
Polymerization (A-level organic chemistry)

Polymerization
A polymer is a high molecular mass species consisting of regularly repeating units or chemically similar units, linked by primary covalent bonds.
Polymerization is the process by which high molecular mass species are formed many chemically similar units called monomers.
Types of polymerization.
- Addition polymerization: monomers add one to each other to form polymers without loss of any molecule.
(a) Alkenes undergo addition polymerization to form polyalkenes


Other common polyalkenes are:
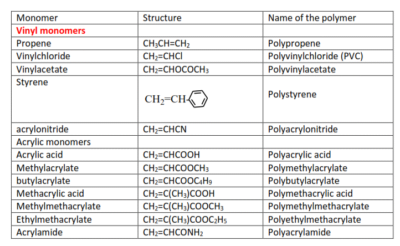
(b) Conjugated dienes undergo addition polymerization to form polydienes.
Examples

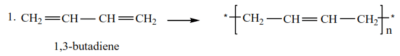


2. Condensation polymerization is the formation of big molecules called polymers from small molecules called monomers accompanied by loss of small molecules such as water, ammonia e.t.c
Examples
- formation of polyester
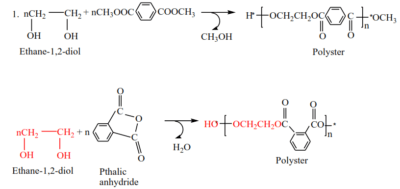

 2. Formation of polyamide
2. Formation of polyamide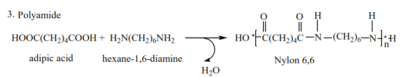
Thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers
Thermoplastic polymers are polymers that soften and can be remolded on heating, e.g. polyethene.
Thermosetting polymers are polymers that cannot be remolded on heating. E.g. phenolic and epoxy resins.
Compiled by Dr. Bbosa Science
End

Very helpful
Major thankies for the articleReally looking forward to read more Great
Fantastic job on this article. Keep it up! Water Bottle
I’m looking forward to your next post! 500 ka redeem code
Start your medical education journey with MBBS Admission Through Management/Nri Quota in Chhattisgarh.
Learn how to secure a medical career through MBBS Admission Through Management/Nri Quota in Punjab.
Make every lottery entry count with the official 82 Lottery Invite Code.
SEO would not be total without understanding the Importance Of Backlinks In SEO.
Redeem the latest 100 Google Play redeem code to enjoy free premium apps.
Host high-traffic sites and service apps with Server Rental in Gurgaon.