
Light energy – upper primary science

Light
It is a form of energy that enables us to see.
Other uses of light
- It is used by plants for photosynthesis
- It is used in photography; photographs are taken only in light.
- Produces heat for drying of produce and clothes
- It is used in decorative lights
- It is used in photography
Sources of light
(a) Natural sources of light: sun, stars, fireflies, glow warms
(b) Artificial sources of light: lamps, candles, electricity
NB. Moon is not a source of light because it only reflects light from the sun
Kerosene lamp
This is a type of lighting device that uses kerosene as fuel. Kerosene lamps have a wick or mantle as light source, protected by a glass chimney or globe; lamps may be used on a table, or hand-held lantern may be used for portable lighting.

Properties of light
- Light travels in a straight line
- Light can be reflected
- Light can be refracted
Experiment to show that light travel in a straight line.
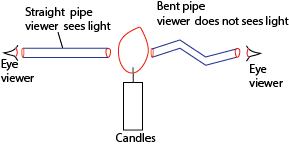
(i) Viewing candle light through a pipe.
With a straight pipe the viewer receives light while with a bent pipe the viewer does not receive light.
(ii) Using cardboards with holes
When the holes are in a straight line the viewer is able to see light
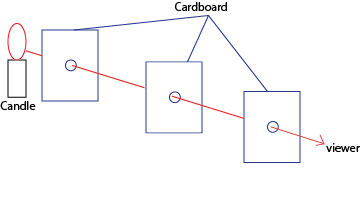
When one hole is removed from the line, the viewer is unable to see light.
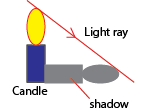
(iii) Shadows
A shadow formed when light traveling in straight light is obstructed by an opaque object.
Effect of different materials on light
- Transparent materials allow light to pass through for example clear glass, clear water, clear air.
- Translucent materials allows some light o pass through for example a patch of oil on paper, translucent glass
- Opaque materials do not allow light to pass through. Examples are brick wall. Tree, human being, stones.
Eclipses
The sun is a luminous object and thus a source of light. The earth and moon are opaque objects in the universe.
Solar eclipse or eclipse of the sun
When the moon rotates and comes between the sun and earth, it cast a shadow on the earth. This is also called solar eclipse
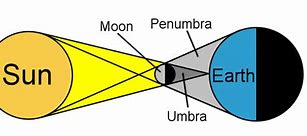
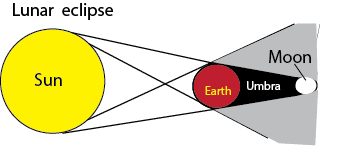
The dark shadow is called umbra while the lighter shadow is called penumbra.
Lunar eclipse or Eclipse of the moon
The earth comes between the sun and the moon, casting its shadow on the moon.
Ways of lighting a house
The house needs to be well lit during the day and at night. We can light our houses in the following ways:
- Open the windows during the day to enable sunlight to light the house.
- Use translucent These are roofs made in a special way to allow light to pass through them. This type of roof allows sunlight to get into the house during the day.
- At night, there is no sunlight and therefore artificial lighting may be Examples of artificial lighting are: using fire from firewood, a torch, lamp, candle, gas lamp or electricity.
Light rays
The path taken or indicating the direction along which light energy travels is known as a ray of light. A ray is indicated with an arrow.
![]()
Beam of light
A group of light is called a beams. There are three types of beams namely

Reflection of light at a plane mirror
Reflection is the bouncing back of light energy when it meets an obstacle
Laws of reflection of light
Consider a ray of light AO incident on a plane surface and then reflected along OB as shown.

O = point of Incidence.
AO = incident ray
OB = reflected ray.
ON = normal to the reflecting surface
Ði = angle of incidence
Ðr = angle of reflection
Laws of reflection
LAW 1:
The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
LAW 2:
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Types of reflection:
(i).REGULAR REFLECTION: This occurs when a parallel beam of light incident on a smooth surface such as a plane mirror gets reflected as a parallel beam as shown.

