
Magnetism-upper primary science

Magnetism
A magnet is a piece of metal which has ability to attract other metals.
Magnetic substances are those substances which can be attracted by a magnet, for example iron, steel, cobalt and nickel
The substances that cannot be attracted by a magnet are described as nonmagnetic substances, for example sand, wood, pen and so on.
The ends of a magnet are called poles, one being North Pole (N) and the other South pole (S)
Types of magnets
There are two types of magnets, these are
- Natural magnets e.g. lodestone or magnetite and earth. All natural magnets are permanent magnets
- Artificial magnets, these may be permanent or not.
Shapes of magnets
The common shapes of magnets are shown below

Properties of magnets
- Unlike poles attract while like pole repel.
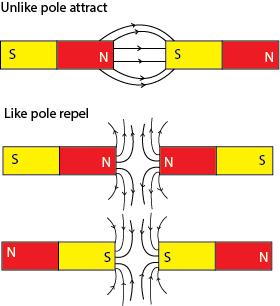
2. A magnet has a magnetic field lines which is covered with magnetic field lines running from the North to the South Pole.
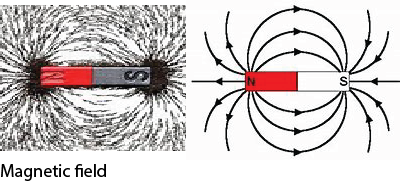
Magnetic field is an area around a magnet in which its magnetic field. This means that a magnet cannot attract magnetic objects outside the magnetic field.
- Freely suspended magnet points in the N-S direction

- The strength of a magnet (magnetism) is greatest at the pole
- Magnetism can pass through nonmagnetic objects
Magnetization
It is a process of making metals acquires the force of magnet (magnetism)
Methods of magnetization
-
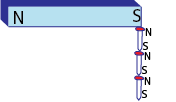
Induction
It is when a magnetic bar or nail is put on a magnet and is able to attract other magnetic substances, if a magnet is removed the nail also loses its magnetism
-
Electric method
It is when electricity is used to magnetize a magnetic bar. The more volts used the stronger the magnet. The more coil wound around a bar, the stronger the magnet. The nail or iron bar acquires magnetism only when the circuit is complete. The magnet formed by electric method is called electromagnet.

-
Single Touch method
It is when a single (one) magnet is used to magnetize a metallic bar by stroking. The more times you stroke the iron bare, the more powerful magnet it will become. The pole at the magnet being used to stroke the Iron bar
-
Double touch
In this method two magnets are used to magnetize, each one has a different pole exposed to stoke. Both bar magnets are brought into contact at the center of the bar at the same time and drawn apart maintain the poles of contact with the bar. the bar will be magnetized but the pole will be opposite of the ones that were used to magnetize that end of the bar.

Demagnetization
This the method of making a magnetic object lose its magnetism
- Heating a magnet to red hot
- Hitting a magnet on a hard surface repeatedly
- Keeping like poles of magnets facing each for a long time
- Passing a magnet through a coil of alternating current for a long time
- Keeping a magnet facing in East-West direction for a long time
Uses of magnet
For manufacturing compasses, generators, microphones, refrigerators, electric bell.
Electric bell
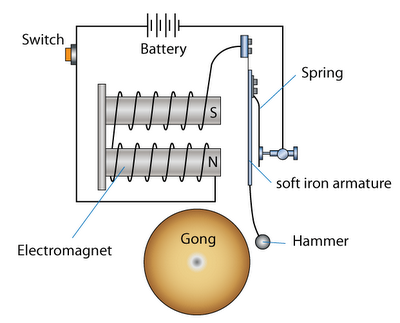
How does electric magnet work?
- The switch is pressed and current flows through the circuit.
- The electromagnet is powered and generates a magnetic field that attracts the iron strip towards it.
- The hammer strikes the gong (bell).
- When the striking arm strikes the gong, the contact is broken and current stops flowing through the circuit. The spring pulls back the hammer.
For revision questions and answers download PDF below

Nice
Need your email
digitalteachersuganda@gmail.com
Hello. Great job. I did not expect this. This is a splendid story. Thanks!
I learned something new today. Thank you! Baby Products
I’m always amazed by your insights. 500 ka redeem code
Explore the Top MBBS Colleges in Chandigarh, offering top-notch infrastructure and experienced faculty.
Sign up using the Raja Luck Invite Code for an exciting start.
I like how merely you discussed Backlinks Definition. SEO jargon can be confusing!
I was looking for a reliable source on SEO Link-Building and finally found it.
Explore the latest in football transfers and matches with our Indian Football coverage.