
Internal structure of a leaf or cross-section of a leaf

Internal structure of a leaf
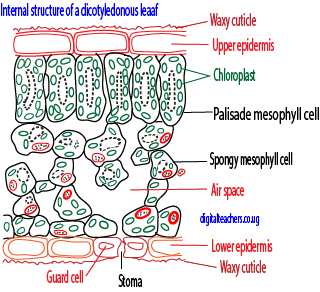
Functions of tissues in dicotyledonous leaves
| Tissue | Structure | Function |
| 1. Upper and lower epidermis | One cell thick
External walls covered with cutin (waxy substance) Contain stomata (pores surrounded by guard cells) |
– Protective
– Cutin is water proof and reduce water loss from the leaves – Allow gaseous exchange |
| 2. Palisade mesophyll | Column-shaped cells with numerous chlorophyll in thin layer of cytoplasm | – Main photosynthetic tissue. Chloroplast may move towards light |
| 3. Spongy mesophyll | Irregular shaped cells fitting loosely to leave large air space | – Photosynthetic, but fewer chloroplast than palisade cells. Gaseous exchange can occur through the large air space via stomata. |
| 4. Vascular tissue | Extensive finely branching network through leaf | – Conduct water and mineral salts to the leaf in xylem
– Remove photosynthetic products through phloem – Provide a supporting skeleton to the lamina, aided by turgidity |
Please Subscribe to promote this website. Subscription is free
Share with a friend
Your comments are highly welcome
Thank you so much
CATEGORIES o level biology revision questions
TAGS Dr. Bbosa Science

Like your activities
Why do you feel thirsty after eating salty foods