(ii). DIFFUSE / IRREGULAR REFLECTION: This occurs when a parallel beam of light incident on a rough surface such as a paper gets reflected while scattered in different directions as shown

Differences between regular and irregular reflection
| Regular reflection | Irregular reflection |
| Occurs on smooth surface | Occurs on a rough surface |
| Parallel incident beam is reflected parallel | Parallel incident beam is scattered after reflection |
| Reflected beam is very bright | Reflected beam is dull |
Properties of images formed by a plane mirror
- They are upright
- They are the same size as the objects
- They are equal distance from the mirror as the mirror as the object
- They appear behind the mirror
- They are laterally inverted.

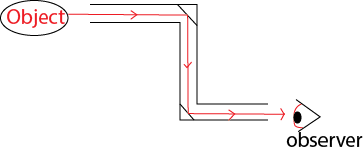
The periscope
It is an instrument used to observe things around corners. It is commonly used by submarines to see objects on the sea or ocean.
Refraction of light
Refraction is the bending of light rays as it travels from one medium to another. The medium can be water, air glass.
Applications of refraction of light
Refraction of light can be observed under the following condition
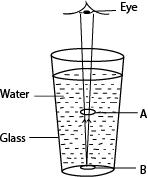
- A ruler placed in water appears bent at the surface of water
- Floor of swimming pool appear shallower.
- Things appear larger in water
- A coin put in water appear raised.
Rainbow

It is formed due to refraction of light that forms when the sun shines while it rains.
The splitting of white light to form a band of seven colors is known as dispersion of white light.
The band of colors is known as a spectrum
The rainbow spectrum can be remembered from acronym “ROYGBIV” starting with topmost color red.
The same spectrum like that is rainbow obtained by dispersion light through a glass prism

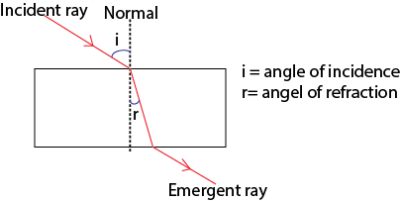
Refraction of light in a glass block
When light travels from a less dense medium e.g. air to a denser medium such glass light rays bend towards the normal as shown below
Lenses
Lenses are made of transparent materials.
They have curved smooth surfaces that helps them to refract light that passes through them
They are two main types
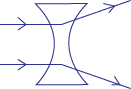
(a) Convex or converging lens
![]()
When light passes through a convex lens, it refracts light in such a way that the rays from the lens meet at one point.

Uses of convex lens
Convex lenses are used in
- Correction of long-sightedness
- In lens camera
- binnoculars
(b) Concave or diverging lens
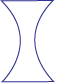
When light passes through a concave lens, it refracts light in such a way that the rays from the lens spread out in all
Uses of concave lens
- Correct short sightedness
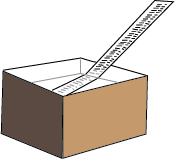
Pinhole camera
It is a dark box or a tin which allows light through a tinny hole made on one side of the box or with a pin. At the end of the box or tin there is a film or a screen
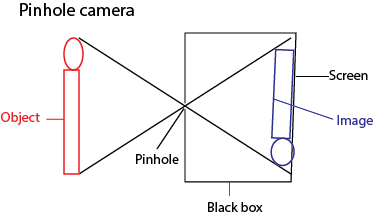
Properties of image formed by a pin hole camera
It is real
It is inverted
For revision question download PDF
Light Energy-upper primary
Sponsored by The Science Foundation College +256 753 80 27 08
Compiled by Dr. bbosa Science +256 778 633 682
Please like our page and subscribe as well

Good notes
Thanks a lot for the blog. Keep writing.
Thanks for being such an inspiration. Home & Kitchen
Thanks for providing such valuable insights. Top adult movies
Choose the best colleges with MBBS Admission Through Management/Nri Quota in Manipur.
Learn about manageable tuition fees at MBBS Fees Structure in Tamil Nadu.
Get instant access to exciting games with the Raja Luck App.