
Eye and camera – upper primary science

Eye
The eye is a sense organ for sight. Since it uses light to function, it is called optical organ.
The human eye is found in a hollow part of the head called the socket or orbit.
The eye is shaped like a ball and is also referred to as the eyeball. The eyeball is attached to the socket by muscles.
The external parts of the eye are shown in figure below

Cross section of the eye
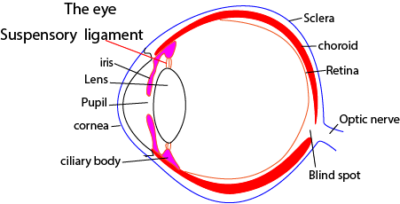
Functions of the parts of the eye
- Eyelids are covers of the eye. They close to protect the yes danger.
- Lens refracts and focus light to the retina
- Iris adjust the size of the pupil and thus the amount of light that enters the eye
- Retina is where the image forms
- Pupil allows light to pass through into the eye.
- Optic nerve is a sensory nerve that sends sight message from the eye to the brain for interpretation of what we see.
- Pupils allow light into the eye.
Characteristics of images formed in the eye
- They are upside down
- They are smaller than the object (diminished)
- They are real
Controlling amount of light entering the eye
The amount of light entering the eye is controlled by the iris.
In bright light, the iris circular muscles to contract and pupil constricts.
In dim light iris radial muscles contract and the pupil widens.
Accommodation
Is the ability of the eye to see near and far objects
(a) To see near objects, the ciliary muscle contract releases the tension on the lens allowing it to adopt a more
spherical shape. The lens then refracts light strongly.
(b) To view distant objects, the ciliary muscles relax, the suspensory ligament exert a pull on the lens and it flatten

