
Organic chemistry (O-level chemistry)

O-level organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is the study of compounds of carbon
Uniqueness of carbon
- Carbon forms very many useful compounds with different physical and chemical properties.
Importance of organic compounds
Organic compounds are used as
- Drugs
- Perfumes
- Clothes
- Shoes
- Dyes
- Detergents for washing
- Packing materials
- Herbicide to dry weeds
Terminologies
Hydrocarbons are compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen only
Functional groups are reactive parts of organic compounds for example
Double bonds (C=C) for alkenes
Triple bonds for C ≡C) alkynes
Hydroxyl group (-OH) for alcohols
Carboxylic groups (-COOH) for carboxylic acids
Homologous series
These are a group of compounds with members related as follows
- Members have similar general formula e.g. the general formula of alkanes is CnH2n+2.
- Have similar functional groups and thus same chemical properties
- Have similar methods of preparation
- Show gradual change in physical properties for instance alkanes range from gases to liquids to solids
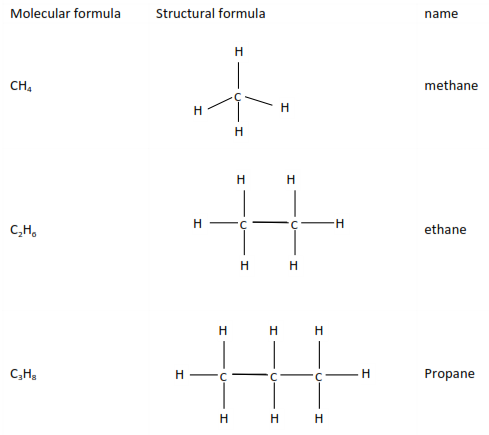
Alkanes
This is the simplest homologous series with saturated hydrocarbons with a genera
l formula CnH2n+2.
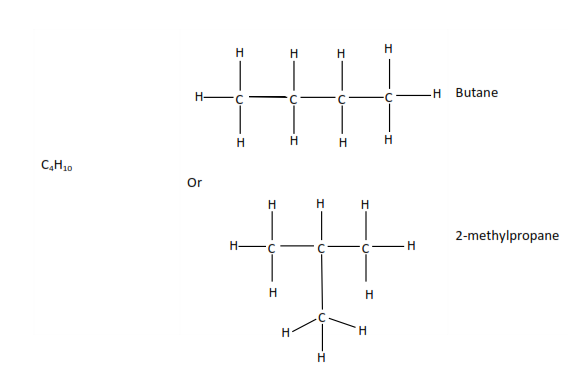
Compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural formulae like butane and methylpropane are called isomers
Physical properties of alkane
- they are insoluble in water
- they are soluble in organic solvents
- they range from gases to liquids to waxy solids
Chemical properties
- They burn in air to produce carbon dioxide, water, and heat. Due to the production of heat, they are used as fuel.
Example
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O + heat
- Chlorination: they react with chlorine in the presence of sunlight or u.v-light to produce chlorinated alkanes.
Example
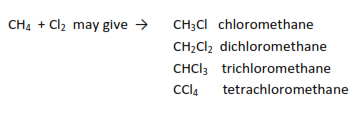
Preparation of alkanes
- By distillation of petroleum oil
- By cracking: cracking is the breakdown of long-chain hydrocarbons into useful short-chain hydrocarbons by heat (thermos-cracking) or by a catalyst (catalytic cracking)
- From Biogas: methane is the main component of biogas. Biogas is produced by anaerobic decomposition of organic matter (cow dung, feces, plant remains) in the presence of water
Alkenes
These are hydrocarbons that contain aa double bond
The general formula is CnH2n n ≥ 2
Examples are
Ethene CH2=CH2
Propene CH3CH=CH2
But-1-ene CH3CH2CH=CH2
But-2-ene CH3CH=CHCH2
Preparation of ethene

By dehydration (removal of a water molecule from) of ethanol with hot concentrated sulphuric acid
Testing or ethene
- Ethene decolorizes bromine water
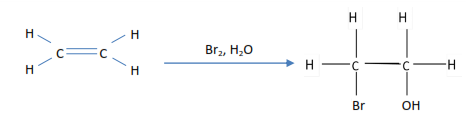
2. Ethene decolorized bromine tetrachloromethane
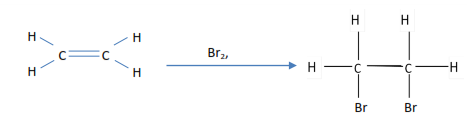
3. Ethene decolorizes acidified potassium permanganate (VII)
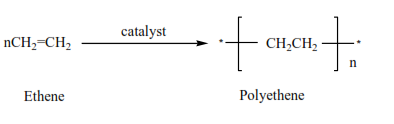
4. Alkenes form polymers called polyalkenes
A polymer is a molecule with a high molecular mass formed combination of very many small molecules called monomers.
