
Carbonyl compounds (aldehydes and ketones) (A-level organic chemistry)
Carbonyl compounds
These are compounds that contain carbonyl group

Aldehydes
These are carbonyl compounds with the following structure.


Nomenclature of aldehydes
- Aldehyde are named by replacing the final “e” of the names of corresponding alkanes with “al.”
- Since the aldehyde group must be at the end of the chain its position in not indicated.
- When other substituents are present, the carbonyl carbon is assumed to occupy position one.
Example
HCHO Methanal (40% solution is called formalin) or formaldehyde
CH3CHO Ethanal or Acetaldehyde
CH3CH2CHO Propanal or propionaldehyde
CH3CH2CH2CHO Butanal or butyraldenhyde
CH3CH2CH2CH2CHO Pentanal or veraldehyde
Nomenclature of ketones
- Their names end in suffix “one”
- The position of the ketone group (-CO-) is given the lowest number.
CH3COCH3 Propanone
CH3CH2COCH3 Butanone


Preparation of carbonyl compounds
(a) Oxidation of alcohol with acidified potassium dichromate, sodium dichromate or potassium permanganate. Primary alcohols give aldehydes whereas secondary alcohols give ketones.


(b) Oxidation of alcohols using pyridiumchlorochromate [PCC, {C5H5NH+}Cl.CrO3] and pyridinium dichromate [ PDC, {C5H5NH+}2Cl.Cr2O72-] are currently the reagents of choice, particularly for oxidation of α,β- unsaturated primary and secondary alcohols to give aldehydes and ketones respectively.
![]()
(c) Hydrolysis of gem dihalide, (RCHCl2, R2CCl2)

![]()
(d) Reduction of acid chloride by hydrogen on palladium which is supported on barium sulphate or by using LiAlH(OBut).


(e) Cleavage of 1,2-diol using either lead tetraacetate or sodium metaperiodate
![]()
Example

(f) Preparation of ethanal
(i) By oxidation of ethane with palladium chloride in water
CH2=CH2 + H2O + PdCl2 → CH3CHO
(ii) Passing ethyne through dil sulphuric acid in presence of mercury sulphate as a catalyst.


(iii) Oxidation ethanol


Physical properties
(a) The polar carbonyl group makes carbonyl compounds polar and therefore, the have melting and boiling points than non-polar compounds with similar molecular mass.
(b) Lower members are soluble in water but the solubility decreases with the increase in chain length.
Chemical properties
The structure of carbonyl compound is sp2 hybridized


As a result of the partial positive charge, the carbonyl carbon is subjected to nucleophilic attack by a large number of nucleophiles.
This results in nucleophilic addition reaction a cross the carbon-oxygen double bond. The nucleophilic addition to the carbon-oxygen double bond, can be regarded to occur in two possible ways generally.
(i) In presence of a strong nucleophile.


(ii) Weak nucleophile, the carbon oxygen bond has to be protonated first.


Generally, aldehydes undergo nucleophilic addition reaction more readily than ketones
Reasons
(i) Steric effect: the bulkiness of the alkyl groups attached to the carbonyl carbon hinders the approach of nucleophile.
(ii) Inductive effect: the positive inductive effect of the alkyl groups attached to the carbonyl carbon in ketones, reduce the positivity of the carbonyl carbon thus rendering it less reactive towards nucleophiles.
NB. Presence of an electron withdrawing group on the alkyl carbon make the carbonyl carbon more reactive towards nucleophilic addition reaction. For example, CCl3CHO is more reactive than CH3CHO.
General scheme of nucleophilic reaction to carbonyl compounds


(a) Reaction of carbonyl compounds with aldehydes and ketones.
The reaction for addition of HCN is catalyzed by NaOH or KOH


 Mechanism
Mechanism![]()

This reaction can be used to increase the carbon chain by one carbon atom
Exercise
Complete and write a mechanism
CH3COCH3 + KCN →
(b) Addition of sodium hydrogen sulphite, NaHSO3.
Example


Mechanism


The reaction can be used to purify carbonyl compound since the products formed are solid. After crystallization, the can be redissolved.
(c) Addition of alcohols
1mole of aldehyde + 1mole of alcohol in presence of an acid the product is hemiacetal
1mole of aldehyde + 2moles of alcohol in presence of an acid is acetal.


The reaction is used to protect the aldehyde group in chemical synthesis.
Example



Note that
(i) Formation of acetals is sensitive to steric hindrances, i.e. depends on the size of groups attached to carbonyl carbon and the size of alcohol. Simple compounds give up to 80% yield, but the yield decrease with the increase in the size of the groups.
(ii) Reaction is reversible; therefore, it’s necessary to reduce the concentration of the acid to minimize the reversibility of the reaction.
(iii) Ketals are not prepared by direct reaction between ketones and alcohol. This is because the equilibrium of the reaction lies mainly to the left. In this case orthoformate is used.


