
Air and water in environment-Upper primary science

Air
Air is composed of the following gases shown in the pie chart below:
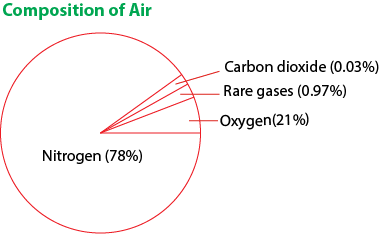
- oxygen (21% of air) for respiration and is given out during photosynthesis
- carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and is given out during respiration
- nitrogen (75% of air) is fixed by bacteria in leguminous plant into nitrates for protein synthesis
- oxygen is used by microorganism in the soil to decomposed dead matter.
Industrial use of gases
- oxygen use in hospitals to save life and welding
- oxygen supports burning
- carbon dioxide is used in sodas, and fire extinguishers
- nitrogen is used as coolant in refrigerators and air conditioners
Air Pollution
Air pollution is introduction of poisonous wastes in the air. The materials that cause pollution are called pollutants.
Air pollutant include
(i) smoke
(ii) Industrial gases
(iii) Vehicle exhaust fumes
(iv) Dust
Effect of air pollution
- Soot settle on to the plant leaves and blocks and suffocates the plant
- Blacken building roofs and walls
- Acid gases dissolve in water suffocates and also dissolve in water to form acid rain that burns plants
- Acid rain damages soil
- acid rain cause weathering
Water
Water covers 70% of the earth’s surface. Water supports life and no living thing can survive without water. Lack of water in the environment would mean no life hence death of all the living components.
Pure water is a colorless and odorless
Liquid. It has a freezing point temperature of 0°C and a boiling point temperature of 100°C at sea level.
Importance of water
- Water forms a big part of living The human body for example, is made up of 70% water.
- Water is the habitat of many living things such as fish, whales and water plants such as water lily, water hyacinth and arrow roots,
- Some organisms do not live in water but depend on water for food. Such organisms
- Water is necessary for germination
- Water is used as raw material during photosynthesis
Use of water to man
- Bathing
- Domestic use such Washing clothes, bathing, cooking, washing plates
- Recreation
- Industrial use
- Fishing
- Transport
- For irrigation
- Generation of electricity
Sources of water
- Rainfall
- Rivers
- Dams
- Springs
- Wells and bore holes
- Lakes
- Seas or oceans
Water cycle
The water cycle is the path that all water follows as it moves around our planet.
Of the many processes involved in the water cycle, the most important are evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation and runoff.

Evaporation is the change of a liquid into vapour below its boiling point.
Transpiration is the loss of water vapour from the plant through the stomata.
Condensation is process by which water vapor turns into a liquid.
Precipitation is any liquid or frozen water that forms in the atmosphere and falls back to the Earth in form of rain.
Runoff, is the waters that travel over the land surface and through channels to reach a stream.
Dangers caused by water
In as much as water may help us in many ways, it may also be dangerous in the following ways:
- Polluted water cause diseases such as typhoid and cholera
- Flood destroy plants and properties
- Water washes away soil causing soil erosion.
Transporting water
Water may be transported in tanks and Jerri can on bikes, head, and motor cycles or through pipes (piped water)
Water storage
Water is stored in tanks, jerricans, and dams

Pollution of water
Pollution means making something unclean or impure. Pollution of water is making water and water sources unclean or impure. The things that cause pollution are called pollutants. Pollutants are released into water and water sources making the water unclean or not fit for human consumption.
Source of pollutants
- Sewage from homes and industries
- Fertilizers from farm land
- Oil spillage from boats and ships
- Wastes from mining areas
- Animal feces from farmland
Making water safe for drinking
Methods used to make water safe are
- decanting,
- filtering,
- boiling,
- distilling
- adding chemicals.
Decanting
Here dirty water is left in a container to settle and then clean water is poured into another container leaving settle particles behind. The particles that settle at the bottom of the container are called sediments. Decanted water contain germs and is not fit for consumption until it is boiled

Filtration
Unclean water can be made clean by passing the water through a piece of cloth or a filter paper.
The cloth or filter paper acts as a sieve.
Water produced by this method is not fit for drinking because it may contain germs.