Eye defects
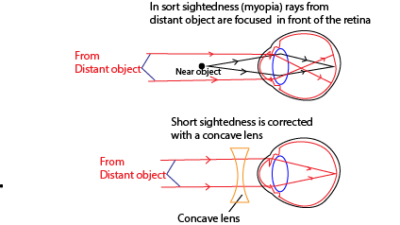
Short sightedness is inability to see distant objects clearly because rays from a distant object are focus in front of the retina.
Causes (i) Lens too strong
(ii) Eyeball too long
Correction: by use of a concave or diverging lens
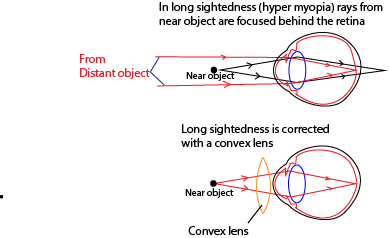
Long sightedness is inability to see near objects clearly because rays from a near object are focused behind the retina
Causes (i) lens too weak
(ii) eye ball too short
Correction: by use of a convex lens
Astigmatism
This is a condition in which a person is not able to see both vertical and horizontal objects clearly at the same time. It is caused by having
Causes
The unevenly curved cornea
Correction of astigmatism
By wearing spectacle which have special cylindrical lenses
Color blindness
This is a condition when one is not able to differentiate between some colors.
Common diseases
Conjunctivitis (red eyes)
It is a contagious disease caused by virus or bacteria
Spreading by touching the eye with infected fingers
Sign and symptoms
- The white of the eye becomes pink
- Burning, itching and pain of the eye
- Tears in the eye
Control
- Isolation of a sick person
- Avoid sharing basin, towels and shaking hands with infected persons.
Trachoma
It is an infectious disease caused by bacteria known as chlamydia
The disease is spread by touching the eye with infected person or by houseflies.
Symptoms
- Mild redness, Painful itching of eyes
- Eye turns reddish with tears
- Discharge from the eye containing pus after sleeping
- Eyelid swelling
- scarring
Control
- Isolation of a sick person
- Avoid sharing basin, towels and shaking hands with infected persons.
- Properly wash the eye with water and soap.
- Proper hygiene
Treatment: tetracycline ointment
River blindness
It is caused by a protozoa (Onchocerca vilvus). The disease is transmitted by black flies also called Jinja flies. The flies lives on the banks of fast flowing rivers.
If untreated it leads to blindness.
Symptoms
- Swelling on the skin
- Itching skin
- Skin rush
- Damaged iris
Control
- Keeping away from black flies infected river banks
- Clearing the bushes around the house
- Spraying the black flies with insecticide
- Antibiotics
Cataracts
In this condition, the lens of the eye become grey and opaque. A person with cataract does not see clearly.
It is corrected by an operation where the grey layer is removed.
Night blindness
It is caused by lack of vitamin A in one’s diet.
The affected person cannot see well especially in the evening and at night
It is corrected by eating food with vitamin A such as carrots, mangoes, pawpaw, liver and onions.
Sty
It is a small swelling which forms on the eyelid
It looks like a small boil. It is caused by bacterium.
Control
Proper hygiene
Strength of the eyes
The strength of the eyes is measured by how clearly one can sees far or near objects in a hospital, eye checking involves standing about two and a half metres away from a board with letters written in different sizes. A person is then required to close one eye and read the letters as they are pointed out by the optician. Thereafter, one is supposed to close the second eye and read with the other eye.
This test identifies:
- People who are long sighted; that is, those that can see distant objects clearly and are unable to see objects that are very near.
- People who are short sighted; that is, those that can see near objects clearly and are unable to see objects that are very far.
- Blind people that cannot see at all.
Care for the eye
- Avoid looking directly at the sun or blight light.
- Wash your eyes regularly
- Avoid reading too bright or too dim light because both spoil the eye.
- Eat food containing vitamin A.
- Avoid sharing handkerchiefs, eye glasses and face towel
- Wear sunglasses in bright light.
The lens camera
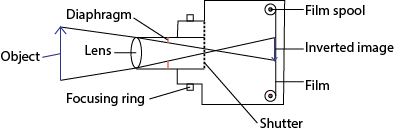
Parts of a lens camera
- The lens focuses light from the object to the film
- Diaphragm is a hole of adjustable size and controls the amount of light entering a camera
- The photographic film has alight sensitive chemical on which the image is formed
- Focusing ring adjusts the position of the lens to focus light on the film
- Shutter opens to allow in light.
After taking the photographs and the film is filled up, the film is removed and developed in some chemicals in the darkness to form a negative. From the negative, photographs are printed.
Characteristic of images formed in a lens camera
- they are upside down or inverted.
- They are real
- they are diminished
Comparison between the mammalian eye and a lens camera
Similarity
- Images formed are upside down or inverted.
- Images formed are real
- Images formed are diminished
- Both contain focusing convex lens
Differences
| Eye | Lens camera |
| 1. The pupil admits in the light | The shutter admits in light |
| 2. Images forms on the retina | Image form on film |
| 3. Eye covered with eyelids | Shutter protects the light from the camera |
| 4. Lens focuses by change of shape | Lens focuses by change of distance from the camera. |
Revision questions
- Name one body organ in man that makes use of light energy from the sun.
…………………………………………………………..………………………………………………………………………………………….
- In the table below, some of the diseases are given below with their symptoms and prevention/controls. Study it and answer the missing information.
| Trachoma |
………………………… |
Washing of eyes, avoid sharing articles with sick person, e.g. basin, towel, medical treatment |
|
………………… |
Swelling on the skin, Itching skin, Skin rush, Damaged iris
|
Keeping away from black flies infected river banks, Clearing the bushes around the house, Spraying the black flies with insecticide
|
- Complete the rays of light in the diagram below to show a condition of short-sightedness.
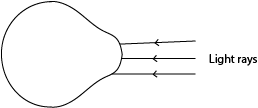
- Why is a concave lens used to correct short sightedness?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
- Which part of the eye function like a film in a camera?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
- State one way is the retina of human eye similar to the film of a pinhole camera.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Musa is log –sighted. Draw the type of lens he should use to correct his eye problem.
- Which part of human eye works like a film in camera?
………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Give any one use of wearing sun glasses.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
- Give the difference between river blindness and night blindness
…………………………………………………………………………………………………
- In the space provided below, draw a lens used to correct short sightless.
- Name the human body organ that uses light for it to function.
………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Name the part of the human eye that works like the film in a camera.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
- Apart from trachoma, name one other eye disease.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
- The illustration below show different types of light rays. Use them to answer questions that follow:

(a) Name the following rays of light.
(i) Q ………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) S …………………………………………………………………………………..
(b) Suggest the type of lens that can be used to make light rays move as shown is R above.
………………………………………………………………………………………
(c) What eye defect is corrected by a lens which makes rays move as shown in R?
…………………………………………………………………………………..
- Below is a diagram of an eye. Study it and use it to answer question that follow.

