
Characteristics /features of economic underdeveloped Countries or Features of economic under development

- Low standards of living for the majority of the people. The low levels of living are manifested, in form of low incomes, inadequate housing facilities, poor health conditions, high illiteracy rates, high infant mortality rates, low life expectancy and general sense of hopelessness.
- Low levels of labour productivity. Under developed countries are characterized by low levels of labour productivity due to absence or inadequate co-operant factor inputs such as capital, better technology and low levels of education and skills.
- High population growth rate and dependence burden. The high population growth rate is due to high birth rates with high fertility levels of women. The major implication of this is demographic information is that a large proportion of the population is in the younger age group and this results into a high dependence burden which limits both savings and investments.
- Persistent capital outflow due to importation of luxurious items to match the developed country style
- Unfavorable terms of trade since the underdeveloped countries import more than they export
- High corruption and embezzlement of funds by government official
- High and increasing levels of unemployment and under employment. In developing countries there are many people of the working age who are able and willing to work but cannot find the jobs at the prevailing wage rates hence involuntary unemployment. This is mainly due to the limited employment creating ventures, abundant supply of unskilled labour, limited skills and experience needed at work and low rates of entrepreneurship.
- High degree of dependence on agricultural production and primary exports. The majority of the people in developing countries depend on agricultural activities for food and source of economic activity for livelihood. The majority of the people live and work in rural areas where agriculture is the major economic activity characterized by low returns and highly subjected to natural hazards.
- Technology backwardness. This is due to limited capital for research; innovations and inventions necessary for technological progress. Technology backwardness is reflected in low labour productivity and production of poor quality goods and services.
- High levels of economic dependence. Developing countries highly depend on developed countries for consumer and capital goods, technical, financial resources and manpower as well as decision making. This leads to foreign dominance and influence by the rich nations.
- Existence of dualism. Most developing countries have dualistic economies in which there is co- existence of two different sectors with contrasting characteristics. For example co-existence of large traditional subsistence sector with a commercialized market economy, technological dualism with backward technology coexisting with modem technology etc.
- Poor and unreliable social and economic infrastructure. Developing countries have inadequate and poor quality transport systems, banking facilities, communication networks, and water and power supply facilities. People do not have access to such facilities in order to improve on their livelihoods.
- High levels of conservatism and traditionalism. Most people in developing countries believe in cultural norms and they are deeply rooted in cultural beliefs to the extent that they cannot allow positive reforms necessary for development to take place.
- Existence of excess capacity. There is underutilization of natural resources in most sectors of developing economies due to inadequate capital, use of poor technology, limited markets and poor management and entrepreneurial skills. This leads to low economic growth rate.
- High levels of political instability. This is due to greed for power and bad leadership by leaders of developing countries.
- High level of incomes inequalities. The income gap between the rich and poor keeps on widening in developing countries. There are many extremely poor people while a few remain extremely rich.
- Existence of poor terms of trade and balance of payment problems. This is reflected in the exportation of mainly cheap primary products and importation of expensive consumer capital goods.
- High levels of economic instabilities. This is in form of high inflation rates and fluctuations in the foreign exchange rates due to scarcity of goods and services and importation of highly priced manufactured and petroleum products.
- Existence of Limited domestic and foreign markets. This is due to limited commercialization of economic activities, low incomes and poor quality of goods and services produced. This leads to low aggregate demand in the economy.
- There is existence of limited entrepreneurial skills. This is due to poor education system which trains job seekers rather than job creators.
- Brain drainage due to increasing unemployment and poor working conditions
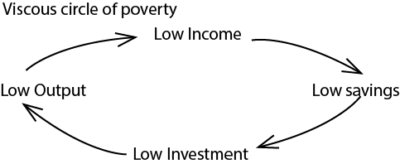
- Existence of high levels of poverty. This is reflected in low per capita income and low standards of living. The persistent poverty is due to the vicious circle of poverty, an economic phenomenon characterized by low incomes, low savings, low investments, low output or low capital accumulation and then back to low incomes.
CATEGORIES Economics
TAGS Dr. Bbosa Science