Boiling
Boiling kills germs
Distillation
Here water is boiled to form vapor/steam that is cooled to form water or distillate. This method produces the purest water. This water is no good for drinking because it lacks minerals.
Distillation is also used to prepare alcohol from its fermented mixture as shown in the diagram below

The mixture is boiled, alcohol with low boiling point forms vapor first; the vapor is condensed with cold water to form liquid alcohol.
Preventing and controlling water pollution
- sewage must be treated before it is released in water
- industrial wastes should be treated before release in water
- plant around lakes and river must not be cleared to act as sieve to water entering water
Water borne diseases
These are diseases spread by contaminated water. Examples are
Cholera
Cholera is water borne disease which infects people who handle or drink contaminated water or eat contaminated food. Water gets contaminated by feces from an infected person that have not been disposed of properly.
Signs and symptoms
- Frequent passing of watery stool [diarrhea).
- The victims become dehydrated due to the loss of water in the stool.
- If not attended to by a medical person, the victims become unconscious, go into a coma and eventually die.
Typhoid
Typhoid is caused by drinking or handling contaminated water or food. Water or food which is contaminated with feces of a person suffering from typhoid is another way in which typhoid is transmitted.
Signs and symptoms
- Continuous fever and severe headache.
- Vomiting,
- Severe diarrhea.
- Pain in the abdomen and constipation.
- May result to death.
Bilharzia
Bilharzia is a water-borne disease. The germ that causes bilharzia is carried by snails that live in fresh water ponds. When the disease-causing germs leave the snail, they easily penetrate into a person’s body through the skin. They then get into the blood system, then into the bladder or intestines. Fertilized eggs are passed out of the body through urine or feces.
Signs and symptoms
- Coughing and sneezing.
- Victims experience abdominal pains especially when passing stool.
- Passing of urine or stool with blood. (iv)Loss of blood which may lead to Anemia is the shortage of blood in the body.
Control and prevention of water borne diseases
- Boil drinking water.
- Maintain good hygiene by washing the hands with soap and clean water before meals and after visiting the toilet
- Foods that are eaten raw like fruits and vegetables should be washed thoroughly with clean water before they are eaten.
- Maintaining proper sanitation or cleanliness.
Those infected should:
- visit the doctor as soon as possible.
- drink plenty of liquids to regain water that is lost from the body.
- drink Oral Rehydration Solution or Sugar Salt Solution. Oral Rehydration Salt (ORS) is a packet containing some minerals like salt and are available commercially.
Water conservation
Water is conserved or unspoiled to maintain adequate supply in a community.
Ways of conserving water
- Harvesting: rain water is collected in water tanks and used during dry weather
- Recycling: dirty used water is purified and reused
- Water is used
- Water may be stored in arms
Soft and hard water
Soft water easily form lather with soap unlike hard water
Soft water contains fewer minerals.
Advantages of hard water
- Contain minerals that make bones and teeth strong
- Contain minerals used by the plants
- Has good taste
Disadvantage of hard water
- Wastes soap
- Deposit scales in kettles
- Forms scales in pipes that carry hot water
- Form scum that stain garments
Types of hard water
Temporary hard water is softened on boiling while permanent hard water is not
Means of softening hard water
- Boiling for temporary hard water
- Distillation
- Adding chemical
For questions and answers download PDF
Sponsored by The Science Foundation College + 256 753 802709

You are a very clever person!
This is exactly what I needed to read today. Industrial & Scientific
I really enjoyed reading this. Well done! TamilBlasters Com
Access comprehensive details for Rajasthan through the MBBS Cutoff Of Private Medical Colleges in Rajasthan.
Learn about guaranteed seats at MBBS Admission Through Management/Nri Quota in Orissa.