(a) Name the part marked:
(i) P: ……………………………………………………………………..
(ii) Q: ………………………………………………………………………
(b) What is the function of the part marked R?
…………………………………………………………………………………..
(c) Which letter on the diagram shows where images are formed?
………………………………………………………………………………….
The diagram below is of a human eye.
Use it to answer question 17 and 18

- Name the part marked with letter X
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Give the use of the part marked with letter Z. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..………
- (a) Which part of the body is affected by each of the following diseases
(i) Scabies …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii)Trachoma ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- Name the type of lens used to correct long sightedness
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
- The table below, shows source of food, the food nutrients in it and the related deficiency disease. Complete it correctly.
| Source of food | The food nutrient | Related deficiency |
| ……………………………. | Vitamin A | Night blindness |
- The table below shows diseases, the vectors that spread them and disease-causing germs. Study and complete it correctly.
| Disease | The vector that spread them | Disease-causing germ |
| River blindness | Blackflies | ……………………………… |
- The table below shows some common infection, organisms that cause it and the body part affected. Study and complete it correctly.
| Common infections | Organism that cause it | Body parts affected |
| ………………………… | Chlamydia | Eyes |
- The diagramshows a defect of the human eye. Study and use it to answer the questions that follow
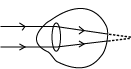
(a) Name the eye defect above
……………………………………………………………..…………………………………………………………………………………………….
(b) State two causes of of the eye defect shown above
………………………………………………………………………..…………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(c) What type of lens is used to correct the above defect?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
- The table below shows some common infections, organism that cause it and the body parts infected. Study and complete it correctly
| Common infection | Organism that cause it | Body parts infected |
| Trachoma | eye | |
| River blindness | onchocerca volvulus/worm | ………………………….. |
- Give two similarities and differences between the eye and a lens camera
(a) Similarities
(i) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..………………………………
(ii) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) Differences
(i) ………………………………………………………………………………………….………………………………………………………………
(ii) ………………………………………………………………………..…………………………………………………………………
- Give the functions of the following parts of the eyes
(a) Lens ……………………………………………………………………………
(b) Iris ……………………………………………………………………………….
(c) Retina …………………………………………………………………………..
(d) Pupil ……………………………………………………………………………….
- Below is a diagram showing an eye defect.
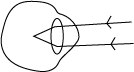
(a) Name the eye defect shown in the diagram above.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….…………
(b) Give reasons for your answer in (a) above
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………
(c) How can this eye defect for your answer in (a) above corrected?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…………………
- Why is a concave lens used to correct short sightedness?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…………………………
The diagram below shows parallel rays striking a comes lens. study it and answer question 30 and 31.

- Complete the diagram to show the path of the rays after passing through the lens
- What eyes defect does this type of lens correct?
……………………………………………………………………………………
- The table below shows part of human eye in A and that of a lens camera in B.
| A | B |
| Iris
Pupil Eye lid Retina |
Shutter
Film Diaphragm Aperture |
For each of the parts of the human eye, write the part of the lens camera from B which performs a similar function.
(i) Iris ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) Pupil ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..….
(iii) Eye lid ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(iv) Retina ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….…….
- State the eye disease which is spread by houseflies
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….……………………………………………….
- State any one characteristic of images formed on the retina.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….……………………………………………….
Suggested answers
- Eye
- In the table below, some of the diseases are given below with their symptoms and prevention/controls. Study it and answer the missing information.
| Trachoma | Mild redness and itching of the eyes, pus in eyes after sleep, scarring | Washing of eyes, avoid sharing articles with sick person, e.g. basin, towel, medical treatment |
|
River blindness |
Swelling on the skin, Itching skin, Skin rush, Damaged iris
|
Keeping away from black flies infected river banks, Clearing the bushes around the house, Spraying the black flies with insecticide
|
- Complete the rays of light in the diagram below to show a condition of short-sightedness.
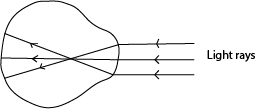
- Diverges light rays such that the image forms at the retina
Retina
- It is where the image is formed
- Musa is log –sighted. Draw the type of lens he should use to correct his eye problem.
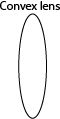
- Retina
- Prevent direct sun rays that may damage the eye
- River blindness is caused by Onchocera volvulus while night blindness is caused by lack of vitamin A.
- In the space provided below, draw a lens used to correct short sightless.

