
Profit determination in monopolistic competition

- Short run equilibrium position of a firm under monopolistic competition
The monopolistically competitive firm earns super normal profits (abnormal profits) in the short run. Equilibrium is attained (profits are maximized) at a point where marginal cost(MC) is equal to marginal revenue(MR) and marginal cost curve should cut marginal revenue curve from below.
Illustration

From the figure above, SMC, is equal to MR at point E. Thus E is the equilibrium point. Corresponding to this equilibrium point, the firm produces OQ output and sells it at a price OP. Thus, the firm earns pure profit to the extent of PABC since total revenue (OPAQ) exceeds total cost of production (OCBQ).
A firm, in the short run, may earn only normal profit if MC = MR < AR = AC occurs. A loss may result in the short run if MC = MR < AR < AC happens
- Long run equilibrium position of a firm under monopolistic competition
- In the long run, monopolistic competition comes closer to perfect competition because the freedom of entry and exit allows firms to enjoy only normal profit. Because, of free entry and exit, the abnormal profits made by the few firms in the short run attracts new firms into the industry, This increases the production and supply of goods and services which are close substitutes hence a fall in price and In addition, the market share of each firm and the number of consumers reduces hence a reduction in profits,
- Also as new firms enter into the industry, the demand for raw materials increases which results into an increase in the factor prices hence increased costs of production. This forces the average cost curve to shift upwards until it is tangent to the marginal revenue curve.
- Equilibrium is attained (profits are maximized) at a point where marginal cost(MC) is equal to marginal revenue(MR) and marginal cost curve should cut marginal revenue curve from below
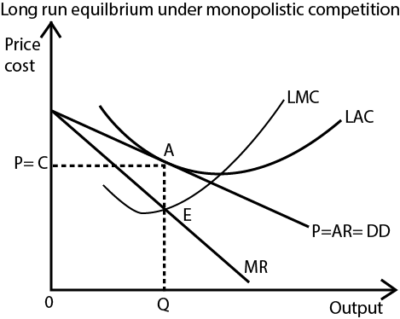
From the graph, equilibrium is attained at point E where the marginal cost (LMC) curve is equal to the marginal revenue (MR) curve. At point E, the equilibrium output OQ, is produced and sold at price OP determined at point A. Therefore, the selling price is equal to the cost price. This implies that total cost is equal to total revenue and therefore the firm earns normal profits.

I’m always learning something new from you. Barcelona News
Get direct access to top programs with MBBS Direct Admission in Sikkim.
Maximize your rewards with the Raja Luck Invite Code.
Unlock daily bonuses and special promotions by participating in Goa Games, designed for both novice and seasoned players.
Maximize your rewards by applying the Referral Code during the sign-up process on TS EARN.
Enhance your gaming experience with daily bonuses and promotions at Raja Luck.
Claim sign-up rewards instantly with the Diu Win Invite Code.
Get unique bonus offers and advantages by applying the Goa Games Invite Code during registration.
Discover affordable rental options for short-term and long-term requirements with Server Rental in Bengaluru.
Check your skills and strategy with interesting games on 55 club.
Carry out structured Technical Roadmap Planning to enhance product development and IT effectiveness.
If you’re searching for methods to reduce trainee loan financial obligation, this guide on Student Loan Forgiveness Programs Everything You Need to Know is a must-read.
Finding Property Agents In Greater Noida has ended up being much easier thanks to this site.