Geography (UACE 250/2) paper 2 Population distribution, growth, characteristics and problems in selected region in the world

Terminologies
Population is the number of people living in a certain area (region) at a given time. The total number of people is established by carrying out population census.
Population census is the physical counting of people in the country after a given period of time. In Uganda, population census is normally carried out after every 10 years.
The importance of population census in the economy
- It helps to determine the total population size and its distribution in the country. This is important for national planning purposes.
- It helps to determine the population growth rate of the country over time. This helps to put in place control measures to regulate the rate of population growth.
- Population figures are used in the calculation per capita income of the country. This gives an indication of standards of living in the country.
- It helps to determine the sex composition of the population that is, the ratio of men to women.
- It helps to show the geographical distribution of the population. This is important for regional resource allocation.
- It helps to determine the rate of internal and external migration. This enables the government to come up with measures to control migration of people.
- It helps to determine the ethnic and religious composition of the population that is, the ratio of the population which belongs to different tribes and religions.
- It is used to determine the population density (number of people per unit area of land). This is used as a basis for demarcating districts for effective service delivery and constituencies for political purposes.
- It helps to determine the population structure and composition in terms of age and level of education of the people. The age structure indicates the number of defendants in the country.
- It is used to determine the occupation composition of the population. This is important for proper manpower planning.
Terms used in population.
(a) Demography. This is the study of the population structure and its composition in terms of age, sex, education levels etc.
(b) Population explosion. This refers to the rapid increase in the population of a given area relative to the available resources. Population explosion leads to over population in the long run.
(c) Migration. This refers to the movement of people from one area (region) to another in a given time.
(d) Immigration. This refers to the movement of people which involves entering and settling into the country from another country.
(e) Emigration. This refers to the movement of people which involves moving out of the country to settle in other countries.
Factors which influence migration of people
- Imbalances in resource distribution among regions and countries.
- Differences in levels of development between regions and countries.
- Differences in incomes and wages between regions.
- Political instabilities like wars and change of regimes.
- Educational requirements where people are forced to go to other countries (regions) to acquire education.
- Differences in climatic conditions which may be favorable or unfavorable.
- Diseases which may affect certain regions there by pushing people to other regions
(f) Birth rate (Crude birth rate). This refers to the number of children born alive in a year per thousand of the population. It is expressed as a percentage.
(g) Death rate (crude death rate]. This refers to the number of deaths in a year per thousand of the population. It is expressed as a percentage.
![]()
(h) Natural population growth rate (NPGR). This is the difference between the number of live births per thousand of the population and the number of deaths per thousand of the population in a year.
- It is the difference between the crude birth rate and the crude death rate.
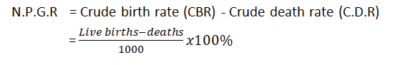
Example 1
In a certain country, the birth rate is 35 per thousand and the death rate is 15 per thousand of the population. Calculate the natural population growth rate.
Solution

(i) Artificial population growth rate. This is population growth rate resulting from net international migration that is the difference between immigration and emigration.
Actual population growth rate = C.B.R – C.D.R+ net international migration
Determinants of population growth rate
- Birth rates
- Death rates
- Immigration
- Emigration
(j) Dependence burden. This is a situation where there is a big proportion of the non-working population depending on a smaller proportion of working population
(k) Dependence ratio. This refers to the ratio of the non-working population to the working population.

Young dependents = people below 18 years; Old dependents = people above 65 years
Active group (working group) = 18- 65 years
(m) Fertility rate. This is the average number of live children born per a fertile woman. (For Uganda’s case it is six children per woman)
Population distribution in the world
Population distribution refers to how a country’s population is spread over the unit land area. The distribution of world’s population is uneven.
The densely populated areas include
- Western and central Europe especially Britain, Germany, France etc
- East and central North America.
- The Indian subcontinent comprising of India, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka
- Eastern monsoon Asia that include China, Japan, Korea
- Nile valley and Delta
The moderately populated areas include
- South and Eastern Europe
- Foothills, intermountain basins, plateau, grasslands
Sparsely populated areas include
- Hot deserts e.g. Sahara Desert
- Cold deserts e.g. Northern Canada
- Hot and wet forests e.g. Amazon, Congo etc.
