
Describe the structure and functions of the placenta

Describe the structure and functions of the placenta
Structure of the placenta
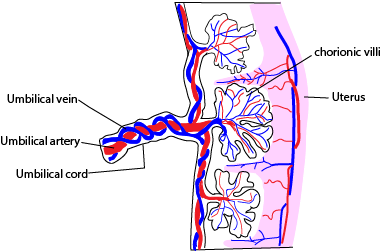
The placenta is a disc-shaped organ which provides the sole physical link between mother and fetus.
From the outer surface of the chorion a number of finger like projections know as chorionic villi grow into the tissue of the uterus. These villi penetrate the tissue of the uterine wall of the mother and form placenta
Functions of placenta
- Nutrition: Food materials pass from the mother’s blood into the foetal blood through the placenta.
- Digestion: the trophoblast of placenta digest proteins before passing them into foetal blood
- Gaseous exchange: through the placenta oxygen passes from maternal blood to the foetal blood, and carbon dioxide passes from foetal blood to maternal blood through the placenta
- Excretion: nitrogenous wastes such as urea pass from foetal blood into maternal blood through placenta and are filtered by kidney of the mother.
- Storage : The placenta stores glycogen, fat for foetus before liver is formed
- Barrier: Placenta functions as an efficient barrier preventing harmful substance from entering the blood circulation of fetus
- Endocrine function: it secrets hormones like oestrogen, progesterone and HCG
Please Subscribe to promote this website. Subscription is free
Share with a friend
Thank you so much
CATEGORIES Bio Questions and answers
TAGS Dr. Bbosa Science

Hello sir thanks for the work