks of the horst.
- The side blocks did not rise high enough but formed the sides of the horst in stages as illustrated below;

Formation by relative sinking;
- When faulted blocks experienced sinking which was not uniform. The side blocks sank faster than the central block.
- The central block remained relatively higher to form the peak of the horn as illustrated below;

Fault scarps/ fault escarpments.
It’s a steep slope along a fault formed when one block along the fault line is thrown up and the other own thrust e.g. Butiaba, Kicwamba in Uganda and Mau Escarpments in Kenya, Manyara, Elgeyo, Chunga etc.

Grabens
These are narrow , regular shaped and deep depressions on the floor of the rift valley formed as a result of secondary faulting.
Secondary faulting led to the formation of secondary normal faults and subsequent displacement of rock blocks to the formation of Grabens e.g. Grabens occupied by Lake Tanganyika, Turkana, Albert, Edward etc.

Fault guided valleys
Fault guided valleys are faulted valleys found along single faults where the fault zone is crushed susceptible to weathering and erosion.

Examples of fault guided valleys are River Aswa in Nonhem Uganda, Kerio Valley between Eigeyo Escarpment and Kamasiya Ridge in Kenya.
The candidates should then identify other processes which have led to formation of relief land forms in East Africa
Vulcanicity is the process through which molten rock /magma, gases and liquids are either ejected on to the earth’s, surface or injected into the earth’s crust through lines of weakness leading to formation of extrusive volcanic features and intrusive volcanic features
The extrusive volcanic features consist of
- Composite volcanoes e.g. Kilimanjaro,
- Ash /cinder cones g. TeJeki, Nabuyatom,
- Cunulo domes e.g.Mt. Ntunbi in Tanzania,
- Shield volcanoes/basalt domes g Marsabit,
- Lava plateaus e.g. Laikipia, Uasin Gishu
- Calderas e. Ngorongoro
- Explosion craters e.g. L. Karwe.

The Intrusive vulcanicity has led to formation of the following landforms after exposure of intrusive features by denudational processes
- Batholith with resistant rocks are exposed to form inselbergs, low hills e.g. in Mubende,
- Less resistant B1&1olithsform Arenas e.g. Rubanda in Kabale.
- Dykes with resistant rocks are exposed to form ridges e.g Parabong ridge, while dykes with soft rocks are worn out to form linear trenches e.g. near L. Turkana,
- Sills form flat toped hills.
Warping:- The up-warping and down warping led to formation of plateaus and basins respectively e.g. L. Kyoga and Victoria basins. ·
Coastal uplift – Has led to formation of raised beaches, raised cliffs, raised wave, cut platforms and exposed caves. .
Coastal subsidence: -Has led to formation of Rias, Dalmatia islands, estuaries, mudflats etc. formed due to Isostatic re – adjustment
- Weathering:
- Chemical weathering has produced landforms in karst regions e. stalactites, stalagmites, caves pillars
- Physical chemical weathering has led to formation of exfcliarion domes, rectangular rock block.s etc.
- Glaciation has led to formation of
- Erosional landforms like cirques, pyramidal peaks, hanging valleys, glacial troughs, Aretes
- Depositional land forms e.g. hill plains, Eskers, drumlins, moraines etc.
- Rivers have led to formation of:
- Erosional landforms e.g. valleys, plunge pools, Georges, Interlocking spars etc.
- Depositional landforms g. flood plains, braiding, slip – off slopes etc.
- Wave action has led to formation of
- Erosional landforms e.g. like notches, caves, blow holes, goes, headlands, bays etc.
- Depositional land forms e.g. beaches, spits, bars, tombolo etc.
- Sea depositing of coral polyps skeletons building coral reefs.

Well done
Excellent work. it gives the right way of answering questions.
Perfect and it makes teaching ok by giving the teacher ability to own the subject
Well and good