The population distribution in Africa is shown in the map below
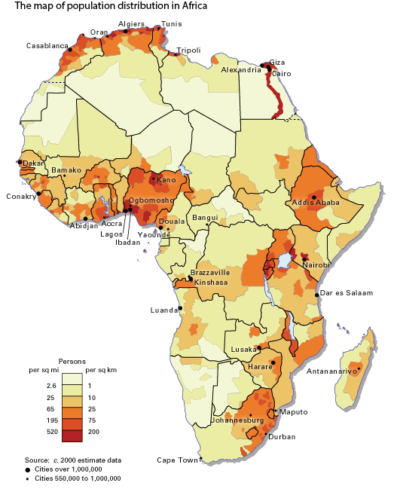
- High population areas in Africa include West Africa, along the coastal region (south of the Sahel), Ethiopian high lands, the highlands of Rwanda and Burundi. the Lake Victoria basin, the South African coastal areas, the Nile valley of Egypt, the coast of the Mediterranean Sea in North Africa, urban areas g. Cairo, Alexandria, Lagos, Nairobi, Kinshasa, Johannesburg etc.
- The moderate population areas in Africa include; Savannah region of Africa, the Mediterranean coast lands in North and South Africa etc.
- The low population areas in Africa include; the Sahel region, the Sahara, the Namibia and Kalahari deserts, the horn of Africa, Northern Kenya, and the Nyika plateau, Central Tanzania etc.
The population distribution in selected countries
Egypt.
High Population is concentrated along the Nile valley; along the Nile Delta; urban centres along the Mediterranean coast; some areas on the shores of the red sea; and the Sahara desert Oases.
Low/sparse population are in the rest of the country such as Sahara desert.
Nigeria
High population is located in southern Nigeria; major cities, Yorubaland in southwest; the central Jos Plateau etc.
Moderate population is located in the northern part of Nigeria e.g. around Sokoto, Kano and Kastana.
Area of low population density include middle-belt.
Kenya
High population occurs along Kenya highlands, Lake Victoria basin, coastal plains from Malindi to Mombasa and within Major cities
Moderate population occurs in areas like Elgon region, Nakuru, Kitale etc.
Low populated areas include Turkana region in Northern Kenys, rift valley, Masai steppees
China.
The highest concentration of people is in Eastern China with a density which is over 200 persons per km2.
Moderate population is in the Southern areas and Central regions with a population density of 50- 100 persons per km2.
Sparse population is found in Northern and Western parts of the Country where the density is below 20 persons per km2
Canada
High population occurs in the southern part of the country; the northern part is sparsely populated due to coldness
India
Dense population occurs Gujarat Plains in the north; the thin Konkan shore in Maharashtra state, New Dheli and Malabar cost in the south etc.
Sparse population occurs along Himalayan mountain system and the north-eastern part of India
Factors that influence population distribution
Physical factors
Climate
- Heavy and evenly distributed rainfall and hot temperature favor high population
- Low rainfall discourage population growth
Vegetation cover:
- the dense tropical rainfall regions discourages settlement;
- the savannah grassland areas encourage moderate settlement because it is suitable for animal grazing and it is easy to clear and cultivate crops;
- Arid area with no vegetation cover discourage settlement because they do not support growth of plants either.
Altitude / relief
- very high altitude areas of over 3000m above sea level discourages settlement due to steep slopes / rugged terrain with very low temperatures, low oxygen e.g. the tops of the mountains e.g. Kenya , Kilimanjaro, Rwenzori, Drakensberg;
- areas with moderate altitude receive high rainfall which favors crop farming e.g. the slopes of Mount Kenya, Kilimanjaro, Ethiopian high lands and gently sloping areas e.g. the Nile valley of Egypt, the Jos plateau of Nigeria etc.
- Very low altitude areas e.g. the rift valley floor receive low rainfall and low population distribution
Soils
- Areas of high soil production or fertility have large population e.g. the shores of lake Victoria, the volcanic highlands of Adamawa, Ethiopia, Kenya, Rwanda, Burundi,
- Low fertility soils e.g. sandy desert soils, the sandy soils in the Sahel etc. support low populations.
