
Heat energy – upper primary science

Heat energy
This is a form of energy that flows from one point to another due to temperature differences.
Temperature a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the degree of hotness or coldness.
The difference between heat and temperature is that heat is a form of energy that increases the temperature of the body while the temperature is the degree of hotness or coldness of an object.
Source of heat include sun, burning firewood, electricity, microwaves etc.
Uses of heat
- cooking food
- warming rooms in winter
- ironing
- drying clothes
Method of heat transfer
Heat is transferred from one point to another by conduction, convection and radiation.
Conduction
is the method of heat transfer in solids. Solids that conduct heat are called good conductors while those that do not conduct heat are called bad conductors or insulators.
Good conductors such as metals are used as electric cables, cooking utensils
Insulators such as wood and plastics are used as handle for electric appliances such as electric ion and electric cooker. Feathers and clothes insulate bird’s and human body respectively on cold days.
Importance of heat transfer by conduction
Ironing clothes
warming spouse in the bed
loosing heat by sleeping on bare floor
Experiments to demonstrate conduction of heat through solids
(i) A nail heated on one end, and feeling heat on another end. Heat reaches the hand by conduction

(ii) Using metal wax on the a nail
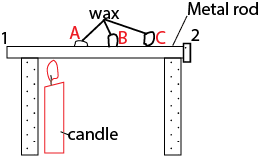
Wax will melt in order A to B to C as heat travel from side 1 to side 2 of the rod
Convection
Convection is a method of heat transfer in gases and liquids. Here heat moves by means of convectional currents as shown in the diagram below
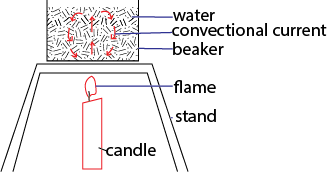
Radiation
Radiation is heat transfer through the vacuum. A vacuum is an empty space without any medium. Heat travels from the sun to the earth by radiation
For instance heat energy from the sun to the earth is by radiation
Appliances that save heat energy/ fuel/cost of heating
(i) Using charcoal stove

(ii) Pressure cooker
(iii) Thermos flask keep hot things hot and cold things cold
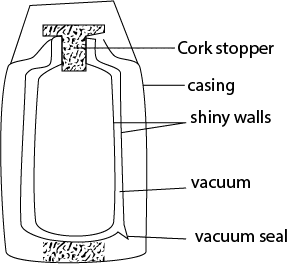
Functions of parts of vacuum flask
(i) Cock stopper prevent s heat loss by conduction
(ii) Vacuum reduce heat loss by conduction and convection
(iii) Shinny material reduce heat loss by convection and radiation
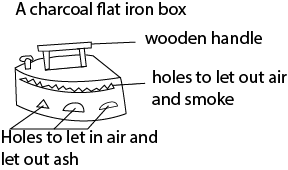
It is used for ironing clothes and heat transfer between the box and clothes is conduction.
Wooden handle is an insulator that prevents burning of hands
Effect of heat on substances
Heat causes
- Temperature increase
- Melting or change from solid form to liquid form
- Evaporation or change from liquid form to liquid form to vapor form
- Expansion or increase in length of size
The linear expansivity of a substance is the fractional change in length of a sample of the substance per degree C change in temperature. Units °C–1
Substances with a bigger linear expansivity lengthen more heating than one with low linear expansivity. For example, the diagram below shows three MCK with equal length before heating and different length after heating.
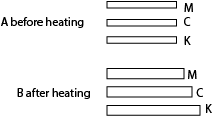
This shows linear expansivity of K is higher than that of metal C than that of metal M
Effect of cooling on substances
It causes
- Contraction or reduction in size. Contraction may lead to breakage electric wires in winter if they were tightly fixed

Water is the only substance that expand on cooling. this can break glass bottles that contain water
- Solidification/freezing or change from liquid to solid
- Sublimation is change from solid directly to gas
- Condensation or change from gases to liquid
Evaporation and condensation processes may be used in purification of liquids such as alcohol. Here a fermented mixture is heated and alcohol turns into vapour which is cooled to form liquid alcohol. This process is called distillation.

Thermometer

It is an instrument for measuring and indicating temperature.
It consists of a narrow, hermetically sealed glass tube marked with graduations and having at one end a bulb containing mercury or alcohol that expands and contracts in the tube with heating and cooling
Properties of liquids in the thermometer
- It should be visible.
- It should have uniform thermal expansion.
- It should have a low freezing point.
- It should have a high boiling point.
- It should not wet glass.
- It should be a good conductor of heat.
- It should have small specific heat capacity.
Advantages mercury in the thermometer
- It can measure high temperatures
- Mercury is visible without any dye
- Expansion of mercury is regular
- Mercury does not wet the capillary tube wall
- It gives precise results
Disadvantages of mercury thermometer
- It is expensive
- It is poisonous
- Responds slowly
Advantages of alcohol in thermometer
It is nontoxic but has low boiling point
It is nontoxic but has low boiling point
It is cheap
Can measure low temperature
Disadvantages of alcohol thermometer
less durable
it can not measure high temperature
wets glass
Clinical thermometer

Clinical thermometer one used to determine the temperature of the human body
Before using mercury thermometer shake it to get the mercury down to the bulb and then put it in the armpit or the anus.
For a typical adult, body temperature can be anywhere from 97 F to 99 F. Babies and children have a little higher range: 97.9 F to 100.4 F or 36 -37.20C
However mercury thermometer have been replace by more accurate digital thermometer. Secondly mercury is very poisonous in case the thermometer breaks.
Scales of temperature
There are three temperature scales in use today, Fahrenheit, Celsius and Kelvin.
Celsius temperature scale also called centigrade temperature scale, is the scale based on 00C for the freezing point of water and 1000C for the boiling point of water.
Fahrenheit temperature scale (F) is a scale based on 320F for the freezing point of water and 2120F for the boiling point of water, the interval between the two being divided into 180 parts.
![]()
Kelvin temperature scale is the base unit of thermodynamic temperature measurement in the International System (SI) of measurement
Temperature in kelvin scale = 273 + temperature in Celsius temperature scale

I really like this because i got what i never had. may the Almighty God bless u abundantly.
This is really good I must say
You’ve got a talent for storytelling. Transfer Latest
Discover the competitive benchmarks with the MBBS Cutoff Of Private Medical Colleges in West Bengal.
Learn about cost-effective learning opportunities at MBBS Fees Structure in Orissa.