
Carbon and its compounds (O-level chemistry)

Carbon and its compounds
Carbon exists in 3 allotropic forms, diamond, graphite and amorphous carbon (charcoal, lampblack, soot, and coke) diamond and graphite are crystalline while amorphous carbon is noncrystalline.
Allotropy is the existence of an element in more than one form without change of state
A. Graphite
In graphite, each carbon atom is covalently bonded to 3 carbon atoms to form a layer of hexagons. Each layer is bonded to another by weak van der Waal forces.

Properties of graphite as a result of its structure
- Has open structure and low density.
- It is slippery and used as a lubricant.
- Has un-bonded that is free to move about making graphite a good conductor of electricity and heat
Uses of graphite
- Manufacture of lead pencil
- As lubricant
- Diamond
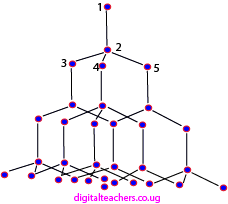
Structure of diamond
Each carbon atom is bonded tetrahedrally to four carbon atoms to form a 3D compact structure by strong covalent bonds as shown below. As a result, diamond has a high density, melting and boiling point. It is the hardest substance known.
Diamond is used as an ornament, and to drill, glass cutters and cut other substances.
Differences between diamond and graphite
| Graphite | Diamond |
| The density of graphite is lower 2.3 gcm-3 | The density of diamond is3.5 g cm-3 |
| Soft | hard |
| Slippery | Not slippery |
| Conducts electricity | Does not conduct electricity |
Experiment to show that graphite and diamond are both allotropes of carbon
Equal masses of graphite and diamond burn in oxygen to give equal volume/mass of oxygen
Properties of carbon
- Carbon burns in excess oxygen to form carbon dioxide
C (s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
2. Carbon burns in limited oxygen to form carbon monoxide
2C (s) + O2(g) → 2CO (g)
3. Carbon reduce oxides of metals (lead, copper, zinc, iron) to metals
2PbO(s) + C (s) → 2Pb(s) + CO2(g)
2CuO(s) + C (s) → 2Cu(s) + CO2(g)
ZnO(s) + C (s) → Zn (s) + CO(g)
3. At high temperature, carbon reacts with steam to form water gas
[(CO (g) + H2(g)]
C(s) + H2O (g) → CO(g) + H2 (g)
Carbon dioxide
Preparation
By reaction between calcium carbonate (marble) and dilute hydrochloric acid.
CaCO3 (s) + 2HCl(aq) → CO2 (g) + CaCl2(aq)

Testing for carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide forms white precipitates with lime water. The white precipitate turns colorless with excess carbon dioxide
Calcium hydroxide + carbon dioxide give calcium carbonate (white ppt.) + water
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 (g) → CaCO3 (s) + H2O (l)
Calcium carbonate (white ppt) + carbon dioxide (excess) give calcium hydrogen carbonate (colorless solution)
CaCO3 (s) + CO2 (g) → Ca(HCO3)2 (aq)
Properties of carbon dioxide
- It is colorless
- Denser than air
- Ordorless
- Slightly soluble in water to form an acid solution
- Extinguishes burning splint
- Reacts with magnesium to form black specks
2Mg (s) + CO2(g) → 2MgO(s) + C(s)
Uses of carbon dioxide
- In soda
- In fire extinguishers because it is nonflammable and denser than air thus displaces oxygen from burning item.
- It is a coolant
Carbon monoxide
Preparation
By reacting sodium methanoate with concentrated sulphuric acid
2HCOONa (s) + H2SO4 (aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l) + 2CO (g)

Properties of carbon monoxide
- Very poisonous, it is produced by incomplete combustion of carbon therefore cooking on nigiri should be done when the door and the windows are open to allow in enough air.
- Has no action on litmus paper
- Burns with a blue flame
- Reduce metallic oxides
For example, it reduces black copper oxide and orange lead (II) oxide to brown copper and grey lead respectively
CuO(s) + CO (g) → Cu (s) + CO2 (g)
Cu(s) + CO (g) → Cu (s) + CO2 (g)
Uses of carbon monoxide
- It is used in the extraction of iron; it reduces iron (III) oxide to Iron
Fe2O3 (s) + 3CO (g) → 3Fe(s) + 3CO2(g)
Carbonates
Carbonates are derivatives of carbonic acid, H2CO3.
Properties of carbonate are given in the table below
| metal | Formula of carbonate | solubility | Effect of heat | Reaction with acid |
| K | K2CO3 | soluble | Do not decompose | Produce carbon dioxide |
| Na | Na2CO3 | soluble | Do not decompose | Produce carbon dioxide |
| Ca | CaCO3 | Insoluble | Decompose into oxides and carbon dioxide | Produce carbon dioxide |
| Mg | Mg CO3 | Insoluble | Decompose into oxides and carbon dioxide | Produce carbon dioxide |
| Al | does not form carbonate | – | – | – |
| Zn | ZnCO3 | Insoluble | Decompose into oxides and carbon dioxide | Produce carbon dioxide |
| Fe | FeCO3 | Insoluble | Decompose into oxides and carbon dioxide | Produce carbon dioxide |
| Pb Cu |
PbCO3 CuO |
Insoluble | Decompose into oxides and carbon dioxide | Produce carbon dioxide |
Test for carbonate ion
All carbonates react with nitric acid to produce carbon dioxide with turn lime water milky.
Hydrogen carbonate
It is only group 1 elements (K, Na) that form solid hydro carbonates.
Hydro carbonates decompose on heating liberating carbon dioxide
2NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 (s) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
For revision, questions download PDF below

Its a good work site and I hope to pass well
We give glory and honor to God for this wonderful innovation and may He reward you accordingly.
thanks 4 da wanderful support may almight allah bless u accodingly
Good work
Thax for everything my friends ❤️✅ May God bless you
This is a great site
Im obliged for the blog.Really looking forward to read more. Really Great.
You’ve got a talent for storytelling. Indian Cricket
Explore the best pathways to medical education with MBBS Direct Admission in Gujarat.
Top MBBS Colleges in Telangana are known for their academic rigor and excellent faculty.
Access your account easily through the 82 Lottery Login portal and manage your video gaming activities.
Learn from comprehensive guides and resources available on Goa Game to improve your gameplay and strategies.
Share your unique Invitation Code to invite others and earn referral bonuses through TS EARN.
Host and manage service applications effectively with Server Rental in Delhi.