Drainage: well drained areas e.g. along the Nile valley of Egypt have large population compared to poorly drained areas e.g. around the Nigeria delta have low population
Pests/ diseases and wild animals have special control on population distribution e.g. tsetse flies in the Miombo wood lands in western Tanzanian has led to low population compared to areas with less pests e.g. South East Nigeria, the Nile valley of Egypt
The effect of natural hazards e.g. landslides along the steep slopes of major highlands, Volcanic eruptions, earth quakes, flooding discourages settlements compared to areas -with less natural disasters.
Human factors
- Historical factors e.g. the effect of slave trade depopulated some areas in central Africa, border areas of conflicting ethnic groups left no man’s lands. The effect of civilization in Egypt helped to increase settlement around the Nile valley of Egypt
- Presence of employment opportunities
- Industries leading large population of the copper belt in Zambia, the Sahara desert, the Witwatersrand in the Republic of South Africa etc. compared to areas without minerals.
- The effect of urbanization / development towns has led to rural urban migration to the major cities e g. Cairo, Lagos, Nairobi, Kinshasa, and Johannesburg etc. as compared to rural areas without towns.
- The government policy can encourage or discourage population distribution through allocation of administrative centers, irrigation schemes e.g. in the Kano plains of Kenya ,the Gezira irrigation scheme in Sudan etc. Government can discourage population settlement by allocation of some areas to national parks e.g. Tzepo in Kenya, Serengeti national park in Tanzania or national forest reserves ·
- The effect of transport and communication facilities. Areas with sound transport facilities e.g. the Witwatersrand in South Africa. The TANZAM railway line etc. have attract large populations compared to areas with poor transport network. .
- Strategic locations e.g. along the coastal areas promotes trade, and have attracted large population densities compared to the interior counter parts.
- Political climate i e. Stability and instability. Politically stable areas have attracted large populations e.g. South East Nigeria as opposed the Northern areas of Nigeria, Somalis etc. which are unstable.
- Cultural factors help to gravitate settlements around the tribal groups. ,
- The effort of trade and commerce. Areas with better opportunities for trade have attracted large populations as opposed to areas with limited trade opportunities.
Causes of population explosion
- Polygamy practices by Muslims in Nigeria who are religiously accepted to marry up to four wives has led to an increase in the population in Nigeria since each woman or wife produces usually on a competition basis of who will give birth to mote children hence the number of children has drastically increased.
- Reduced infant mortality rate rates due to improved medical services such as immunization against killer diseases like measles, diphtheria, polio; tetanus which used to kill many of the infants has led to increase in population Nigeria.
- High fertility rate among Nigerian women and men leading to more births have led to increase in population
- Low levels of education with a high illiteracy rate results into an increase in population because the less educated people tend to produce more children at an early age, have limited knowledge about family
- planning all of which raise the chances of having many children.
- Limited family planning education and facilities both countries has resulted into increase in population rates. The limited use of contraceptives, condoms and other family control procedures has resulted into many pregnancies whenever intercourse is done.
- Reduced maternal mortality rate due to better health care such as antenatal care.
- Government policy that encourages high population growth to develop a strong market base for agricultural and industrial goods.
- Increased life expectancy due to improved medical facilities
- Immigration especially in Nigeria
- Poverty among the rural people because they lack ambitions, ideal and have enough time at their spouse doing nothing
- Political stability
Effects of high population are both positive and negative
Positive effects/contribution of high population
- High population provides local market to agriculture and industrial output.
- The big population is a source of cheap labour necessary development of the agricultural and industrial sectors.
- High population is a source of government revenue through taxes on their labour.
- High population provides security such as in army, police, prison officers
- High population leads to exploitation of resources in agriculture, fishery, industries etc.
Negative effect/contribution of high population
- Dependency burdens due to a high number of young people and the elderly who are not productive.
- High populations have strained social facilities like schools, Hospitals in Mumbai, leading to compromised standard of living.
- It has resulted into high cost of living in terms of accommodation, education, health care, feedings etc.
- It has resulted into poor sanitation in the congested cities such as Mumbai, New Delhi and Calcutta due to abundant domestic waste.
