Agriculture revision questions for agriculture 2 with answers

Agriculture revision questions for agriculture 2 with answers
Agricultural Economics 2021
By Mungudit Davious
+256 394847/7531322587
- (a) Describe the factors affecting labor efficiency (10marks))
Labor efficiency refers to measure of amount of output a unit labor can produce in a given period of time.
The following determine the efficiency of labor on a farm
- Workers will be able to work for longer hours in cool climate than in hot climate.
- Length of work: specific working hours should be given to workers as long working hours discourage workers and reduce their efficiency.
- Individual qualities; most efficient workers have outstanding qualities, e.g. hard work, team worker, intelligence
- Training and education level. Well trained worker performs better than untrained worker
- Equipment used, a good equipment produce more efficient work, for example a tractor does more work.
- Organization, well trained leader obtained more worker from the laborer.
- Fair and early payments encourages workers.
(b) Outline any five ways of improving labor efficiency in agriculture. (05 marks)
- Carry out proper supervision of works
- Provide conducive working environment
- Proper allocation of duties to individuals
- Train workers
- Motivate workers
- Pay on piece rate basis
- Better selection of workers.
(c) With illustrations explain the effects of wages in labor. (05marks)

As wages increase from wage (W1) to W2 workers will abandon leisure and resort more hours to work and therefore leading to increase in the hours of worker from time T1 to T2.
When wages are increased from W2 to W3, the workers get contented because they raise more money for a few hours of work which leads to a reduction of the number of hours from T2 to T3 since workers resort much of their time to leisure.
- (a) With examples describe the following
- Risks (04marks)
A risk is a situation in which the future outcome of a certain event can be predicted, in a certain degrees therefore it can be insured against. Its probability of occurrence can be estimated based on the post experience.
Examples of risks include
- Accident
- Fire outbreak
- Pest and diseases
- Weather changes
- Uncertainties (04marks)
It is a situation whose occurrence cannot be predicted and cannot be insured against
Examples
- bleach of contract
- price fluctuations
- changes in government policy
- unavailability of labor
- reliability of transport
(b) Explain ways of counteracting risks and uncertainties. (12marks)
- By insurance; this involves taking an insurance policy against a particular risk through paying funds called Premium annually. In case of occurrence of a risk, a farmer seeks compensation.
- Diversification; this involves producing a variety of commodities on a farm such that in case of failure in one the farmer is compensated from another.
- Input rationing- a farmer applies less input than the optimum quantity such that should unfortunate happening occur, the farmer suffers less losses than if he had employed all the resources.
- Flexibility- this refers to how swiftly a farmer can change from one enterprise to another in case of loss
- Production on contract- a farmer may sign a contract with a marketing company on the prices of their commodities and this will minimize price fluctuations and loss in case of high production
- Liquidity; this involves the conversion of farm assets especially current assets e,g. animals, crops into cash and bank the money in anticipation of loss.
- Using extra inputs such as use of fertilizers, irrigation, pesticides to limit losses
- Price support
- Ensuring employment
- Selecting the most suitable enterprise.
- (a) Describe any five ways by which prices in agricultural sector are determined (05marks)
– Bargaining/haggling; here a buyer negotiate price with a seller
– Sale by auctioning: commodity sold to the highest bidder
– fixing of prices by buyer and seller through treaties
– fixing of prices by government
(b) With clear illustrations, explain how prices are determined in a competitive market. (05marks)
In a competitive market; prices are determined by forces of demand and supply illustrated below
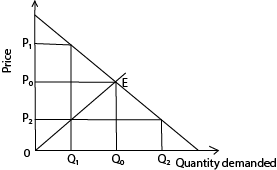
At a higher P1, supply exceeds demand because producers supply too much due to high prices. As a result suppliers reduce the prices to P2 so as sells exceed supply.
At low prices demand increases leading to shortage of commodities
The fluctuations of prices and demand continues until equilibrium point E is reached where the quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded. P0 is thus the equilibrium price while Q0 is the equilibrium quantity demanded
- (a) Explain the marketing functions carried out by farmers. (14 marks)
Marketing involves the following processes
- Assembling and bulking: commodities are produced, collected and brought together to a convenient point. This reduce transport and handling costs.
- Grading: grading involves sorting of products into uniform lots according to color size, shape, flavor for easy pricing and selling
- Standardization is the attachment of specific value to graded products
- Packaging; putting of the products in labelled containers to facilitate easy handling
- Transportation; is the physical movement of good from the point of production to the consumers. It increases the sizes potential market
- Financing; paying for transport and other costs
- Advertising in the media
- storage
(b) Outline the problems a farmer faces in marketing agricultural products (06marks)
- Seasonality of agricultural products
- Long gestation period
- Perishability
- Production of small quantities
- Bulkiness of agricultural products
- Fluctuations of prices
- Poor storage facilities
- Low value commodities
- High advertising costs
- Climate changes
- Bad roads
- (a) Explain the causes of price fluctuations in agricultural production
- Seasonality of products; most agricultural products are seasonal which brings about periods of scarcity and abundance.
- Long gestation periods; most products take long to mature making it difficult to increase supply easily when the prices increase.
- Inadequate storage facilities; many farmers fail to store their produces to wait for favorable prices
- Natural hazards such as floods, storms, draught may destroy and reduce supply leading to higher prices
- Inflation
- Lack of price control measures
- Perishability of commodities
- Quality fluctuations of products
(b) State the effects of price fluctuation in agricultural production (04marks)
- Fluctuations of revenues
- Producers are discouraged from borrowing
- Farmers fail to meet budget estimate
- may lead to rural urban migration
(c) Give the measures being adopted to standardize prices of agricultural products. (04marks)
- introduction of buffer stocks
- price stabilization funds
- price legislation
- production on contract
- introducing quota systems
Good luck
Yours
Mungudit Davious
Please Subscribe to promote this website. Subscription is free
Share with a friend
Your comments are highly welcome
Thank you so much

Well done
Thanks for being such a source of insight. Garden & Outdoor
This is a must-read for everyone. Thanks! cgdpr news
You have a real talent for this subject. TamilBlasters Com
Gain direct entry to prestigious colleges via MBBS Direct Admission in Orissa.
Learn about advanced healthcare education at Top MBBS Colleges in Kerala.
The Raja Luck App brings you thrilling games at your fingertips.
Explore the influence of Raja Luck in today’s world.
Get exclusive lottery benefits with the powerful 82 Lottery Invite Code.
Enhance your Free Fire Max experience with exclusive redeem codes available at free fire code.
Support your growing business with premium Server Rental in Hyderabad.