Examples
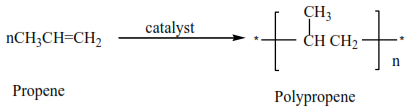
(ii) Propene polymerize to form polypropene
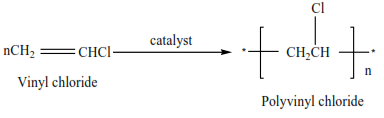
(iii) Vinyl chloride polymerize to form polyvinylchloride (PVC)
Uses of polyethene
- Insulator
- Water pipes
- Packing mate
Polymerization of dienes
Alkenes with conjugated double bond undergo polymerization to form polyalkenes with double bonds
Example
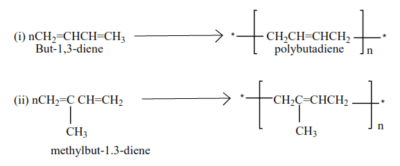
Polymers from conjugated dienes have double bonds, they are elastic and constitute different forms of rubber.
Vulcanization of rubber
It is heating rubber with Sulphur to make it
- Less elastic,
- More resistant to heat
- More durable
- Easier to dye
Uses of vulcanized rubber
- For raincoats
- Boots
- Shoe soles
- Rubber bands
Natural and artificial polymers
Natural polymers are polymers made plant or animal bodies
Examples are
| Polymers | monomers |
| Starch | glucose |
| Cellulose | glucose |
| Protein | Amino acids |
| Cotton | |
| Wool | |
| silk | |
| sisal |
Artificial polymers are polymers that are man-made
Examples
Nylon a
Polyester
Polyethene
Advantage of natural polymers
- Cheap
- biodegradable
The disadvantages of natural polymers
- not durable
- have low property value such as low tensile strength
Advantage of synthetic polymers/plastic
- light and portable
- resistant most chemicals
- they are durable
- they are thermos insulators
The disadvantage of synthetic polymers
- they are nonbiodegradable
- fire hazards
Thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers
Thermoplastic polymers are those that soften and can be remoulded into new shapes. E.g. polyethene
Thermosetting polymers are those that decompose on heating and cannot be remoulded on heating for example vulcanized rubber, melamine, Bakelite.
Alkyne
They are hydrocarbons with a general formula CnH2n-2, n. They contain a triple bond
Examples
Ethyne HC≡CH
Propyne, CH3C≡ CH
But-1-yne CH3CH2C≡ CH
But-2-yne CH3C≡ CCH3
Like alkenes they decolorize bromine water
Alcohols
They are compounds that contain hydroxyl (-OH) group.
Example
Ethanol or CH3CH2OH
Preparation of ethanol
By fermentation of glucose or starch-containing food (cassava, maize, and bananas)

Uses of ethanol
Social drink
Antiseptic in soft drinks
Production of ethene
Fuel
Extraction of sugar
- sugar canes are crushed and juice extracted
- Sulphur dioxide is bubbled through to breach the juice
- Lime is added to clarify the juice and adjust pH and filtered
- The juice is boiled to increase its concentration from 15% to 60%.
- Sugar crystals in ethanol are added to crystalize sugar
- The sugar crystals are washed with water and dried
The reaction of sugar with sulphuric acid
Sugar is dehydrated with concentrated sulphuric acid with the evolution of heat to a black mass of carbon

For questions and answers please download PDF

I like it its interesting and easy to understand
How can I download this content? Someone to help me
On you phone tap the three horizontal lines on the top left of the website and follow the prompts
Thanks so much for your time sir
The best
Thanks for your help
Harus di comment artikel seperti ini, sangat inspiratif, thanks dari IDProperti.com | Pasang Iklan Properti
Always impressed by the depth of your articles Pasang Iklan Properti
Terima kasih atas artikel yang bermanfaat. Semangat dari IDProperti.com | Pasang Iklan Properti
Met de gebakken peren zitten pepe88 betekent Met de gevolgen van iets zitten.