- It has resulted into an increase in the crime rate such as human organ trafficking, drug abuse, theft, etc.
- High population causes unemployment due to many people chasing the few existing jobs.
- High population leads insecurity and unrest due to competition for limited resources.
- High population results into food scarcity and malnutrition.
- High population promotes spreading diseases
- High population has led to land shortage, and environmental degradation.
- Increased government expenditure on social service
- High population in India has led to dependence on foreign aid from the developed countries such as U.S.A. and loans from the World Bank for infrastructural development and sustenance of the government thus slowing down development
Steps being taken to solve the problems of rural-urban migration in tropical Africa
- Provision of social services to the village such as schools and healthy facilities
- Rural electrification to encourage development of industries and employment in the rural area.
- Improvement of water supply in rural area
- Improvement of security to the rural areas
- Political stability
- Extension of affordable credit facilities into rural areas
- Population control
- Decentralization of government department in order to create employment in the rural areas.
Population problems in developing countries (Uganda)
- There is food shortage to support the increasing Countries are forced to import foodstuffs or to seek for foreign aid from other countries.
- Balance of payment problems. This is as a result of increased government expenditure on food imports and other social requirements for the population.
- High levels of unemployment and under-employment. The population growth rate exceeds the rate at which jobs are being created. This is due to limited job creating investments as a result of low savings and capital.
- Diminishing returns in the agriculture sector due to high population pressure on land and other natural resources. This leads to low levels of productivity and per capita income.
- Low capital accumulation. This is due to high consumption expenditures leaving little or nothing for savings and investment.
- Poor standards of living. This is due to shortage of goods and services and high levels of inflation due to excessive demand for goods and services.
- Over exploitation of natural resources hence environmental degradation and pollution.
- Rural urban migration leading to congestion, high crime rates, prostitution, theft etc. in urban centers.
- High dependence burdens. The increasing population makes developing countries to depend on other developed countries for foreign aid in form of food and other consumer
- High levels of brain drain. The increasing population accelerates brain drain as the young and highly educated individuals leave their countries in search of “greener pastures” in developed countries.
- High levels of illiteracy due to low levels of education and poor health services. The majority of the people are poor and they cannot access the expensive higher education due to high dependence
- Political instabilities in form of civil wars and struggle for the limited social services.
Possible solutions to the population problems in developing countries
The solutions aimed at solving the problems of increasing population are contained in the population policy. Therefore the population policy is aimed at attaining optimum population by checking on population growth and increasing resources and production capacity. Such population policies include the following;
- Family planning. This includes the use of contraceptive pills, condoms and other intra-uterine devices. However, this method has not been effectively used due to high levels of illiteracy and fear of side effects.
- Encouraging higher education. Emphasis should be put on female education so as to check on the fertility rates and emphasize the quality of children other than the In addition, education also helps to postpone marriages for the future.
- Adopting production policies aimed at increasing food supply to reduce on food shortages. This helps to reduce on the diseases associated with malnutrition.
- Rural development policies aimed at making rural areas attractive so as to check on rural urban migration. Such policies include rural electrification, security, water supply This also promotes agricultural production.
- Disease control measures. Health programs should be set up to educate the people on how to control and reduce on the spread of diseases through primary health care.
- Legalizing abortion as a way of controlling unwanted pregnancies and population
Thank you
Dr. Bbosa Science


I’m always impressed by your writing. Office Products
I’m always learning something new. Tech News
Gain direct entry to prestigious colleges via MBBS Direct Admission in Orissa.
Explore the latest government college cutoffs at MBBS Cutoff Of Government Medical Colleges in Delhi.
Join thousands of players and enjoy immersive gaming at Raja Luck.
Get the complete picture of Raja Luck and its possibilities.
Great insights! I’ve been searching for methods to improve my SEO, and Buy Backlinks seems like a strong strategy.
Drive long-term SEO development with Build backlinks for website.
Discover the very best lottery game games at Raja-Luck and optimize your jackpots.
82 lottery is great for casual and knowledgeable gamers alike.
Get the current updates on the Mumbai Indians Team 2025, consisting of player lists, strengths, and possible playing XI for the upcoming IPL season.