
Glass prisms and dispersion of light (O-level physics)

Glass prisms and dispersion of light
Path of light through the glass prism
A ray OM making an angle i1 with the normal at M is refracted towards the normal along MN and away from the normal at N along NS.
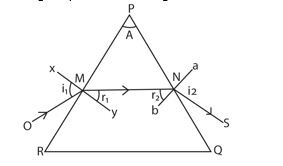
Note that light rays from less dense to a denser medium is refracted towards the normal while a light ray from denser to light medium is refracted away from then normal.
Dispersion of white light by a transparent medium
Dispersion of whit light is the separation of white light in to its component colors by a transparent medium due to their speed differences in the medium.
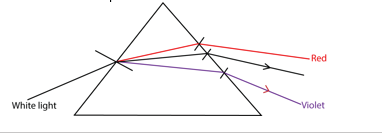
When white light falls on a transparent medium, its different component colors travel with different speeds through the medium.
They are therefore deviated by different amounts on refraction at the surface of the medium and hence dispersion.
NOTE:
- White light is a mixture of various c This is called the spectrum of white light.
- The spectrum of white light consists of red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet light ban
- On refraction, violet is the most refracted colour away from the normal ( violet is the most deviated colour ) while red is least deviated
Color filters and opaque objects
Filters: A filter is a glass or celluloid transparent colour plate which transmit light of only one colour and absorb all the other light.
Opaque objects: They do not allow light to pass through. Opaque objects absorb all other colours.
Mixing Colours:
Primary colours are those that cannot be obtained by mixing any other colours. These are Red, Green and Blue.
Secondary Colours: A secondary colour is one which is obtained by mixing two primary colours
e.g. Yellow = Red + Green
Magenta = Red + Blue
Cyan (Peacock blue) = Blue + Green
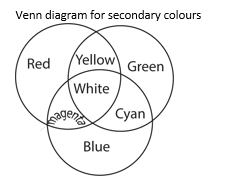
Complimentary Colours These are two colours which give white when mixed
Yellow + Blue = white
Magenta + Green = white
Cyan + Red = white
Mixing pigments
Pigments in dyes are impure and reflect more than one colour light.
When two pigments are mixed, they reflect the colour which is common to both and absorb all the other, e.g. Yellow paint reflects orange, yellow and green, while blue paint reflects green blue and indigo.
Yellow + blue reflects green, absorbs orange, yellow and blue.
Mixing coloured light is called mixing by addition.
Mixing coloured pigments is called mixing by subtraction.
Mixing of coloured filters and pigments
Example 1
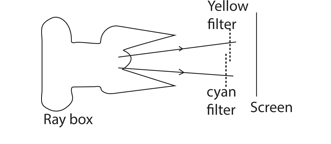
When a yellow filter and cyan filter are placed at some distance from the ray box such that, half of their portions overlap. State and explain what is observed.
Observation
Green light is seen where white light passes through both filters.
Explanation:
For the overlap of yellow and cyan: Cyan filter absorbs the red light and transmits green and blue, but the yellow filter absorbs blue light and transmit green and red (which absorbed by the cyan filter) so only green is transmitted
Example 2
The overlap of yellow and magenta gives red light because the magenta filter absorbs Green and transmits blue and red light is yellow filter absorbs blue and transmits red and Green so red light is transmitted.
Example 3
The overlap of Cyan and Magenta filter give blue filter because cyan absorbs red light and transmits blue and red light so blue is transmitted.
The process of obtaining colours in this way is called colour mixing by subtraction.
Recombining the spectrum
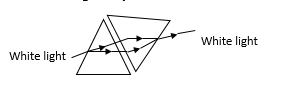
The colours of the spectrum can be recombined to form white light by arranging two prisms as above so that the, light is deviated in the opposite direction.
The above experiment shows that:
i) White light is a mixture of seven colours
ii) The prism merely separates the colours of white light by deviating red light least and violet light most and other colours are deviated to varying intermediate extent,
iii) The prism has different refractive index for different colours.
Note;
White light is separated into seven colours by a prism because (he prism has different refractive index for the different colours of white, light
Production of pure spectrum
Placing an illuminated slit
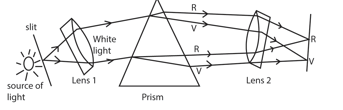
- An illuminated slit is placed at the principal focus of a converging lens, so that a parallel beam of light emerges from it.
- This beam then falls into prism where dispersion of white light occurs.
- The spectrum is then directed to the screen by lens 2.
Uses of prisms
- They enable the refractive index of a glass material to be measured accurately.
- They are used in the dispersion of light emitted by glowing objects.
- They are used as reflecting surfaces with minimal energy loss.
- They are used in prism binoculars and periscopes
Transmission of light rays through the periscope
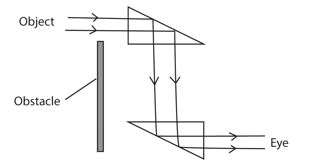
Rays from object are totally reflected until they enter the eye.
Please download pdf: Prisms and dispersion of light (O-level)
Please Subscribe to promote this website. Subscription is free
Share with a friend
Thank you so much

Thanks teacher, these notes are precised for us to understand
I appreciate the effort you put into this. Home Improvement
Thanks for making this topic accessible. Indian Cricket
Discover accurate and up-to-date information on the MBBS Fees Structure in Delhi for top colleges.
MBBS Fees Structure in West Bengal provides insights into affordable programs.
Play the Raja Luck Game for an exciting and rewarding experience.
Gain expert insights into Raja Luck and its advantages.
Stay logged in safely and take pleasure in uninterrupted gaming sessions with the 82 Lottery App.
Get high-end computing power with cost effective Server Rental in Bengaluru.