
Phase equilibrium (A-level physical chemistry)

Phase equilibrium
A phase is a homogenous physical state into which a substance can exist; for example, solid, liquid and vapor/gas
Factors affecting the phase of a substance
These include temperature and pressure. By varying temperature and pressure, it is possible to convert solid into a liquid or gas and vice versa or a liquid into a gas or a gas into a liquid.
A plot of vapor pressure against the temperature of a substance in the liquid, gas or solid-state yield graphs called phase diagrams.
There are three forms of phase diagrams:
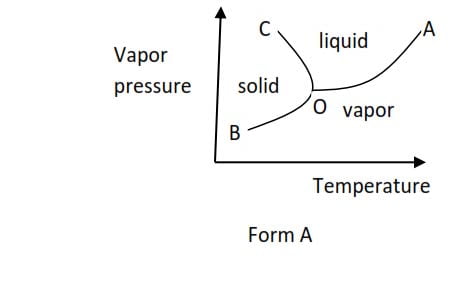
(a) Form A is shown by a substance such as water which is accompanied with a decrease in volume when they melt or accompanied with increase in volume when they solidify.
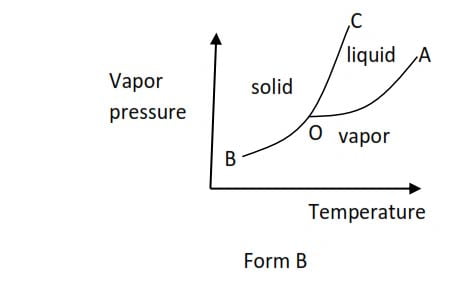
(b) Form B is shown by a substance such as benzene that is accompanied with an increase in volume when they melt
(c) Phase diagram form C is shown by a substance such as sulphur that exists in different solid form (allotropy)
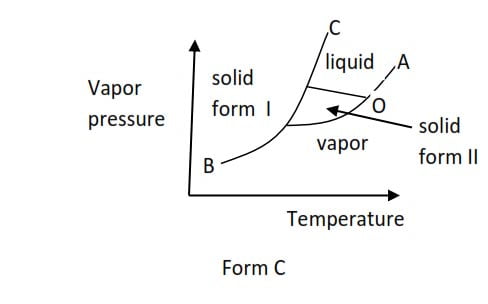
At point O, all the three phases are in equilibrium and is called triple point. I.e. triple point is a point of temperature and pressure at which all three phases (solid, liquid, and vapor) are in equilibrium. The temperature and pressure corresponding to the triple point are triple point temperature and triple point pressure respectively.
The triple point temperature Tt0C and pressure (Pt) for water and carbon dioxide are given below
Substances Tt0C Pt
Water 0.0098 0.0060
Carbon dioxide -56.1 5.0
With the further rise in temperature the curve OA is obtained and this represents the conditions of temperature and pressure under which the liquid and vapor are in equilibrium.
This curve ceases at A and beyond this point the liquid and vapor are indistinguishable. This point is called the critical point and the corresponding temperature and pressure are called critical temperature (Tc0C) and critical pressure (Pc) respectively.
Example Tc0C Pc
Water 374 218
CO2 37 72.8
OB represents conditions of temperature and pressure at which solid and vapor are in equilibrium.
OC represents conditions of temperature and pressure at which liquid and solid are in equilibrium
Watch this
Download PDF

I like the notes
Organised
Techer
This arc was a bit uneven Lots of cool stuff but rushed in parts also I think this ends Priscillas arc though and she withdraws from the selection to stay in the Empire
I’m always amazed by your insights. Toys & Games
This is a must-read for everyone. Thanks! 500 ka redeem code
Accelerate your medical career with MBBS Direct Admission in Orissa.
Streamline your application with MBBS Admission Through Management/Nri Quota in Chandigarh.
Boost your gaming experience with the special Raja Luck Invite Code.
Uncover the latest updates on Raja Luck.
Avoid black-hat methods and focus on How to get backlinks the right way.
Double your excitement with frequent winning chances at Raja-Luck.
Pick highly scalable services for cloud hosting with Server Rental in Chennai.
I’ve tried various lottery games, but 82 lottery keeps me coming back for more.
For a seamless YouTube audio conversion, Ezmp3 is my leading suggestion.
The fan edits and trending clips on https://www.youtube.com/@kpopbuzzindo/shorts are always top-notch!