
Force and simple machine – upper primary science

Force
A force is the pull, push or a lift on an object.
Force is measured in Newtons using a spring balance
Effect of force on an object
- It makes stationary object move
- It makes a moving object to stop or increase speed
- It changes the direction of a moving object
- It changes the shape of an object.
Types of force
- Weight
- Gravity
- Friction
- Magnetic
Weight
Is the amount of force of gravity acting on an object. Weight may vary from one place to another depending of acceleration due gravity
Gravity
Is the force that pulls thngs towards the center of the earth. Forinstance stones through up fall due to gravity.
Inertia is a property of matter that causes it to resist changes in velocity. Either an object remain at rest or continue with constant velocity.
Friction
This is a force that oppose motion or movement
Advantages of friction
- Prevents us from falling while walking
- Enables us to write with a pencil or a pen
- Enable us to use a rubber to eraze
- Cause heat between match box and match stick leading to lighting of match stick
Disadvantage of friction
- wears out shoe, tyres, machines
- produces unnecessary sound
- produces unnecessary heat
- increases effort required to move
- causes blisters on hands
Methods of reducing friction
- oiling
- using ball bearing
- using rollers

- smoothing surface
- making objects streamline like boat or aeroplane
Ways of increasing friction
- making surfaces rough e.g. tarmaking road.
- Having no air trapped between surfaces
Machines
A machine is a device that makes work easier.
In machines an effort (force in neuton) is applied to move the load.
The effort can be
Muscular effort from man or
Force derived from an engine.
Principle of simple machines
The principle used in a simple machine is to produce a big force over a small distance by using a small force over large distance.
The force which we apply to the machine is know as effort (E) and the load we have to overcome is is known as the load (L). Both force and load are measured in Newton.
Types of machines
- Simple machnes
- Complex machine
Simple machines
These are devices that work with one movement and change the size and direction of force.
Examples of simple machnes include levers, pulley, hydraulic, gears, screws, and inclined planes
Levers
A lever is a rigid bar which is free to move about a fixed point, the Fulcrum or povot
Levers are divided into three classes
- The first class levers
- The second class lever and,
- Third class levers
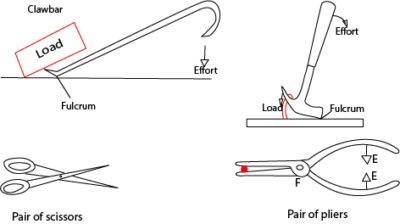
First class lever
This is a type of lever in which the fulcrum is between the effort and the load.
Examples of first class lever include Craw bar, scissor, beam balance, scissor and pair of pliers,
The Principle of Moments
States that when a body is balanced, the total clockwise moment about a point equals the total anticlockwise moment about the same point.
Equation
Moment =force F x perpendicular distance from the pivot d.
Moment = Fd
Second class lever
Here the load is between the effort and fulcrum.
Examples are wheelbarrow, nut cracker and office punch

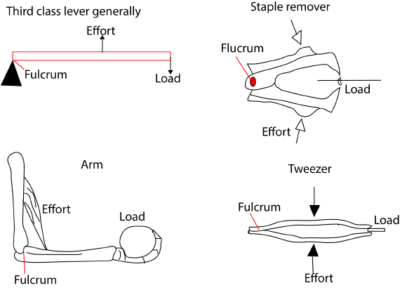
Third class lever
Here the effort isf between the load and fulcrum.
Examples are wheelbarrow, nut cracker and office punch
In the diagram below Isaac and Susan sit on seesaw above, such that Isaac sits at point X and Susan at point Y. Find the mass of Isaac if Susan weighs 45kg.

