
Soil (O-level biology)

For revision tests download PDF. For corrections and additions send comments.
Soil
The term soil is applied to a layer of material overlying the rocks of earth crust. Suitable nutrient contents and soil particle structure are essential for successful growth and production in ecosystem.
Components
Soil contains mainly
| Component | Percentage of the soil |
| mineral salt (inorganic particle) | 50 -60% |
| Organic matter | Up to 10% |
| Air | 15 -25% |
| water | -35% |
Inorganic particles.
They are usually classified by the average size of particular shown below
| Particle diameter (µm) | Particular name |
| <2 | clay |
| 2 – 20 | silt |
| 20 -200 | fine sand |
| 200- 2000 | coarse sand |
| 2 – 20 mm | gravel |
Soil that contains a mixture of sand, clay, silt is the loam soil. Loams soil is a mixture sand and clay soil in equal proportional with humus is the best soil for plant growth.
Physical properties of sand, clay soils are summarized below.
| Properties | sand | clay |
| Texture | coarse | fine |
| Structure | light | heavily |
| Aeration | good | poor |
| Drainage | fast | slow |
| Water retention | poor | good |
| Nutrients | poor | good |
Air and water
Water and air occupy the same space therefore the soil that contain more air will contain less water and vice versa. Aeration is the term used to describe the amount of air in the soil. Drainage is the ability of water to go through the soil. Oxygen is particularly required for respiration of micro organism and plant roots; decomposition of organic matter, germination of seed, root hair formation and growth and water absorption.
Soil water is important
- As a source of water and dissolved mineral salt in plant.
- Promotes seed germination
- Excess water (water logging) slows down water absorption (by lowering the respiration of plant roots since it displaced air from the soil) and decay.
- Water softens soil for easy root penetration
Importance of soil air
- Oxygen is used to breakdown soil organic residue to less poisonous products such as carbon dioxide. In absence of oxygen organic residues are broken to pollutants like methane and organic acids
- Oxygen is used by microorganisms to oxidize nitrogen and sulphur into usable forms.
- Soil oxygen is used by plant roots to respire.
- Soil oxygen is used for respiration of microorganisms leading to oxidation of nitrogen and sulphur and recycling of nutrient,
- Poor aeration results in the development of toxins and other injurious substances such as ferrous oxide, H2S gas, CO2 gas, ethylene, organic acids, etc., in the soil.
- A deficiency of oxygen has been found to check the nutrient and water absorption by the plants
- Insufficient aeration of soil leads to the development of some diseases like, wilt of gram and dieback of citrus and peach.
Experiment to determine the percentage of water in a soil sample
A sample of a known mass of soil is dried in an oven at 1050C to a constant mass. The difference in the initial and final mass is the mass of water in the soil
Results
Mass of crucible = a g
Mass of crucible + soil = b g
Mass of crucible + soil after drying to constant mass at 1000C in an oven = c g
Mass of soil = (b – a)
Mass of dry soil = (c – a)
Mass of water = (b – a) – (c – a) = (b – c)
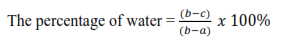

Experiment to determine the percentage of air in the soil
A given volume of soil is placed in a measuring cylinder followed by a given volume of water. The mixture is stirred to a constant volume.
Result
Volume of the soil added to measuring cylinder = a cm3
Volume of water added to measuring cylinder = b cm3
Volume of soil and water after stirring = c cm3
Volume of air = ((a + b) – c)

The percentage of air in the soil ![]()
Organic matter
Dead organic matter is derived from soil organisms and from organism that live above the soil surface. Fungi and bacteria in the soil decompose organic materials to humus. Humus improves the water retention in the soil and therefore the soils containing humus will resist leaching.
Experiment to determine the percentage of humus in the soil
A mass of a dry soil sample is heated to redness to a constant mass. The difference in the masses is the mass of humus.
Results
Mass of the dish = a g
Mass of dish + dry soil = b g
Mass of dish + soil after heating to redness = = c g
Mass of dry soil = (b – a)
Mass of dry soil without humus = (c – a)
Mass of humus = (b – a) – (c – a) = (b – c)

Soil organism.
The soil organism range in size from bacteria and protoctist to fungi, Nematode, insect, worms and a few mammals such as screw:
Role of soil organism
- Microorganisms such as bacteria and fungi.
- Promote germination by breaking seed coats
- Fix nitrogen in the soil
- Decompose and recycle or organic matter
- Macro organism such as rodent, termite and worms turn the soil and improve aeration and drainage
- Promote decay by breaking big pieces into small pieces
- When they die they decay and add humus to the soil
Dissolved minerals
The nature of dissolved minerals in the soil depends on the parent rock, organism growing in and above the soil and whether aerobic conditions prevail chalk soil, for example, are high in calcium carbonate. However, are low in phosphate, nitrogen and iron, again as is the case with oligohophic lakes, species diversity is high. When soils are waterlogged, ions capable of existing in either oxidized or reduced state are found in their reduced form. Fe 2+ for instance occurs instead of Fe3+ some plants are very sensitive to Fe2+, so the vegetation found on waterlogged soil differs from vegetation in well drain condition
Soil pH
is the acidity or alkalinity of the soil. It usually lies between 3 and 8.
Effect of soil pH
- Acidic soil with pH of less than 4.5 reduce the availability of nitrogen and phosphorus to plant on the other hand,
- the concentration of toxic Al3+ ions increase as the pH falls. These two factors enable a few plants to grow in acid bogs. Those that do are often carnivorous and this supplies them with extra nutrients.
- Affect the activity of microorganism which may increase of reduce the rate of decay and nutrient recycling
Soil Structure
This is the arrangement of soil particles, it refers to the looseness or compactness of the soil particle.
Its effects are
- Drainage for loose soil is faster than that of compact soil
- Erosion for loose soil is faster
- Aeration is higher in loose soil
Soil temperature.
High soil temperature increases the rate germination, decay, absorption of water
Soil erosion
is the washing away of top soil
Types of soil erosion
- Sheet erosion: the surface of the soil is removed evenly over the whole surface of a slope
- Rill erosion: top soil is removed to an extent that small channels in which the run-off is concentrated appear
- Gully erosion: top soil is removed to an extent that deep valleys are formed by water run-off.
Agents of soil erosion
- Wind
- Water
- Animals
Man’s activities that cause soil erosion include
- Overgrazing
- Clearing land for agriculture
- Deforestation
- Road construction
Methods to reduce soils erosion are
- Afforestation
- Planting grass cover
- Mulching
- Strip cropping
- Terracing
- Contour cropping
For revision questions download PDF

Thanks for your support in this covid break
What’s Happening i am neew tto this, I stumbld upon this I haave discovered It absolutely helpfu
and itt has aided mme oout loads. I am oping too give a contribution & help different users like its ided me.
Grerat job.
Your writing resonates with me deeply. Toys & Games
I’m constantly learning from your posts. 500 ka redeem code
Explore the finest medical programs at the Top MBBS Colleges in Tamil Nadu.
Enjoy endless entertainment with the thrilling Raja Luck Game.
Explore the influence of Raja Luck in today’s world.
Improve your chances of winning big with the 82 Lottery Invite Code.
Stay updated with the latest Indian Football news, match results, and player updates in Hindi.
Run AI and data-intensive applications smoothly with Server Rental in Mumbai.