12 Eye
- Retina
- Apart from trachoma, name one other eye disease.
- Conjunctivitis (pink eyes) which cause the conjunctiva to swell
- Sty appears like a small boil on the eyelid which is sign of anemia or diabetes.
- Night blindness due to lack of vitamin A
- River blindness caused by small worms called Onchocera
- Syphilis
- Gonorrhea
- Cataract which causes the eye lens to appear opaque
- Corneal ulcer caused by an injury on the cornea.
- The diagram below shows a human eye.
- The illustration below show different types of light rays. Use them to answer questions that follow:

(a) Name the following rays of light.
(i) Q Parallel rays
(ii) S Converging rays
(b) Suggest the type of lens that can be used to make light rays move as shown is R above.
Concave lens
(c) What eye defect is corrected by a lens which makes rays move as shown in R?
Short sightedness
- Below is a diagram of an eye. Study it and use it to answer question that follow.

(a) Name the part marked:
(i) P: lens
(ii) Q: cornea
(b) What is the function of the part marked R?
Controls amount of light entering the eye
(c ) which letter on the diagram shows where images are formed
S (retina)
The diagram below is of a human eye.
Use it to answer question 17 and 18

- Pupil
- Iris
- (a) Which part of the body is affected by each of the following diseases
(i) Scabies: Skin
(ii)Trachoma: eye
- Convex lens or converging
- The table below, shows source of food, the food nutrients in it and the related deficiency disease. Complete it correctly.
| Source of food | The food nutrient | Related deficiency |
| Fish liver, Eggs, carrots | Vitamin A | Night blindness |
- The table below shows diseases, the vectors that spread them and disease-causing germs. Study and complete it correctly.
| Disease | The vector that spread them | Disease-causing germ |
| River blindness | Blackflies | Worm/filarial warm |
- The table below shows some common infection, organisms that cause it and the body part affected. Study and complete it correctly.
| Common infections | Organism that cause it | Body parts affected |
| Trachoma | Chlamydia | Eyes |
- The diagramshows a defect of the human eye. Study and use it to answer the questions that follow

(a) Name the eye defect above
Long sightedness
(b0 State two causes of of the eye defect shown above
- Short eyeball
- Weak lens
(c) What type of lens is used to correct the above defect?
Convex lens
- The table below shows some common infections, organism that cause it and the body parts infected. Study and complete it correctly
| Common infection | Organism that cause it | Body parts infected |
| Trachoma | chlamydia | eye |
| River blindness | onchocerca vilvus | eye |
- Give two similarities and differences between the eye and a lens camera
- Similarities
- ………………………………………………………………
- …………………………………………………………………
- Differences
- ………………………………………………………………
- …………………………………………………………………
- Give the functions of the following parts of the eyes
- Lens refracts and focus light to the retina
- Iris adjust the size of the pupil and thus the amount of light that enters the eye
- Retina is where the image forms
- Pupil allows light to pass through into the eye.
- Below is a diagram showing an eye defect.

(a) Name the eye defect shown in the diagram above.
Short sightedness
(b) Give reasons for your answer in (a) above
Rays from distant object are focused before they reach the retina
(c) How can this eye defect for your answer in (a) above corrected?
Using a convex lens
- Why is a concave lens used to correct short sightedness?
Concave mirror diverges rays to focus on the retina
The diagram below shows parallel rays striking a convex lens. Study it and answer question 30 and 31.

- Complete the diagram to show the path of the rays after passing through the lens
- What eyes defect does this type of lens correct?
Long sightedness (hypermetropia)
- The table below shows part of human eye in A and that of a lens camera in B.
| A | B |
| Iris
Pupil Eye lid Retina |
Shutter
Film Diaphragm Aperture |
For each of the parts of the human eye, write the part of the lens camera from B which performs a similar function.
- Iris diaphragm
- Pupil aperture
- Eye lid shutter
- Retina film
- State the eye disease which is spread by houseflies
Trachoma
- State any one characteristic of images formed on the retina
- Inverted
- Diminished
- Real
Sponsored by The Science Foundation college + 256 753 80 27 09
Compiled by Dr. Bbosa Science + 256 778 633 682

I cannot thank you enough for the article post.Really looking forward to read more. Will read on…
I’m always amazed by your insights. Stationary
I’m always learning something new. Indian Football