Principle: clockwise moment = anticlockwise moment.
Let the mass of Isaac be M
Taking moments at the fulcrum
Clockwise moment = 4 x 45 = 180gm
Anticlockwise moment = M x 6 =180gm
M = 30kg
Therefore, Isaac weighs 30kg
Mechanical advantage (M.A)
This is the ratio between the load and the effort applied.
![]()
Significance of mechanical advantage
The bigger the mechanical advantage the better the machine since small effort can lift a bigger load.
Velocity ratio
This is the ratio of distance moved by effort over the distance moved by the load
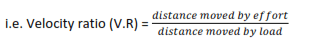
Velocity ratio has no units
Significance of velocity ratio
The bigger the velocity ratio the less effort required to do work and the more efficient the machine. Or the machines requires less effort to overcome a big load when effort moves a bigger distance compared to the load in a unit time.
Example 1
A load of 100N is raised through 6m when an effort of 40N moves through 24m.
Calculate
- mechanical advantage
- velocity ratio
Solution

Pulleys
A pulley is a wheel with a groove ring which passes or string .
- The effort is applied to one end of the rope and the disk of the pulley rotate as the rope moves over it
- If there are several pulleys in a frame work, it is called a block
Single fixed Pulley
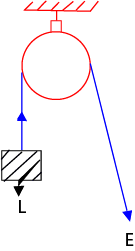
Application of single pulley system
- Removing water from a well
- Lifting building material in the site
- Used on a flag post in the school
- Used at the port to load and unload ship
Inclined Plane
This refers to a type of a machine in which a plane is inclined to an angle to the horizontal such that one end is higher than the other by angle, Θ.
- it used to lift heavy load by pulling/pushing it along the sloping surface.
- It is easier to carry the load along the slope than lifting it through the vertical height, h, since the weight of the load acts vertically downwards (and only a component of weight acts along the plane)
- In order to raise the load through a vertical height, h, th effort, E is applied through a longer distance, l, equal to the length of the plane.

Examples of inclined plane include
- Slopping roads
- Stair case
- Winding road
The Wedges
The wedge is a kind of simple machine which is an inclined plane having one or two sloping sides. With a wedge, the sloping surface is pushed through the material which is held still.
Examples of wedges are: Knife, axe, chisel, needle, nail, razor blade
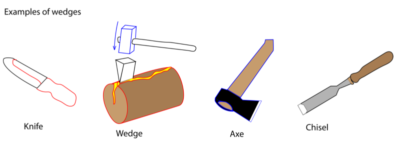
Uses of wedges include: Cutting, pitching
Wheel and axle
A wheel and axle is a type of simple machine made up of a wheel and axles rigidly attached to each other so that they turn together about an axis.
The effort is applied to the larger wheel and the load is raised by string attached to the axle of small diameter as show below:
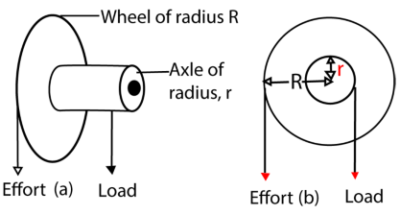
Uses of wheel and axle
- The car steering wheel
- Screw driver
- Windlass (used to raise a heavy bucket of water in a well.
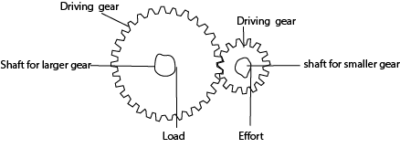
Gears
A gear is a device which consists of a set of toothed wheels. Gears change the direction and speed of rotation. They are similar to wheel and axle. In gear wheel, the effort and the load are applied to the shafts connected to gear.
The screw
A screw may be considered as continuous inclined plane wound round a cylindrical threaded rod.

- The distance between two successive threads is called a pitch
For revision questions download PDF

You always make things easy to understand. Toys & Games
Your content is consistently great. 500 ka redeem code
Discover quality education at the Top MBBS Colleges in Manipur, offering exceptional training in medical sciences.
Discover cutoff insights at MBBS Cutoff Of Government Medical Colleges in Rajasthan.
Join Goa Games today to enjoy a seamless gaming experience with user-friendly interfaces and captivating challenges.
Discover the benefits of using a Referral Code to enhance your TS EARN experience.