
Explain briefly diffraction of X-rays by crystals and derive Bragg’s law.

Explain briefly diffraction of X-rays by crystals and derive Bragg’s law.
A parallel beam of monochromatic X-rays incident on a crystal is reflected from successive atomic planes and super-imposed, forming an interference patterns
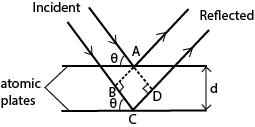
For constructive interference to occur, the path difference is equal to the whole number of wavelength
Thus BC + CD = nλ
dsinθ + dsinθ = nλ
or 2dsinθ = nλ where n = 1, 2, 3, 4 …
Please Subscribe to promote this website. Subscription is free
Share with a friend
Your comment is valuable
Thank you so much
CATEGORIES A-level modern physics
TAGS Dr. Bbosa Science

This is the kind of content I love to read. Health & Personal Care
You have a knack for making things clear. Barcelona News
Learn about the MBBS Fees Structure in Madhya Pradesh for both government and private colleges.