
Ear, nose, tongue – upper primary Science

The human Ear
The mammalian ear has three major functions
- Detecting sound through the cochlea
- Maintenance of body balance by the semicircular canal
- Equalize pressure in the head through Eustachian tube
Structure of mammalian ear

The has three main parts
(a) Outer ear
(b) Middle ear
(c) Inner ear
The middle ear is separated from the outer ear by tympanic membrane, or ear drum. The middle ear is separated from the inner ear by an oval window (fenestra ovalis) and round window (fenestra rotunda) both of which are covered by membranes.
Spanning the middle ear from the tympanic membrane to the oval window are three tiny bone called ossicles (the malleus, incus and stapes).
The Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear with the pharynx, ensures that the air pressure on the both side of the tympanic membrane are equal.
Eardrum contains wax to trap dust and foreign bodies from entering the ear. However, too much wax blocks hearing.
Hearing
- Sound funnels into the ear canal and causes the eardrum to move.
- The eardrum vibrates with sound.
- Sound vibrations move through the ossicles to the cochlea.
- Sound vibrations cause the fluid in the cochlea to move.
- Fluid movement causes the hair cells in Organ of Corti to distort.
- Distortion of hair cells causes firing of impulses through Auditory nerves to the brain that interprets the nature of sound.
A person who cannot hear is said to be deaf.
Caring for the ear
The ear should be cleaned regularly.
Some ways of taking care of the ear include:
- Never insert sharp objects in the ear because they can pierce the eardrum.
- Insects, and foreign bodies in the ear should be removed by specialized person/doctor.
- Avoid loud noises or sound which can burst the ear drum and lead to
- All ear infection should be treated immediately.
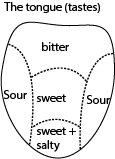
Tongue
This is the sense organ for tasting. The parts of the tongue that sense the taste of food are called taste buds.
There are different tastes:
- Sweet – the sweet taste is detected by taste buds at the tip of the tongue. Anything that is sweet has a sugar taste, and contains sugar. An example is ripe bananas
- Salty the salty taste is also felt at the top of the tongue. anything salty contains salts
- Sour the taste is felts at the sides of the tongue. A sour taste is sharp and is acidic. An example is the taste of lemon or vinegar.
- Bitter- the bitter taste is detected by taste buds at the back of the tongue. Bitter taste is sharp and unpleasant for example the taste of the peels of a lemon or the peels of oranges.
Caring for the tongue.
This is done by brushing it using a soft brush to remove the remaining of food particles. Cleaning the tongue ensures that the taste bud remains fresh and the tongue produce fresh breath.
Nose
The nose is the sense organ that detects smell. This helps to discriminate between good and bad food and also to detect predators.
The inside of the nose has a sensitive moist Lining that sense chemicals in gaseous form.
The hairy lining cleans the air breathed in before reaching the lungs.
Caring for the nose
The nose should be cleaned regularly of the
Rough objects should not be used to the nose as they may injure the delicate inner lining and this could lead to nose infections.
Revision questions
- When a drum is hit, you hear sound.
(a) How does the eardrum help you to hear sound?
……………………………………….………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) There is wax in the outer ear. What is the function of wax?
…………………………………………………………….………………………………………………………………………………………
(c) What is the effect of too much wax in one’s ear?
……………………………………………..………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- What part of the ear is likely to be damaged if you clean your ear with a sharp object?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Give one of the functions of the human ear.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Which organ in your body helps you to find out whether something in sweet or bitter?
……………………………………………………….…………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Name the sense organ for hearing.
…………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Which part of the human ear equalizes pressure in and outside the ear?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Name the body organ which helps a person to know whether there is enough sugar in tea or not
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Study the diagram of the f human ear below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
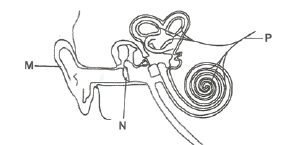
(a) Name the parts marked M and N
(i) M: ………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) N: ……………………………………………………………………………………..
(b) Give the function of the part marked P.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
(c) Use letter B to show the part of the ear responsible for balancing the body
- Which part of a fish performs a similar function as the human ear?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Draw and name parts of the ear
- How can you assist a person who has a foreign body in the ear?
Suggested answers
- When a drum is hit, you hear sound.
(a) How does the eardrum help you to hear sound?
It vibrates and the vibration transmitted to the inner ear for interpretation
(b) There is wax in the outer ear. What is the function of wax?
Traps foreign bodies from entering the ear
(c) What is the effect of too much wax in one’s ear?
Prevents proper hearing
- What part of the ear is likely to be damaged if you clean your ear with a sharp object?
Eardrum
- Give one of the functions of the human ear.
Hearing
Posture
Equalize pressure in the head
- Which organ in your body helps you to find out whether something in sweet or bitter?
Tongue
- Name the sense organ for hearing.
Ear, lateral line, feelers, antennae
- Which part of the human ear equalizes pressure in and outside the ear?
Eustachian tube
- Name the body organ which helps a person to know whether there is enough sugar in tea or not
Tongue
- Study the diagram of the f human ear below and use it to answer the questions that follow.

(a) Name the parts marked M and N
(i) M: pinna
(ii) N: eardrum
(b) Give the function of the part marked P.
Send impulses to the brain
(c) Use letter B to show the part of the ear responsible for balancing the body
- Which part of a fish performs a similar function as the human ear?
Lateral line
- How can you assist a person who has a foreign body in the ear?
Rushing a person to hospital

This is a must-read for everyone. Thanks! 500 ka redeem code
Understand the financial requirements of medical education with MBBS Fees Structure in Chandigarh.
Win big and experience the best in gaming with Raja Luck Game.