
Lines, Angle, parallel line, polygons- upper primary mathematics

Angles
In geometry, an angle can be defined as the figure formed by two straight lines meeting at a common end point.
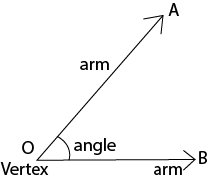
An angle is represented by the symbol ∠. Here, the angle below is ∠AOB.
Parts of an Angle:
Arms: The two rays joining to form an angle are called arms of an angle. Here, OA and OB are the arms of the ∠AOB.
Vertex: The common end point at which the two rays meet to form an angle is called the vertex. Here, the point O is the vertex of ∠AOB.
Types of angle
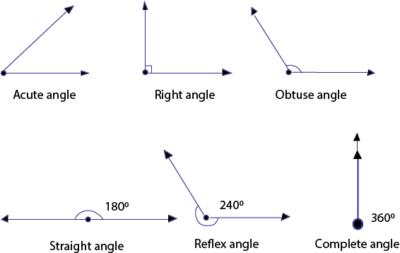
Angles can be classified on the basis of their measurements as
An acute Angle is an angle that measures less than 90 degrees
A right Angle is an angle which is equal to 90°,
An obtuse Angle is an angle has a measurement greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees.
A straight Angles is an angle is 180 degrees
A reflex Angles is an angle that is more than 180deg but less than 360deg
A complete Angle is a straight line makes an angle of 360∘
Interior and Exterior Angles:

Interior angle
- An interior angle of a polygon is an angle inside the polygon at one of its vertices.
- The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon with n sides is (n – 2)180.
- The measure of each interior angle of an equiangular n-gon is 180(n -2) /n
Exterior angle
- An exterior angle of a polygon is an angle outside the polygon formed by one of its sides and the extension of an adjacent side.
- If you count one exterior angle at each vertex, the sum of the measures of the exterior angles of a polygon is always 360°.
- The measure of each exterior angle of an equiangular n-gon is 360 /n
Terms related to sum of angles
Complementary angles add up to 900

Supplementary angles add up to 1800
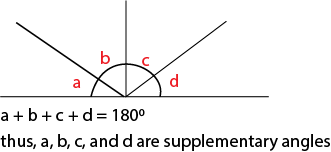
Polygons
Polygons are usually defined by the number of sides that they have.
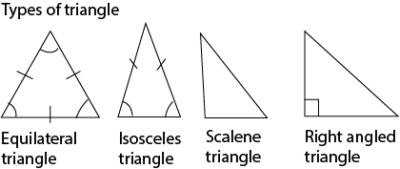
- A triangle
Is a three-sided polygon. Triangles can be defined by the length of the sides.
- Equilateral triangle has all sides equal and all its internal angles are 600.
- Isosceles triangle has two equal sides, with the third one a different length. Two of the internal angles are equal
- Scalene triangle has all the three sides and all the three internal angles different
- Right angled triangle has one of the angle = 900
- All internal angles of triangles add up to 1800.
Quadrilaterals
This are four-sided polygons
The internal angles of all quadrilaterals add up to 3600.
They include the square, rectangle, rhombus, parallelograms, trapezium and kite
- Square: all its sides are equal and each of its internal angles is equal to 900
- Rectangle: has four internal angles each equal to 900 and equal opposite sides
- Parallelogram has equal opposite sides and angles
- Rhombus has all sides equal and equal opposite angles
- Trapezium: has two parallel sides and unequal angle
- Kite has two pairs of equal adjacent sides, the shape has an axis of symmetry

Parallel lines
These are lines that are always same distance apart and will never meet.
Transversal line is a line that cuts through two or more parallel lines
The following about parallel lines are equal
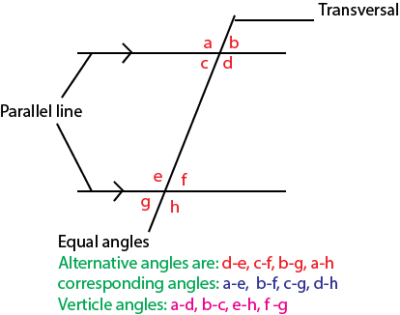
For revision question download PDF below
lines, Angle, polygonss- upper primary

Thanks for being a beacon of knowledge. Sports Fitness & Outdoor
Your writing is truly exceptional. Transfer Latest
Access detailed cutoff data with the MBBS Cutoff Of Government Medical Colleges in Tamil Nadu.
Play your favorite games anytime with the Raja Luck App.
Access Goa Games across multiple devices, allowing you to play anytime, anywhere, without compromising on quality.
Make the most of TS EARN’s platform by entering a valid Invitation Code during registration.
Get instant access to exclusive benefits by getting in the Diu Win Invite Code.
Get industry-leading server services with robust Server Rental in Chennai.
Enjoy an immersive and gratifying video gaming journey with bdg-win.
Play and win exciting prizes with thrilling 55 club games.
Learn how an IT Strategy Roadmap assists organizations line up innovation with business concerns.
If you desire a taste of the mountains, Uttarakhand Foods from Joshital is the very best choice!
If you’re a nurse or physician, have a look at Student Loan Forgiveness Programs Everything You Need to Know for healthcare-specific options.
I had an excellent experience with a Best Property Dealer In Greater Noida. Extremely suggested!
Discover the **Players with Most Centuries in IPL**, including top record-holders in the league.
I’ve always wanted to explore spiritual India and found the perfect guide through Varanasi Trip.