Such valuable insights Thank you for sharing! IDProperticom
Dein Guide zu den besten veganen Restaurants in Deutschland ist fantastisch. agen888 Ich freue mich schon auf die kulinarischen Entdeckungen!
Your article about the best family activities in Germany is great. agen888 I have many great ideas for the next vacation.
A very well-researched article about the development of the German music scene. agen888 Your recommendations are top-notch!
Website ini memang pilihan terbaik untuk membaca artikel berkualitas. Terima kasih telah berbagi, IDProperti.com | Pasang Iklan Properti Gratis
Such a useful post. Enjoyed every bit of it! Best wishes, Pasang Iklan Properti Gratis
Artikel Anda sangat membantu. Menunggu postingan berikutnya! Salam hangat, Pasang Iklan Properti Gratis
So weit wie der Pfeffer wächst pepe88 Sehr weit entfernt oder distanziert sein
Sich in die eigene Suppe einlegen pepe88 Sich selbst in Schwierigkeiten bringen.
agen888 : Telur di hujung tanduk agen888, berada dalam keadaan yang sangat berbahaya atau genting, agen888
Artikel ini adalah contoh luar biasa dari penulisan yang penuh dedikasi. Anda berhasil menyajikan informasi yang kompleks dengan cara yang sangat jelas dan menarik. Saya sangat menikmati bacaan ini dan memperoleh banyak pengetahuan baru. Terima kasih banyak atas kontribusi yang berharga ini. Salam, Pasang Iklan Properti Gratis
This is one of the most impressive articles I’ve come across in a long time. Your detailed analysis and thoughtful presentation of information are top-notch. I particularly appreciate the way you’ve articulated your points with such precision and clarity. This is truly a standout piece. Best regards, Pasang Iklan Properti Gratis
agen888 : Bagai cacing kepanasan agen888, seseorang yang sangat gelisah atau tidak tenang, agen888
Jemanden in die Schranken weisen pepe88 Jemanden in die Schranken weisen.
Ungebetene Gäste pepe88 Unwillkommene Besucher oder Eindringlinge.
Sich einen Überblick verschaffen pepe88 Einen Überblick oder Verständnis einer Situation gewinnen
Die Katze aus dem Sack lassen pepe88 Ein Geheimnis verraten
Klartext reden pepe88 Klar und ehrlich sprechen.
Jemanden aus dem Weg gehen pepe88 Jemandem aus dem Weg gehen oder ihn vermeiden
Alles in de haak pepe88 – Wird verwendet, um zu sagen, dass alles in Ordnung und geregelt ist.
bro138
I blog frequently and I truly appreciate your information. This article has really peaked my interest.
I will take a note of your blog and keep checking for new details about once per week.
I subscribed to your RSS feed too.
godownloader. com
Yes! Finally someone writes about live draw hk.
Your articles are a masterpiece Thanks for sharing your expertise! Pasang Iklan Properti Gratis
ondel4d
I always emailed this website post page to all my friends, for
the reason that if like to read it afterward my contacts will too.
lawu88
It’s nearly impossible to find knowledgeable people about this
topic, but you seem like you know what you’re talking about!
Thanks
hondatoto hondatoto hondatoto hondatoto
It’s a pity you don’t have a donate button! I’d most certainly donate to this excellent blog!
I guess for now i’ll settle for book-marking and
adding your RSS feed to my Google account. I look forward to brand new updates and will talk about this blog with my Facebook group.
Talk soon!
data hk data hk data hk data hk
Greetings from Ohio! I’m bored to tears at work so I decided to check out your site on my iphone during lunch break.
I really like the knowledge you present here and can’t
wait to take a look when I get home. I’m shocked at how fast your blog loaded
on my cell phone .. I’m not even using WIFI,
just 3G .. Anyhow, amazing blog!
hoki777 hoki777 hoki777 hoki777 hoki777
If you want to obtain much from this article then you have to apply
such techniques to your won website.
g200m g200m g200m g200m g200m g200m g200m
great publish, very informative. I ponder why the other experts of this sector don’t
notice this. You should proceed your writing. I’m confident, you have a huge readers’ base already!
slot88 slot88 slot88
Link exchange is nothing else however it is simply placing the other person’s website link
on your page at suitable place and other person will also do same in support of you.
idcash88 idcash88 idcash88
Keep on working, great job!
pos4d pos4d
pos4d
Nice post. I learn something new and challenging on websites I stumbleupon every day.
