
Gaseous exchange – Upper primary science

Gaseous exchange
Animals take in air in order obtain oxygen for respiration.
Respiration is the burning or oxidation of food in the body to obtain energy
Aerobic respiration occurs in presence of oxygen while anaerobic respiration occurs in absence of oxygen.
Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism is termed gaseous exchanges, and the area where gaseous exchange actually takes place is called the respiratory surface.
Qualities of a good respiratory surface
(a) It must be permeable, so that gases can pass through.
(b) It must be thin, because diffusion is only efficient over distances of 1mm or less.
(c) It should possess a large surface area so that sufficient amounts of gases are able to be exchanged according to the organisms need.
(d) It must be moist to ease diffusion of gases across the respiratory surface.
Specialized gaseous exchange surfaces
The specialized gaseous exchange surfaces provide large surface area by developing flaps, sac or tubes.
Specialized gaseous exchange surfaces include
- Body surface/skin in protozoa, earthworm, and flatworms
- External gills in lung worm and tadpole

- Internal gills in fish.

- Lungs in mammals, amphibians, birds and reptiles.
- Trachea system in insects.

In insects air enters and leaves through the spiracles into the trachea. The trachea divides into small tubes called tracheoles that deliver oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from individual cells.
- Skin and buccal cavity in frog and other amphibians.

- In plants gaseous exchange occurs through small pores called stomata.
Gaseous exchange in man
The human lungs and associated structure are shown in figure below.
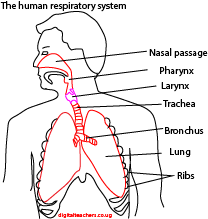
The lungs are situated in the thorax, the walls of which are formed by the ribs and intercostal muscles and the floor of the diaphragm.
The lungs are surrounded by a very narrow pleural cavity lined by pleural membranes.
The pleural cavity contains a thin layer of lubricating which allows the pleural membranes to slide easily over each other as the thorax expands and contracts during breathing.
Function of parts of human breathing system
- Nose
- It lets in and out air
- Contains hairs, mucus and blood capillaries that
- Trap dust particles, germs and cleans the air
- Moisten the air
- Warm the air
- Trachea/wind pipe
It acts as passage of air to and out of the lungs.
It contains cartilages that help to keep the trachea open at low pressure
- Lungs
It is where gaseous exchange takes place in air sacs or alveoli.
- Diaphragm
Is a muscular membrane that separates the chest cavity and abdomen.
Contraction of the diaphragm allow inhalation.
Inspiration.
Air is drawn into the lungs via the trachea and bronchi.
- External intercostal muscles contract and rise the ribs upwards and outwards.
- The radial and circular muscles of the diaphragm contract and diaphragm flattens.
- There is an increase in volume of the thoracic cavity and a decrease in pressure in the lungs.
- Air is drawn into the lungs to equalize the pressure to atmospheric pressure.
Expiration.
- This is a reverse of the inspiration process; air being expelled from lungs.
- It is mainly a passive process resulting from elastic recoil of the tissues that have been stretched during inspiration.
- However, in forced breathing or when breathing tubes are blocked, expiration is aided by contraction of the internal intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles.
- Contraction of the latter raises the pressure in the abdominal cavity, forcing the diaphragm upwards.

