
Types of Isomerism in organic chemistry

Types of isomerism
- Structural isomerism
- Optical isomerism
Structural isomerism
Here compounds differ in arrangement of atoms in a compound.
(a) Chain isomerism: compound have the same molecular formula but different arrangement of atoms in the chain.
(i) Structure isomers:
These are common to alkanes, isomers differ in arrangement of atoms in the chain

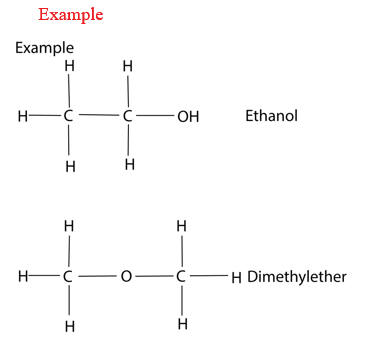
(ii) Functional isomerism
Compounds have the same molecular formula but different functional groups such as alcohols and ether.
(iii) Positional Isomer:
The isomers have the same molecular formula, same functional group but different positions of the functional group on a molecule.
Examples
CH3CH2CH=CH2 but-1-ene
CH3CH=CHCH3 but-2-ene
(b) Stereo isomerism
Compounds have the same molecular formula, the same functional group but different arrangement of atoms in space.
(i) Geometrical isomerism:
atoms, molecules are arranged differently about a double bonds:

(ii) Optical isomers:
Compounds have the same molecular formula, the same functional group but differ in optical properties towards plane polarized light. Those that rotate plane polarized light towards the right are called dextro isomers and those that rotate light towards the left are called levo isomers.
Please Subscribe to promote this website. Subscription is free
Share with a friend
Your comment is valuable
Thank you so much

You have a real knack for this topic. Sports Fitness & Outdoor
Your writing style is truly engaging. Indian Cricket