It’s always exciting to read through articles from other writers and use a little something from other web sites.
baim4d baim4d baim4d
Wonderful blog! I found it while searching on Yahoo News.
Do you have any tips on how to get listed in Yahoo News? I’ve been trying for a while but
I never seem to get there! Appreciate it
slot gacor hari ini slot gacor hari ini slot gacor
hari ini
It is appropriate time to make some plans for the future and it’s time to be happy.
I have read this post and if I could I want to suggest you few interesting things or advice.
Perhaps you can write next articles referring to this article.
I desire to read even more things about it!
wdbos wdbos wdbos
Hurrah, that’s what I was searching for, what a material!
present here at this website, thanks admin of
this web site.
slot demo slot demo
slot demo
WOW just what I was looking for. Came here by searching for 1
slot88 slot88 slot88
I am genuinely delighted to glance at this blog posts which contains plenty of helpful information, thanks for providing these data.
19dewa 19dewa 19dewa
My brother suggested I might like this web site. He was totally right.
This post truly made my day. You can not imagine simply how much time
I had spent for this info! Thanks!
Your articles are always worth reading Keep up the great work! Pasang Iklan Properti Gratis
Fantastic insights in this post! I learned a lot. Best, Pasang Iklan Properti Gratis
Your blog is a beacon of quality content Much appreciated from IDProperticom
Always a pleasure to read your well-crafted articles Thank you from IDProperticom!
This article was a great read. Your insights and analysis are spot on. Best wishes, Pasang Iklan Properti Gratis
Your blog is a must-read for anyone interested in this topic Pasang Iklan Properti Gratis
This article has given me plenty to think about Thanks for sharing your insights! Greetings from IDProperticom
Very supportive of community involvement.
Rtp Enambet
Very informative for fostering collaboration.
Login Enambet
Kapan pun harus meninggalkan komentar untuk artikel yang bagus. Salam dari IDProperti.com | Pasang Iklan Properti Gratis
Your posts often highlight the beauty in everyday life
PASAL4D
Link Alternatif Pasal4D
PASAL4D
Your blog is a beacon of quality content Much appreciated from IDProperticom
Wow, what a fantastic article! Your ability to break down complex concepts into easily digestible segments is truly admirable. This piece is both informative and thought-provoking, and it’s clear that you have a deep understanding of the subject matter. Thank you for this enlightening read. Cheers, Pasang Iklan Properti Gratis
Can’t find any good article like this, thank you Regards, Pasang Iklan Properti Gratis
togel jp slot
Im really impressed by how well the author breaks down such complex ideas It shows a great mastery of the topic
togel jp slot
MHTOGEL
Login MHTOGEL
Login MHTOGEL
YATOGEL : You have a wonderful way of expressing gratitude.
The world you create in your stories is unforgettable.
Enambet
Link Enambet
Daftar Enambet
Your writing never feels rushed or superficialits always thoughtful and wellcrafted
Daftar Pasal4D
Link Alternatif Pasal4D
PASAL4D
Login Pasal4D
You have an amazing ability to make others feel special
YATOGEL
Your attention to detail is impressive
YATOGEL
You have a way of making people believe in themselves
TOGEL ONLINE
Blog dengan konten terbaik ada di sini, terima kasih dari IDProperti.com | Pasang Iklan Properti Gratis
Konten yang sangat baik dan ditulis dengan baik. Salam, Pasang Iklan Properti Gratis
You bring joy and wisdom with every word you write
Daftar Pasal4D
Your blog is a masterclass in meaningful storytelling
Link Alternatif Pasal4D
You write with an authenticity that resonates deeply
Login Pasal4D
Your posts are always worth the wait
Link Alternatif Pasal4D
Your passion translates into impactful content
Pasal4D
Artikel ini adalah contoh sempurna dari penulisan yang mendalam dan bermanfaat. Setiap elemen informasi disajikan dengan sangat jelas dan terperinci, membuat bacaan ini sangat informatif. Terima kasih atas kontribusi yang sangat berharga ini. Salam hangat, Pasang Iklan Properti Gratis
You bring so much joy to the world
TOGEL ONLINE
This article has such high educational value.
sosrotogel