
Vertebrates – upper primary science

Vertebrates
Vertebrates are animals with backbones. Vertebrates can be classified into either cold blooded or warm blooded.
The cold blooded vertebrates can vary or change their body temperature according to the temperature of the surrounding environment. Examples of cold blooded
animals are: fish, Amphibians, reptiles.
The warm blooded animals such as birds and mammals, have a constant body temperature irrespective of temperature changes in the environment.
Fish
Example is tilapia

Characteristics
They live permanently in water.
Their bodies are protected with scales or hard skin
They extract oxygen from water using gills.
Their body temperature varies with that of environment, that is, they are cold blooded.
The eggs and sperms are shed in water where they fuse. That is fertilization is external.
A drawing of a tilapia

Functions of parts of fish
- Operculum protects gills
- Dorsal fin prevents fish from rolling.
- lateral lines detect sound waves
- caudal fin used for propulsion
- Pectoral, pelvic and ventral fins for balancing.
- The fish’s body is protected with scale.
- The scales are covered by slippery layer which help
Easy escape from the grip of its enemy
to reduces friction while moving
Amphibian
These are amphibians which include Toads, newts, and frogs.

Characteristics
- they live both on land and in water.
- They have soft moistened skin with no scales
- They lay eggs in water and are fertilized externally.
- they are coldblooded That is, their body temperature varies with environmental temperature.
- They breathe using gills when they are still young (tadpoles) and lungs when they mature.
Reptiles
Examples are snakes, crocodiles, lizards, turtles, tortoise, python and chameleons.

General characteristics
- they have a dry skin with horny scales
- they use lungs for gaseous exchange
- they are cold blooded
- they lay eggs with a shell
Note that
- Chameleon protects its self by changing color to look like the surrounding not to be noticed by predator
- Tortoise protects itself by hiding in its shell.
- Reptiles that live in water include turtles, some snakes and
crocodile - Land crocodile lizards, tortoises and snakes.
Birds
These are birds e.g cock, hens, ducks, eagles, peacock.
Characteristics of birds
- Their skin is covered with feathers except legs that are covered with scales.
- they have skeletons made of hollow bone.
- have beaks for feeding.
- they are homiothermic. That is they regulate their body temperatures.
- they lay eggs with shells
- they undergo internal fertilization
- parents take care of the young ones
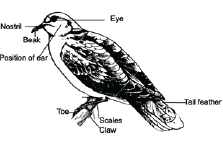
Feathers
Functions of feathers
- protect inner part of the body .
- Keep the body warm and dry
- some feathers e.g. quill feather is used for flight.
Types of feathers.
- Quill feather: used for flight, protection and warmth.
- Down feather for protection and warmth
NB: Ostrich, kiwi, penguin are flightless because they lack strong flight muscles.
Bird’s beaks
Grain eaters like chicken have short, strong and pointed beaks for picking up grains or seeds from the ground.
Filter feeders like ducks have flat and broad beak for sieving or filtering fish, and other water animals from mud
Nectar feeders like sunbird and humming bird have long, thin and slanted beaks to reach through the petals of a flower to suck the nectar.
Flesh eaters like Hawks have strong, short and hooked beak that is used for tearing flesh or meat from the bones of their prey. They feed on animals such as rats and chicks.

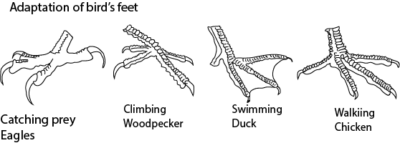
Bird’s feet
These are modified according their use as shown below
Mammals
Examples are cow, man, dogs and cats.
What characteristics do mammals have?
Mammals have the following characteristics:
- Has specialized teeth
- Has external ear
- Has teats leading to mammary glands
- Body is covered with fur or hair
Others
- They breathe by the use of lungs
- Most mammals live on land, though some for example whales, seals and dolphins live in water. These mammals that live in water are called marine
- Most have four limbs – some walk on two legs for example man,
some walk on four limbs for example cats and cows,
some fly using wings for example bats,
some hop or leap like the kangaroo, while others swim for example dolphins and whales.
The mammals that have hooves and are called hooved mammals. They include cows and goats. The kangaroo has a porch on its stomach area which it uses to carry its young one.
- They reproduce by giving birth to young ones though some primitive ones called monotremes, lay eggs which hatch to produce young ones. An example of mammals that lay eggs is the duck-billed platypus.
- Fertilization is internal
Classification of mammals
Mammals may be classified according to their feeding habits.
- Herbivores feed on plants only e.g. cow, goat, sheep
- Carnivores feed on animal flesh only, examples, lion, leopard
- Omnivores feed on both plants and animals, examples, man, pig
For revision questions and answers please download the PDF below
Sponsored by The Science Foundation College +256 753 80 27 09

So good and precised notes
Thanks for shedding light on this. Garden & Outdoor
I learned something new today. Thank you! Real Madrid News
MBBS Direct Admission in Punjab makes it easier to secure a seat in top colleges.