
Soil-upper primary science

Soil
It is the loose material that covers the earth’s surface.
It forms 25% of the earth’s surface. The rest is water.
Importance of soil
- Soil is a habitat for animals such as earthworms, termites and ants
- Soil contains plant nutrients
- Soil supplies plants with water
- Provide anchorage for the plant
- Sand soil is used for building
- Clay is used in pottery.
Weathering
This is a process of soil formation by break down of rocks
Agents of weathering
- Running water slowly wear out rocks
- acid
- Wind wear out rocks
- Animals: animal hoofs break rocks into pieces.
- Heating and cooling of rocks at night: continued expansion and contraction of rock weaken then leading their break down
- Plant roots can break down rocks
Components of soil
Soil contains
Water
Living microorganisms
Organic matter
Humus
Air
Investigating the presence of water in the soil
Requirements
A tin, Source of heat, Some soil, Cold lid
Procedure
Heat the soil in a tin covered with cold lid
Observations

On heating the lower part of the lid is covered by water droplets
Conclusion
Soil contains water
Investigating the presence of humus in the soil
Requirements
Test tube, Source of heat, Some soil
Procedure
Heat the soil strongly in a test tube
Observation

Smoke is produced
Deduction
Smoke contain humus (organic matter)
Investigating the presence of air in the soil
Requirements
Dry soil, a container, water
Procedure
Pour water to the soil in a glass container
Observation

Air bubble seen
Conclusion
Soil contain air
Sandy soil contains more air than clay soil due to its bigger particle size.
Properties of the soil
Types of soil
There are three types of soil: sand, clay and loam whose properties are given in the table below
| Soil property | Soil type | ||
| Sand | Clay | Loam | |
| Soil particles | Big | Small | Mixture |
| Water drainage | High | Low | Moderate |
| Water retention | Low | High | Moderate |
| Capillarity | Low | High | Moderate |
| Air spaces | Big | Small | Moderate |
Uses
Sand for building
Clay for pottery
The soil properties are:
Capillarity, Drainage and Soil texture
Capillarity
It is the rising up of water in the soil.
The set up below demonstrates soil capillarity
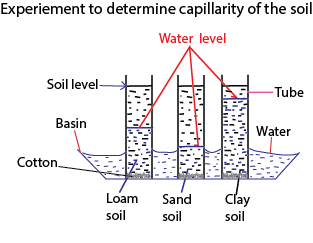
Observation
Clay soil has highest capillarity followed by loam soil followed sand soil
Application of capillarity
- Raising of water in soiling during dry spells to be used by the plant
- Transport of water and mineral salts up the stem of plants
- Rising up of kerosene of in a wick of a lamp to initiate burning
- Wetting lower part of the walls of a house
Drainage
It is the ability of water to pass through soil
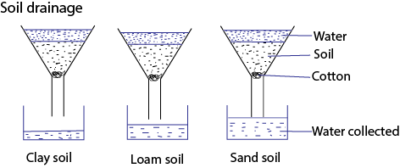
The size of the soil particles determines the ability of water to pass through.
Soil with large particles allows water to pass through easily and is said to have good drainage.
Soil with small particles does not allows water to pass through easily and is said to have poor drainage
Sand soil has good drainage while clay soil has poor drainage.
Water retention
This is the ability of soil to hold water.
A soil with good drainage has poor water retention.
Sand soil has poor water retention while clay soil has good water retention.
Water retention of sand soil can be improved by adding humus.
The ability of sand soil to increase water retention.
Loam soil is the best soil for farming because it has moderate capillarity, water retention and drainage.
Soil erosion
This is the washing away of top soil by its agents
Agent of soil erosion
- Water: running water loosen soil particles making it easy to carry away
- Wind: blows away top soil from bare ground
- Animal hoofs loosen soil particles making easy erode
Types of soil erosion
- Splash erosion: occurs when soil is displaced by a rain drop.
- Sheet erosion: occurs when a thin uniform sheet of top soil is carried away.
- Rill erosion: occurs when water removes top soil leaving small channels in the soil
- Gulley erosion occurs when running water carry away top soil leaving deep U-shaped or V-shaped gulley.
Human activities that lead to soil erosion
- Over cultivation of soil
- Deforestation
- Bush burning
- Road construction
Means of stopping soil erosion
- By terracing
- Couture ploughing
- Strip cropping
- Planting trees
Soil fertility
This is the ability of the soil to produce high yield and maintain production of long time
Means of improving soil fertility
- By crop rotation: crop rotation prevent exhaustion of minerals and allow leguminous plants or plants with root nodules to add nitrogen.
- Addition of manure or fertilizers: fertilizers can be organic or artificial
- By mulching
- mulching retains soil moisture
- mulching prevents soil erosion
- mulching add soil nutrients when the mulch decompose.
Pollution
Pollution is the introduction of wastes or harmful substances into the environment, making the environment unfit to support life in a healthy way. The materials that cause pollution are called pollutants. The components of the environment that can be polluted include air, water and soil.
Sources of soil pollutants
- sewage
- industrial effluents/wastes
- use pesticides
- excessive use of fertilizers
- urban wastes, glass, plastics
Effects of soil pollution
- Oil spillage suffocates microorganism
- Plastics and glass prevent proper growth of plant root and drainage
- Burning alter soil quality
Soil conservation
It a means of taking cares of the soil to maintain soil fertility
Methods of soil conservation
- Avoid excessive use of pesticides and fertilizers
- Avoid dumping of industrial wastes in the soil
- Avoid burning vegetation cover
- Control soil erosion
- Control grazing
For revision questions download PDF

Some really nice stuff on this internet site, I love it.
I really like what you guys are usually up too This type of clever workand exposure! Keep up the awesome works guys I’veincorporated you guys to our blogroll
Thanks for shedding light on this. Stationary
Thanks for being a source of inspiration. Indian Football
Explore quality educational options with MBBS Admission Through Management/Nri Quota in West Bengal.
Understand academic benchmarks at MBBS Cutoff Of Private Medical Colleges in Sikkim.
Sign up using the Raja Luck Invite Code for an exciting start.