
Invertebrates – upper primary science

Animals
Characteristics of animals
Animals are different from plants because animals do not make their food while plants do.
Characteristics of animals as living things
- They grow
- They feed
- They reproduce
- They move; – animals move to look food mates and running away from enemies.
- They excrete;- excretion is the removal of waster metabolic products from the body
- They respire; – respiration is the oxidation of organic food material to produce energy
- They respond to the environment
Classification of animals
- Microscopic animals virus and bacteria
- Invertebrates or animals without a backbone
- Vertebrates or animal with a backbone.
Viruses
- they are the smallest living organism
- they do not have a cellular structure
- they can only reproduce in the cells and therefore they are all obligate parasites
Importance of virus
- they cause diseases such as covid-19 , flue
- some viruses provide immunity against bacteria pathogen
Bacteria
Are small microscopic organisms
Importance of bacteria
- Some bacteria are used in treatment of sewage
- Some bacteria fix nitrogen into the soil
- Some bacteria are used to make butter and cheese
- Saprophytic bacteria decay rubbish
- Some bacteria make antibiotics
- Pathogenic bacteria cause disease such as
- Cholera
- Syphilis
- Pneumonia
- Typhoid
- Tuberculosis
- Tetanus
Protozoa
Examples; amoeba, Euglena, paramecium and trypanosome
Characteristics of amoeba
- It is single celled
- It is microscopic, that is, it is observed using a microscope.
A microscope is an instrument used to observe small organisms.
- It reproduces by means of binary fission.
- It moves by pseudopodia

Functions of parts of amoeba
- Cell membrane
- Protects internal structures
- Regulates substances that enter or leave the cell
- Senses external stimuli.
- Nucleus: controls activities of the cell.
- Contractile vacuole: eliminates excess water from the cell
Feeding
Amoeba feeds by use of cell membrane to engulf the food particle. The food particle is taken in the cytoplasm and enclosed in food vacuole where it is digested.
Economic importance of protozoa
- Amoeba – cause amoebic dysentery
- feeds and control other disease causing organisms e.g. bacteria
- Trypanosome – causes nagana in cattle and sleeping sickness
Worms
These are invertebrate animals that typically have soft, slender, elongated bodies
Examples of worms
(a) Earthworm

Characteristic
- It has a segmented body
- It is hermaphrodite i.e. it has both male and female reproductive organs
- Its excretory organ is called nephrida
- Gaseous exchange occurs over the body
- Uses chaeta for locomotion
Economic importance of earthworms
- Make tunnels in the soil thereby improving aeration and drainage of soil
- Death and decay lead to formation of humus
- source of food to other animals e.g. chicken
- Mixes soil layer
(b) Round worms e.g. ascaris or hook worm

It is unsegmented
It has a cylindrical body
It exist as male or female
Gaseous exchange occurs by diffusion over the body surface
Importance of round worms
- Round worms are parasites in duodenum are transmitted in feces; they enter the human body as larvae through the skin of bare feet or through the mouth.
- They cause anemia because they feed on blood
- Transmission is controlled by proper hygiene, eating fruits after washing them
A parasite is an organism which feeds on another organism
(c) Filarial worms
They are roundworms, parasitic that cause elephantiasis/filariasis in man.
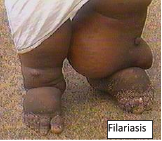
Filarial worms are transmitted by Aedes mosquitoes
Its spread is controlled by sleeping in mosquito net.
(d) Tape worms
They are parasitic flat worms, transmitted by eating infected beef or pork
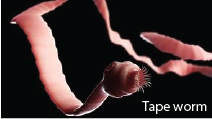
Harmful effects of tape worms
- They are parasites by absorbing digested food through their skins in the intestines
- They may block the intestine and cause constipation and other problems
- Lead to anemia by competing with the host for digested food. Tapeworm absorb digested food through their skin
Control of human intestinal worms
Just like livestock are attacked by parasites, human beings are also attacked by worms.
A parasite is an organism that feed on another organism
Source of worm infection
Eating unready meat (tape worm)
Walking bare foot (round worm)
Drinking contaminated water (roundworms)
Signs of worm infection
Pains in the stomach
Having an itchy body
Feeling hungry after eating
Swollen body (stomach)
Diarrhea
Weight loss
- Poor health
- Anaemia
- irritation
Control of spread of worms
- proper disposal of feces
- eat well cooked food
- proper sanitation
- regular deworming with drugs
Arthropods
General characteristics
- have segments bodies
- have exoskeleton
- have jointed legs
- they have a dorsal heart with open vascular system
They are divided into five classes
- crustacea
- chilopoda
- diplopoda
- arachinida
- insecta
Crustacean
Characteristic
- have two compound eyes
- mostly aquatic or live in water
- have five or more pairs of legs.
Examples

Economic importance
Source of food to man and other animals
Few are parasitic
Centipede
Characteristics
Have cylindrical bodies with numerous segments each with one pair of leg.
Carnivorous

Importance
It inflict poisonous sting
Millipedes
Characteristics
- their bodies are cylindrical with numerous segments that are similar except around the head region.
- Each segment has two pair of walking legs

Economic importance
- Millipedes are herbivores and pest to farm crops.
- They burrow and aerate the soil and improve drainage.
Arachnids
Characteristics
- the body is divided into two main body parts, cephalothorax and abdomen
- have no antennae
- have four walking legs on cephalothorax
Examples

