
Equilibrium position of a firm under oligopoly

The firm under oligopoly earns abnormal profits both in the short and long run. Equilibrium is attained at a point where marginal cost (MC) curve is equal to the marginal revenue (MR) curve and MC curve should cut the MR curve from below.
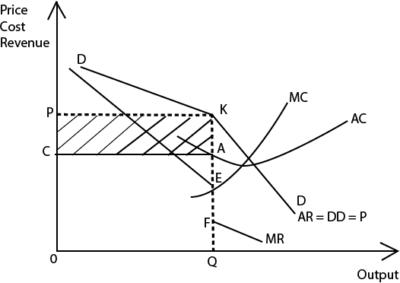
- From the graph, DKD is a kinked demand curve and K is the kink. Because of the kink, the MR curve is separated by the discontinuous gap, EF into two MR curves. The marginal revenue curve above the gap is inelastic and the one below the gap is elastic.
- The discontinuity in the marginal revenue curve implies constant revenue as price and output remain fixed at the kink.
- Equilibrium is attained at the kink where MC is equal to MR in the discontinuous portion, At equilibrium, output OQ is produced at the cost price OC and sold at an administered price, OP determined at the kink.
The shaded area AKPC represents the super normal profits.
CATEGORIES Economics
TAGS Dr. Bbosa Science