When the rubber sheet is pulled downwards by a string, the balloons get inflated
When the rubber sheet is pushed upwards, the balloons get deflated.
Thus, the model can be used to demonstrate breathing in (inhalation) and out (exhalation)
| Parts | Comparison |
| Plastic bottle | Rib cage |
| Balloons | Lungs |
| Straw | Trachea |
| Rubber sheet | Diaphragm |
Diseases of the respiratory system
- Bronchitis
- Whooping cough
- Pneumonia
- Tuberculosis
- Lung cancer
- asthma
Good habits of keeping lungs healthy
- stay in well ventilated place
- exercise regularly
- avoid smoking
- avoid people with infections
- regular treatment
Revision questions
- How does a tadpole differ from adult frog in the way it takes in oxygen?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…………
- State one reason why burning and breathing are similar.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…………
- Which structure of an insect has the same function as gills in fish?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….…………………………………
- Suggest one reason why blood goes to the lungs before it circulates to all parts of the body.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Give any one reason why it is not advisable to breathe through the mouth.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………
- If a person enters a room and begin smoking, how does that habit affect the health of the people in the room?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- What structure in an insect work like lungs in a mammal?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- How does the breathing of an adult frog differ from of a tadpole?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….……………
- Give any one way in which the breathing of a housefly is different from that of a rat.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….…………………
- Give any one reason why human beings breathe in.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………
- In which human body organ does gases exchange take place?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….……………
- Which structures enable the trachea to remain open all the time?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………
- Which organ are used by both fish and tadpoles for breathing?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Name the human body organ where blood gets oxygen while carbon dioxide is removed.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..……
- What is the importance of the rings of cartilages of the trachea in the respiratory system?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………
- Which property of air makes the lungs expand when we breathe in?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- (a) Apart from the skin, give any one example of a respiratory organ.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) List any two diseases which affect the respiratory organ in humans
(i)…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii)…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(c) Give any one practice by humans which may lead to a respiratory disease.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- (a) What is the use of the hairs found in the nose of a human being?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..…………
(b) Name any one disease that attacks the respiratory system.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(c) What happens to the diaphragm when we breathe?
(i) in? ……………………………………………………………………………………..
(ii) out? ……………………………………………………………………………………..
- (a) Name the process that takes place in the air sacs of a human lung.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) What prevents the trachea (wind pipe) from closing during breathing?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(c) Give two products found in the air we breathe out.
(i)………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- The diagram below shows the way in which one of the systems of the human body works. Use it to answer the question that follow
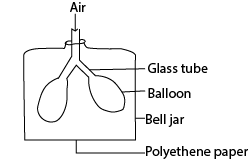
(a) Name the system.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….…
(b) What does a balloon represent?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….…
(c) What does the polythene paper represent?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….……………
(d) What would happen to the polythene paper if air filled the balloon?
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….………………
- The table below shows a group of animals in A with their respiratory organ in B.
| A | B |
| Tilapia
Mosquito Frog Dog |
Moist skin
Lungs Gills spiracles |
Write against each animal below, its respiratory organ from B.
(i) Tilapia: …………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) Mosquito: ……………………………………………………………………………….
(iii) Frog: …………………………………………………………………………………….
(iv) Dog: …………………………………………………………………………………….
- Why is smoking of tobacco harmful to the body?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- Why is it more difficult to breath in a room full of smoke than in open compound?
………………………….…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
- State one disease that both a passive and active smoker may suffer from.
………………………………………………………….………………………………………………………………………………
- Give any one special characteristics of the air we breathe out.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Suggested solution
- How does a tadpole differ from adult frog in the way it takes in oxygen?
Tadpole breathes through external gills whereas a frog breathes through the skin, lungs and buccal cavity.
- State one reason why burning and breathing are similar.
They need oxygen.
- Which structure of an insect has the same function as gills in fish?
Spiracles
- Suggest one reason why blood goes to the lungs before it circulates to all parts of the body.
To get oxygenated
- Give any one reason why it is not advisable to breathe through the mouth.
You may take germs and dust because the air is not filtered by hair and mucus in the nose
- If a person enters a room and begin smoking, how does that habit affect the health of the people in the room?
They become passive smoker and can suffer from lung disease like cancer
- What structure in an insect work like lungs in a mammal?
Spiracles
- How does the breathing of an adult frog differ from of a tadpole?
Adult frog breathe by lungs, skin, and buccal cavity whereas tadpole use gills
- Give any one way in which the breathing of a housefly is different from that of a rat.
Insects breathes through spiracles whereas rat breathe through lungs.
- Give any one reason why human beings breathe in.
To get oxygen for the body
- In which human body organ does gases exchange take place?
In the lungs
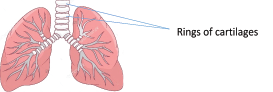
- Which structures enable the trachea to remain open all the time?
Cartilaginous rings
- Which organ are used by both fish and tadpoles for breathing?
Gills
- Name the human body organ where blood gets oxygen while carbon dioxide is removed.
Lungs
- What is the importance of the rings of cartilages of the trachea in the respiratory system?
Help to keep the trachea open during breathing out
- Which property of air makes the lungs expand when we breathe in?
It occupies space
- (a) Apart from the skin, give any one example of a respiratory organ.
Lungs, kidney
(b) List any two diseases which affect the respiratory organ in humans
(i) Lung cancer
(ii) Pneumonia
(iii) Cough
(c) Give any one practice by humans which may lead to a respiratory disease.
Smoking
- (a) What is the use of the hairs found in the nose of a human being?
Trap dust from air breathed in so that it does not enter the lungs
(b) Name any one disease that attacks the respiratory system.
Pneumonia
Cough
Lung cancer
Bronchitis
Tuberculosis
(c) What happens to the diaphragm when we breathe?
(i) in? contract and flattens
(ii) out? Relaxes ad become dome shaped
- (a) Name the process that takes place in the air sacs of a human lung.
Gaseous exchange
(b) What prevents the trachea (wind pipe) from closing during breathing?
It is made of cartilage rings that do not collapse under low pressure
(c) Give two products found in the air we breathe out.
- Carbon dioxide
- water
- The diagram below shows the way in which one of the systems of the human body works. Use it to answer the question that follow

(a) Name the system.
Respiratory system
(b) What does a balloon represent?
Lungs
(c) What does the polythene paper represent?
Diaphragm
(d) What would happen to the polythene paper if air filled the balloon?
Would burst/ expand outside
- The table below shows a group of animals in A with their respiratory organ in B.
| A | B |
| Tilapia
Mosquito Frog Dog |
Moist skin
Lungs Gills spiracles |
Write against each animal below, its respiratory organ from B.
(i) Tilapia: Gills
(ii) Mosquito: spiracle
(iii) Frog: moist skin
(iv) Dog: lungs
- Why is smoking of tobacco harmful to the body?
Causes lung cancer
Causes pneumonia
- Why is it more difficult to breath in a room full of smoke than in open compound?
Smoke suffocates
- State one disease that both a passive and active smoker may suffer from.
Lung cancer
Pneumonia
- Give any one special characteristics of the air we breathe out.
Contains high percentage of carbon dioxide
It is warm
Contain high percentage of moisture
Sponsored by The Science Foundation College +256 753 80 27 09

You have a way of making things come to life. Sports Fitness & Outdoor
I always leave your blog feeling inspired. TamilBlasters Com
Discover detailed information on the MBBS Fees Structure in Manipur for a smooth admission process.
Pursue your dream medical career at Top MBBS Colleges in Gujarat.
Enhance your gaming skills by playing on Raja Luck.
Experience top-notch customer support and assistance on Goa Game, ensuring all your queries are promptly addressed.
Get more chances to win big by redeeming the Diu Win Invite Code.
Reduce capital expense while guaranteeing reputable computing power with Server Rental in Pune.
Experience smooth gameplay and interactive features with 55 club app.
Discover an immersive gaming platform with bdg win and take pleasure in endless enjoyable.
Construct a clear and actionable Tech Roadmap to stay ahead in a competitive market.
Great insights about regional transport! I discovered having company from Escort Service In Nainital practical for navigating the area too.
The commitment to Organic Ingredients makes sure a healthy and tasty meal.