Economic importance
- Tick and mites are parasites to domestic animals
- Tick spreads diseases to man e.g. coastal fever
- Spiders feed on vectors.
- Scorpions and spiders inflict fetal stings
Insects
Characteristic
- Has three main body parts; head, thorax and abdomen.
- Has three pairs of legs.
- Thorax is divided into pro-, meso-, and metathorax.
- Increase in size through moulting
Common insects include
(a) housefly
Characteristics of housefly
- has a pair of compound eyes for vision
- has expanded or club shaped proboscis
- has a pair of wings and a pair of halters.
- The body is hairy.
- Has a pair of short hairy antenna
Life cycle of a housefly
Has a complete life cycle
.
Economic importance
Transmits diseases e.g. dysentery, cholera, trachoma, typhoid fever and poliomyelitis.
Ways by which housefly transmit diseases
Carry bacteria on hairy body, on their feet and proboscis
Control
General cleanness and hygiene
Cover food
Eat hot food.
Use insecticides.
(b) Cockroach

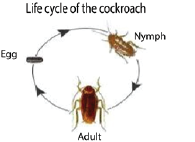
Economic importance
- Transmit germs from the toilets
- Their feces stain clothes
- Destroy document and clothes
(c) Bee
Characteristics of bees
- have two pairs of membranous wings
- have a waist between the thorax and abdomen
- They live in colonies

Economic importance of bee
Pollinate flowers
Make bee wax and honey
Types of bees and their role in a bee colony
- Queen bee is produced from fertilized eggs that are feed on royal jelly. It lays eggs after it has been fertilized by drone. When a new queen is born in hive bees swarm.
- Drone – male bee. It is produced from unfertilized egg and mates with the queen
- Worker bee – they are infertile female are produced from fertilized eggs. Their role is to look after the hive and other bees and collect nectar and pollen grains to make honey.
Type of bee hive
A beehive is a structure — either made by humans or bees — in which bees live and make honey.
Nature beehive is usually a hole in a tree
Traditional be hive are beehive made of local materials
Modern beehive are well constructed wooden box. The advantage of modern beehive is that they produce clean
Chambers of beehive
Brood chamber (Usually in the bottom box) this is where eggs, larvae and pupa develop.
Honey chamber: this where honey is collected
Harvesting honey
Smoke the beehive to calm the bees and then open to remove honey. Honey is then removed from honey combs by crushing honey combs and honey isolated byby filtrations or centrifuging.
Dangers of bees
They sting when disturbed
(d) Termite
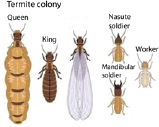
Economic importance
- turns the soil over to keep it loose and aerated
- source of food
- destroy wooded properties
- destroy plants
(e) Grasshopper

Economic importance
- source of food
- they are plant pests
Importance of mosquitoes
They transmit diseases.
(f) 
Table showing diseases carried by mosquitoes.
| Mosquito | Diseases | Causative organism |
| Female anopheles | malaria | plasmodium |
| Aedes | Yellow fever,
dengue fever |
Virus
virus |
| Culex | Elephantiasis | Filarial worm |
Life cycle of a mosquito
Mosquitoes undergo complete lifecycle
Eggs → larva → Pupa → adult
The mosquito larva of culex mosquito and that anopheles mosquito are distinguished from the way they orient on water surface
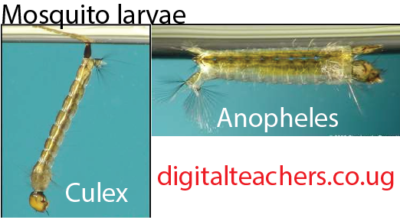
Control of malaria and diseases spread by mosquitoes
- Sleep in a mosquito net
- Draining stagnant water
- Removing bush in and around the house
- Close the house to prevent entry of mosquitoes
(g) Butterfly

Feeding: feeds on nectar using sucking mouth parts.
Life cycle: undergo complete metamorphosis i.e. eggs → larva → pupa → adult,
Importance
- Pollinate flowers
- Larva stage (caterpillar) are pest; destroy plant leaves
(h) Wasp

Characteristics
- has two pairs of membranous wings
- has a narrow waist between the thorax and abdomen
- Has three main body parts; head, thorax and abdomen.
- Dark colored for camouflage
- Use sting to defend them selves
Importance of wasps
Inflict painful sting
(i) Sugar ant

Characteristics
- lack wings
- has three main body parts; head, thorax and abdomen
- has three pairs of legs
- has biting mouth parts
- has thin waist between thorax and abdomen
- dark colored for camouflage.
Economic importance
Are part of food webs
Snail

They protect themselves by hiding in their shells
Importance
- source of food
- crop pest
- are vectors for diseases such as bilharzia
Adaptation of some animals for movement
| Movement behavior | Part of body involved | Examples of small animals |
| swimming | fins webbed feet | fish, frog |
| running | legs | cockroach, lizard |
| leaping | long strong hind legs | frog, grasshopper, flea |
| crawling | body muscles | earthworm, snake, caterpillar |
| .flying | wings | housefly, butterfly, weaver bird |
| hopping | limbs/ legs | frog, grasshopper, flea |
| walking | limbs/legs | tortoise, cockroach, housefly |
Protective behavior Adaptation/part that helps Examples of the small animal
| in protection | ||
| stinging | sting | bee, wasp |
| running away | legs/limbs | lizard, cockroach |
| biting | mouth parts; fangs | spider, centipede, safari ant, snake |
| flying | wings | wasp, weaverbird, housefly |
| coiling | body muscles | snake, millipede, earthworm |
| hiding in shells | hard shells | snails and tortoise |
For revision questions download the PDF below
Sponsored by The Science Foundation college +256 753 802709
Compiled By Dr. Bbosa Science + 256 778 633 682
Please help and subscribe before you leave the site

Thanks for being a beacon of knowledge. Water Bottle
Your content is always on point. TamilBlasters Com