
Describe an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism in plant roots and shoots.

Hydrotropism:
1. Hydrotropic movements refer to a plant’s movement or growth in response to a water stimulus, while hydrotropism refers to the analogous response to a water stimulus.
2. Roots migrate and grow towards the water in this type of movement, displaying a positive hydrotropic response.
3. The process of root growth or migration towards a water source is known as hydrotropism.
Experiment to prove hydrotropism:
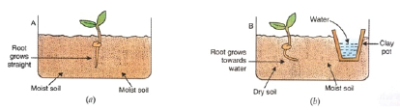
Procedure
- 1 and 2 beakers are taken.
- Beaker 1 is filled with moist soil, which is used to sow the seeds.
- In one part of beaker 2, dry soil is added, while in another section, moist soil is added, and the seeds are sown
- Place a tiny beaker of water next to it as well.
- Keep it for a while to allow the plants to flourish
Result:
- It was discovered that in Beaker 1, plants will grow normally and roots will be straight due to the presence of moist soil.
- The presence of the water beaker next to the plant in beaker 2 causes the plant to grow towards the water, as illustrated in the above illustration.
Conclusion:
- As the roots bend towards the porous pot of water, it proves that the plant exhibits hydrotropism.
- Hydrotropism is a type of plant growth response in which the direction of growth is regulated by a water concentration gradient stimulus.
Diagram
CATEGORIES Bio Questions and answers
TAGS Dr. Bbosa Science
