
Kingdom plantae, dicot, monocot, mosses, ferns (A-level biology)

Kingdom plantae
Specific objectives
The learner should be able to
- To identify lower plants and higher plants using structural features.
- Name the plant groups to phyla
- Outline the characteristic and structures of the named plant groups
- State the role of the plants in the environment
Characteristics
- Are made of more than one eukaryotic cell.
- Have cell wall containing cellulose
- Have chlorophyll as their main photosynthetic pigment.
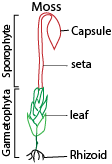
Phylum Bryophyta(moss)
- It is made of small plants generally found in moist terrestrial habitats
- They have no root and no vascular tissue
- Show alternation of generation in which the sporophyte and gametophytes are almost equally conspicuous, although the sporophyte is attached to and depends on, gametophyte throughout life.
Phylum Filicinophyta (ferns)
Ferns have large leaves with chlorophyll called fronds which are coiled in bud.
Have roots and well developed vascular systems.
Phylum Angiospermophyta: Flowering plants
They are made of two classes, monocotyledoneae (monocotyledonous plants) and dicotyledoneae (dicotyledonous plants).
Comparison of monocotyledonous plants and dicotyledonous plants.
| Monocotyledoneae | Dicotyledoneae |
| Embryo has one cotyledon | Embryo has two cotyledons |
| Narrow leaves with parallel venation | Broad leaves with network veins |
| Scattered vascular bundles in stem | Ring vascular bundles |
| Rare cambium present and normally no secondary growth | Vascular cambium present which can lead to secondary growth |
| Many xylem groups in root | Few xylem groups in the root |
| Flower parts in threes | Flower parts in fours or fives |
| Calyx and corolla not usually distinguishable | Calyx and corolla are distinct. |
| Often wind-pollinated | Often insect-pollinated |
| e.g. maize and rice | e.g. bean |


Roots of flowering plants
This is the non-leaf, non-nodes bearing parts of the plant’s body that usually grow into the ground.
Primary functions of the root
- Anchors the plant in the soil
- Absorbs water and mineral salts
Secondary functions of modified root
- Food storage e.g. cassava tubers, carrot (taproot)
- Vegetative reproduction e.g. potato tubers
- Breathing root for gaseous exchange especially for plants that live in waterlogged places
- For support e.g. clasping root, prop roots, buttress root, stilt roots,

Section through a monocotyledonous root

Section through dicotyledonous plant root

Differences between monocot and dicot roots
| Monocot root | Dicot root | |
| 1 | Xylem polyarch | Xylem tetrarch |
| 2. | Pith is present | Pith absent |
| 3. | Has a limited number of Xylem and Phloem | Has a higher number of Xylem and Phloem |
| 4. | Conjunctive tissue is sclerenchymatous in maize | Conjunctive tissue is usually paranchmatous |
| 5. | There is no secondary growth | Secondary growth is present |
| 6. | Pericyle gives rise to cork cambium, parts of the vascular cambium, and lateral roots | Gives rise to lateral roots only |
| 7. | Cambium absent | Cambium present |
| 8. | Cortex wide | Cortex wide |
| 9. | Older roots are covered by an Exodermis | Older roots are covered by a Cork |
Stem
A stem is the plant axis that bears buds and shoots with leaves and roots at its basal end.
Function of stem
- Conducts water and mineral salts from roots to leaves.
- Conducts manufactured food from leaves to other parts of the body
- Supports leaves to receive enough light
- Stores food e.g. sugar cane
- For vegetative reproduction
- Supports flowers in space for fertilization
Section through dicotyledonous plant stem

Section through monocotyledonous plant stem
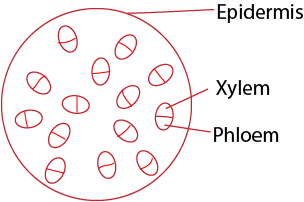
Similarities between monocot and dicot stem
- The epidermis is made of a single layer
- Have thick cuticle
- Ground tissue parenchymatous
- Xylem and phloem are organized in a vascular bundle.
Differences between monocot and dicot stem
| Dicot stem | Monocot stem | |
| 1. | Endodermis present | Endodermis absent |
| 2. | Vascular bundles are arranged in a ring | Vascular bundle scattered in ground tissue |
| 3. | Vascular bundles are few in number 4-8 | Vascular bundle numerous |
| 4. | Xylem elements polygonal | Xylem elements are circular |
| 5. | Pericycle present | Pericycle absent |
| 6. | Pith present | Pith absent |
| 7. | Medullary rays present | Medullary rays absent |
| 8. | Undergo secondary growth | No secondary growth |
| 9. | Bundle sheath absent around the vascular bundles | Vascular bundles are surrounded by sclerenchmatous bundles sheath |
| 10. | Vascular bundles open | Vascular bundles closed |
| 11. | Hypodermis is made of collenchymatous cells | Hypodermis is made up of sclerenchymatous cells |
| 12. | Ground tissue is differentiated into cortex, endodermis, pericycle and pith. | Ground tissue is not differentiated |
| 13. | Starch sheath present | Starch sheath absent |
Leaves
Functions of leaves
- Photosynthesis.
- Transpiration
- Floral induction: the plant leaves synthesize and translocates the flower- inducing hormone called florigen to buds.
- Food storage
- Have tendrils for support

Coniferous plant

Economic importance of plants
- For decoration
- For food, timber, medicine, raw materials for industries (fruits juices), fiber producing plants (sisal, hemp, cotton)

Přijetí hypoteční platby může být problematické pokud nemáte
rádi čekání v dlouhých řadách , vyplnění mimořádné formuláře , a odmítnutí úvěru
na základě vašeho úvěrového skóre . Přijímání hypoteční platby může být problematické,
pokud nemáte rádi čekání v dlouhých řadách , podávání extrémních formulářů ,
a odmítnutí úvěru na základě vašeho úvěrového skóre .
Přijímání hypoteční platby může být problematické ,
pokud nemáte rádi čekání v dlouhých řadách , vyplnění extrémních formulářů a odmítnutí úvěrových rozhodnutí založených na úvěrových skóre .
Nyní můžete svou hypotéku zaplatit rychle a efektivně v České republice. https://groups.google.com/g/sheasjkdcdjksaksda/c/BJeU7ld4nQ0
Your insights are always on point. 500 ka redeem code
Get complete details on the MBBS Fees Structure in Kerala for aspiring medical professionals.
Learn about the qualifying scores for top colleges at MBBS Cutoff Of Private Medical Colleges in West Bengal.