2. Addition of ammonia derivatives
Carbonyl compounds react with compounds of the general formula H2N-Y with elimination of water. The reaction is catalysed by acids. A reaction in which two molecules combine with elimination of small molecules e.g. water is called condensation reaction.
General equation
![]()


The products of these condensation reactions, i.e. oxime and hydrazones are orange crystalline solids with sharp melting points. Thus, they can be used to characterize carbonyl compounds. The most commonly used ammonia derivatives to characterize carbonyl compounds is 2,4-dinitrophenyl hydrazine (Brady’s reagent). Reaction of carbonyl compounds with this reagent produces orange colored crystalline solids.
3. Reduction of carbonyl compounds
Reduction of carbonyl compounds to alcohols
Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols and ketones are reduced to secondary alcohols


Reducing agents include
(a) H2/catalyst (Ni, Pt, Pd): the disadvantage with this reagent is that it reduces double bonds when present.


mechanism

(ii) Reduction of carbonyl compounds to methylene. i.e.


(a) Clemmensen’s reduction: it is useful for compounds that are stable under acidic conditions
It is carried out by refluxing a ketone with hydrochloric acid containing amalgamated zinc. Zinc and hydrochloric acid also reduces nitro groups to amines.
![]()
Example


(b) Hong-Mislon modification of Walf-Kishner reaction: a carbonyl compound is heated in presence of high boiling polar solvent, e.g. ethane-1,2-diol with hydrazide + KOH


4. Polymerization of aldehyde
Aldehyde(methanal) polymerizes, mainly under basic conditions.


Paraformaldehyde is a useful form for transportation of methanal
5. Reaction of Grignard’s reagents
Reaction of carbonyl compounds with Grignard’s reagents produces all the three types of alcohols. Thus this is an important reaction for the preparation of alcohols.


6. Aldol condensations
Carbonyl compounds which contain at least one alpha hydrogen, react in presence of alkali to form hydroxyl carbonyl compounds called Aldol


(i) Two molecules of ethanal combine to form 3-hydroxybutanal


Crotonaldehyde is used to calibrate spectrometer because it’s absorbance is known


(ii)


then

7. Cannizzaro reaction
This is a reaction between sodium hydroxide solution and aldehydes with no α-hydrogen
It’s a self-oxidation – reduction reaction
Examples



Mechanism

then


8. Iodoform reactions
Iodine in presence of sodium hydroxide solution react with carbonyl compounds with structure CH3CO -R to form a yellow ppt.
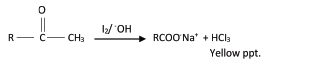

NB
(i) the reaction is useful when identifying compound with the group CH3CO -R
(ii) Ethanal is the only aldehyde that gives a positive iodoform test
(iii) All ketone with the structure RCOCH3 give positive iodoform test
(iv) Secondary alcohols of the group RCHOHCH3 give positive iodoform test
(v) Ethanol is the only primary alcohol that gives a positive iodoform test.
Exercise
Give one reagent that can be used to distinguish between the following pairs of substances. In each case state what would be observed the reagent is treated separately with the reagent you have mentioned.
(i) CH3OH and CH3CH2OH
(ii) HCHO and CH3CHO
(iii) CH3COCH2CH2CH3 and CH3CH2COCH2CH3
9. Oxidation of carbonyl compounds
Aldehydes are easily oxidized to carboxylic acid. The oxidizing agent, normally used are K2Cr2O7/H+, Na2Cr2O7/H+, KMnO4/H+.
Example


Ketones are not oxidized under mild condition
Distinguishing between aldehydes and ketone

|
Reagent |
Observation |
|
|
Aldehydes |
Ketones |
|
|
Fehling’s solution |
Brown ppt |
No observable change |
|
Tollen’s reangent or ammoniacal silver nitrate |
Black ppt or silver mirror |
No observable change |
|
Acidified potassium dichromate |
Orange solution turns green |
No observable change |
Exercise
Give one reagent that can be used to distinguish between the following pairs of substances. In each case state what would be observed the reagent is treated separately with the reagent you have mentioned.
- CH3CH2CHO and CH3COCH3
Thank u
Dr. Bbosa Science


It’s really a great and helpful piece of info. I
am satisfied that you shared this useful info with us.
Please keep us up to date like this. Thank you for sharing.
Having read this I thought it was very enlightening.
I appreciate you spending some time and energy to put this informative article together.
I once again find myself personally spending a significant
amount of time both reading and leaving comments. But so what, it was still worth it!
This design is incredible! You obviously know how to keep a reader
entertained. Between your wit and your videos,
I was almost moved to start my own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Wonderful job.
I really enjoyed what you had to say, and more than that,
how you presented it. Too cool!
Its really a nice and a great piece of information the notes r easily understood and they r awesome thank out so much
Thanks for being a source of wisdom. Car & Motorbike