
Food and nutrition – upper primary science

Foods
Food is a solid or liquid that is taken through eating or drinking to provide necessary nutrients to the body.
Nutrition is the process by which living things take up food in order to grow and stay healthy
Functions of food
(i) To repair worn out tissue
(ii) Provide energy required to do work like talking and walking.
(iii) Protect the body against infections and diseases
(iv) To build the body.
Classification of foods and nutrients in food
They are classified according to the role they play when eaten
(a) Carbohydrates or energy giving food.
These provide energy when eaten.
Examples of foods that contain carbohydrates include, rice, maize, wheat, cassava tubers.
(b) Fats and oils
Fats are solids at room temperature while oils are liquids
Functions of fats and oils in the body
- Provide energy
- They are deposited beneath the skin to insulate the body against heat loss.
- They act as energy store
- The protect delicate organs against shock.
Sources of fats and oils
Animal fat
Sun flower
Sim sim
Ground nuts
Castor oil.
(c) Proteins are body building food
Functions of proteins
- Repair worm out tissues
- For growth
Sources of proteins
Animals: Fish, meat, chicken, pork
Plant sources: beans, peas, cashew nuts, soya bean
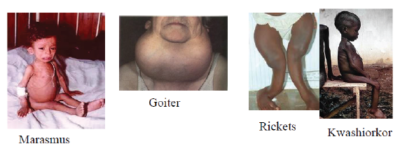
Deficiency of proteins causes kwashiorkor in children
Signs of and symptoms of kwashiorkor
Vitamins or protective food.
They are required in small amounts but protect the body against diseases. Lack of a particular vitamin in the diet may lead to deficient diseases
The table below shows types of vitamins, their sources, importance and name of deficient disease cause in their absence.
| Vitamin | Source | Importance | Deficient disease |
| Vitamin A | Carrots, fruits, greens pumpkins | Good for skin and eyesight | Night blindness |
| Vitamin B | Cereals, liver, kidney and vegetables | Proper working of the brain, | Various diseases |
| Vitamin C | Fruits and vegetables | Healthy gum and skin | Scurvy |
| Vitamin D | Milk, sunlight | Strong bone and teeth formation | Rickets |
| Vitamin K | Vegetables | Clotting | Poor clotting |
Mineral salts
Minerals are required in very small amounts but very important
The table below shows common mineral, their sources and uses
| Mineral | Source | Importance | Deficient disease |
| iron | liver | Manufacture of red blood cells | anemia |
| Calcium | Meat, milk | Formation of bone | |
| Phosphorus | Meat, eggs, beans | Formation of strong bones |
Fibres/ roughages
They are thread-like foods that prevent constipation or difficult in defecating.
Water
Role of water in in the diet include
- Soften food foe easy swallowing
- Prevents constipation
- Sweating cools the body
- Helps in digestion
Balanced diet
This is a diet consisting of the proper quantities and proportions of foods needed to maintain health or growth.
A balanced diet must have proteins, carbohydrates, mineral salts, water and vitamins in their right proportions
Examples of balanced diet include
- Breast milk
- Meat (proteins), posho (carbohydrates) and fruit juice (vitamins and water)
- Fish (proteins), millet (carbohydrates) and greens (vitamins)
- Beans (proteins), cassava (carbohydrates) and fruits-like apples (vitamins)
Deficiency diseases
They are diseases caused by lack of certain nutrients in the diet.
The table below shows the name of deficient disease, name of lacking nutrient, and common symptoms
| Deficient disease | Lacking nutrient | Common symptoms |
| Marasmus or near starvation | Lacking enough food | – Bones visible from skin
– Child is very weak – Child cries a lot |
| Kwashiorkor | Proteins | – Brown hair
– Swollen belly – Loose skin – Mouth sore |
| Anemia | Iron | – Pale whitish skin
– One become weak and tire very fast |
| Rickets | Calcium | – Bow legs in children |
| Goiter | Iodine | – Swollen neck |
Picture of deficient diseases
Food preservation
This is the treatment of food to enable long shelf life
Reasons for preserving food
(i) To prolong time in which it is useful
(ii) For storage
(iii) To avoid wastage
(iv) For easy transportation
Method of preservation include
Traditional methods
(a) Salting
This is often used to preserve fish and meat
Salt dehydrates and also kills germs
(b) Smoking
Smoking is used to preserve fish and meat
Smoke and heat kill germs. Heat dehydrates fish and meat
(c) Sun drying
Sun drying is used to preserve fish such as silver fish
It dehydrates.
Modern methods
(a) Freezing
Freezing is use to preserve meat, fish, chicken, fruits
Freezing paralyzes microorganism
(b) Canning
Foods like fruits, beans, meat and biscuits are preserved in metal cans.
(c) Pasteurization
Special groups
General all people must feed balanced diet for proper functioning of the body. However, balanced diet must be emphasized in the following groups of people
- Babies and children,
- Pregnant mothers,
- Elderly,
- The sick such as with HIV and
- Breast feeding mother
Food poisoning
This is the illness caused by eating contaminated food. This illness attacks the stomach but can spread to other parts of the body.
Causes of food poisoning
- food contaminated with poisons such as pesticides, detergents
- food contaminated with pathogens/disease causing organisms
Symptoms of food poisoning
- nausea and vomiting
- fever
- stomach pain
- dizziness
- headache
- death
How to prevent food from becoming poisonous
- proper storage of food
- eat fresh food
- do not eat expired food
For revision questions and answers download
Food and nutrition- upper primary
Sponsored by The Science Foundation college + 256 753 802709
Compiled by Dr. Bbosa Science + 256 778 633 682

Your content is always enlightening. Stationary
I appreciate the effort you put into this. Top adult movies
Get expert assistance for MBBS Admission Through Management/Nri Quota in Karnataka.
Learn about the minimum marks required at MBBS Cutoff Of Private Medical Colleges in Orissa.
Claim exciting bonuses today with the Raja Luck Invite Code.
Get reliable insights on Raja Luck from trusted sources.
Your breakdown of Backlink Strategy is actually practical. Certainly carrying out a few of these suggestions.
Discover the best lotto games at Raja-Luck and optimize your payouts.
Select high-performance infrastructure with personalized Server Rental in Mumbai for business and start-ups.
Delivering premium images, the Spotlight is a vital diagnostic tool.
This post restores fantastic memories! My experience was enhanced by Escort Service In Nainital which offered great business throughout evenings.
Winning on bdg win feels satisfying because of the reasonable and transparent system.
I can now take my preferred YouTube audio anywhere with Youtube MP3 Converter.