
Kingdom Protoctista, spirogyra, algae (A-level biology)

Kingdom Protoctista
Specific objectives
- State characteristic of Protoctista.
- Describe the structure of protozoa
- Outline the role of protozoa and algae in environment.
- Name common disease caused by protozoa
- Outline methods of preventing spread of diseases caused by protoctists.
The kingdom Protoctista consists of eukaryotic organisms which are assemblages of similar cells. It includes algae, all protozoa and slime molds.
Characteristics
- Have no stems, roots or leaves
- No sclerenchyma
- No vascular tissue
- No archegonia
- Have other photosynthetic pigments in addition to chlorophyll a.
| Phylum: Chlorophyta (green algae) | Phylum Phaeophyta (brown algae) |
| Chlorophyll a and b present | Chlorophyll a and c |
| Food reserve is starch | Food reserve include mannitol and laminarin |
| Cellulose cell wall | Cell wall include alginic acid. |
| Unicellular, filamentous or thalloid | No unicellular form |
| Mostly freshwater | Almost all marine |
| e.g. spirogyra | e.g. Fucus |
Structure of Spirogyra
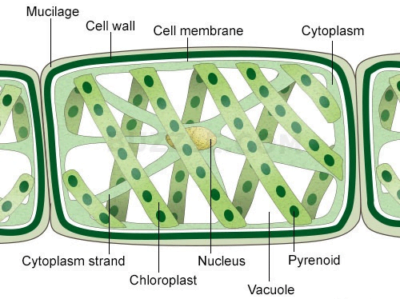
Reproduction
Asexual reproduction by fragmentation
Sexual reproduction by conjugation
Stages of conjugation in spirogyra
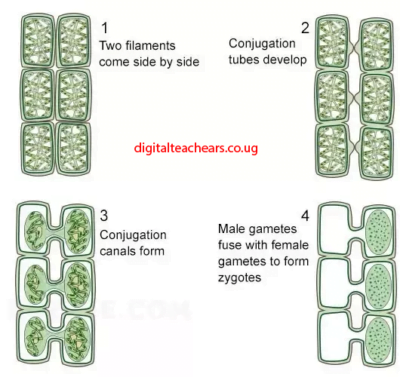
The economic advantage of algae
- Primary producer
- Food
- Provide oxygen in water through photosynthesis.
- Alginic acid derivatives are used as a thickener in food, cosmetics, and drug industry.
- Algal bloom causes water to smell and may lead to depletion of oxygen and the death of fish.
Sponsored by The Science Foundation College +256 80 27 09
Compiled by Dr. Bbosa Science
CATEGORIES A-level Biology
TAGS Dr. Bbosa Science

Thanks for being such a source of insight. Sports Fitness & Outdoor
This is exactly what I needed to read today. 500 ka redeem code
Learn about the competitive MBBS Cutoff Of Private Medical Colleges in Delhi for top-ranked institutions.
Explore efficient enrollment options with MBBS Admission Through Management/Nri Quota in Chhattisgarh.
Invite your friends and enjoy bonuses with the Raja Luck Invite Code.
Find out how Raja Luck can be useful to you.
Maximize your rewards by applying the Raja Games Invite Code upon signing up.
Take advantage of recommendation bonuses by sharing the Diu Win Invite Code.
Run advanced software and AI applications with Server Rental in Delhi.
Contend versus skilled players and display your skills on bdg-win.
Sign up with countless players worldwide on 55-club and experience the thrill of winning.
Step into the future of video gaming with bdg win and delight in non-stop home entertainment.
Develop a strategic IT Strategy Roadmap to drive service innovation and efficiency.
Discover essential Best Kitchen Tools And Gadgets that bring performance and design to your kitchen.
OnlyMP3 is by far the very best free MP3 converter I have actually used online.
This guide is so handy for first-time visitors! I would recommend adding Escort Service In Nainital to your resource list for those desiring companionship.
If you value good food, you’ll love the Homemade Taste.