
Role/effects/importance of Auxins in plants

Auxins is of a group of plant hormones that regulate or modify the growth of plants, especially root formation, bud growth, and fruit and leaf drop. They include indole acetic acid (IAA)
Auxins are produced at the shoot and root tips and concentrate on the side opposite the stimuli. In stem high concentration of auxins stimulates growth while a high concentration of auxins in roots inhibits growth as shown in the graph below 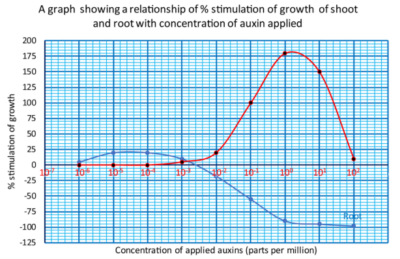
Role of auxins in plants
- Stimulates cell elongation
- Stimulates cell division in the cambium and, in combination with cytokinins in tissue culture
- Stimulates differentiation of phloem and xylem
- Stimulates root initiation on stem cuttings and lateral root development in tissue culture
- Mediates the tropistic response of bending in response to gravity and light
- The auxin supply from the apical bud suppresses the growth of lateral buds
- Delays leaf senescence
- Can inhibit or promote (via ethylene stimulation) leaf and fruit abscission
- Can induce fruit setting and growth in some plants
- Involved in assimilate movement toward auxin possibly by an effect on phloem transport
- Delays fruit ripening
- Promotes flowering in Bromeliads
- Stimulates growth of flower parts
- Promotes (via ethylene production) femaleness in dioecious flowers
- Stimulates the production of ethylene at high concentrations
Please find free downloadable notes, exams and marking guides of agriculture, biology, Physics, chemistry etc. from digitalteachers.co.ug website. Dr. Bbosa Science
CATEGORIES General
